Human chorionic gonadotropin hormone (HCG) and its uses
Recently I watched a movie where a drug was created with this hormone and it seems incredible but in the film this hormone was related to the creation of the human being and the world including, it was interesting. Therefore, investigate to bring you this article.
source
The hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (also called beta-HCG subunit) is produced only by pregnant women since the embryo begins to evolve around the tenth day of pregnancy.
HCG is a glycoprotein hormone produced in pregnancy, manufactured by the developing embryo soon after conception and later by the syncytiotrophoblast (part of the placenta). Its function is to prevent the disintegration of the corpus luteum of the ovary and, therefore, maintain the production of progesterone that is essential for pregnancy in humans.
FUNCTIONS OF THE HUMAN CORONIC GONADOTROPIN
The main function of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) in pregnancy is to maintain the corpus luteum, which in turn is responsible for the synthesis of estrogen and progesterone. These hormones are essential for the pregnancy to develop and maintain correctly.
source
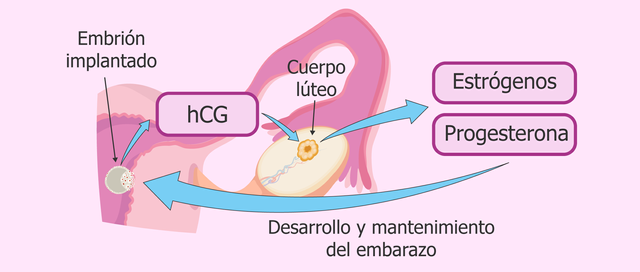
Progesterone enriches the uterus with a thick lining of blood vessels and capillaries, so that it can support the growth of the fetus. Due to its high negative charge, HCG can repel the mother's immune cells, protecting the fetus during the first trimester.
It has been considered that placental HCG can be a link for the development of maternal immunotolerance. For example, endometrial cells treated with HCG induce an increase in apoptosis of T cells (T cell solution). These results suggest that HCG may be a link in the development of peritrophoblastic immune tolerance, and may facilitate trophoblast invasion, a process that accelerates fetal development in the endometrium.
It has also been suggested that HCG levels are linked to the severity of morning sickness in pregnant women.
Because of its similarity to luteinizing hormone (LH), HCG can also be used clinically to induce ovulation in the ovaries, as well as the production of testosterone in the testes. As the most abundant biological source is women who are currently pregnant, some organizations collect urine from pregnant women to extract HCG and use it in fertility treatments.
HCG also plays a role in cell differentiation and proliferation, and can activate apoptosis (the process by which cells self-destruct under the impulse of a signal).
STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CORONIC GONADOTROPIN
HCG is a glycoprotein composed of 244 amino acids, with a molecular weight of 36.7 kDa. Its total dimensions are 75 × 35 × 30 angstroms (7.5 × 3.5 × 3 nanometer). It is heterodimeric, with a subunit (beta) that is unique to hCG, and with a subunit (alpha) identical to that of the luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
The subunit (alpha) is 92 amino acids long and has dimensions of 60 × 25 × 15 angstroms (6 × 2.5 × 1.5 nm). The subunit of hCG contains 145 amino acids and dimensions of 6.5 × 2.5 × 2 nm, encoded by six highly homologous genes that are arranged entándem and in inverted pairs on chromosome 19q 13.3 - CGB (1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8).
The two subunits create a small hydrophobic core surrounded by a large surface with a volume area ratio 2.8 times greater than that of a sphere. The vast majority of the outer amino acids are hydrophilic.
Se ha superado el límite máximo de caracteres permitidos
5000/5000
329 carácter por encima de los 5000 máximos permitidos:
testicular, así como la producción de testosterona endógena. Sin embargo, si la HCG se utiliza durante demasiado tiempo y en una dosis demasiado alta (con el consiguiente aumento de la testosterona natural), eventualmente inhibirá su propia producción a través de retroalimentación negativa sobre el hipotálamo y la hipófisis.
EVIDENCE OF HUMAN CORONIC GONADOTROPIN
The levels of hCG can be measured in the blood or urine. More often, it is done as a pregnancy test, intended to indicate the presence or absence of an implanted embryo. HCG tests can also be done for the diagnosis or monitoring of germ cells and trophoblastic tumors.
*.- Urine test:
The urine test can be a chromatographic immunoassay performed in the home, the medical center, or the laboratory. Detection thresholds range from 20 to 100 mIU / ml (milli international units per milliliter), depending on the brand of the test.
The earlier the stage of pregnancy, the more accurate the results can be obtained by using the first morning urine, since that is when hCG levels are higher.
When urine is diluted (specific gravity below 1.015), the concentration of hCG may not be representative of the concentration in the blood, and the test may give a false negative.
*.- Serum test:
The serum test, using 2-4 mL of venous blood, is typically a chemiluminescent or fluorimetric immunoassay, which can detect βhCG levels as low as 5 mUI / ml and allows the quantification of βhCG concentration.
The ability to quantify the level of βhCG is useful in tracking germ cells and trophoblastic tumors, monitoring after miscarriage, and diagnosis and follow-up after treating an ectopic pregnancy.
The absence of a visible fetus in the vagina by ultrasound after βhCG has reached levels of 1500 IU / ml is very indicative of an ectopic pregnancy.
A gestational trophoblastic disease, such as hydatidiform moles ("molar pregnancy"), or choriocarcinoma, can produce high levels of βhCG (due to the presence of syncytialtrophoblasts, part of the villi that make up the placenta), despite the absence of an embryo High levels of hCG are also a component of the triple test, a screening test for certain fetal chromosomal abnormalities and birth defects.
USES OF HUMAN CORONIC GONADOTROPIN
1.-Tumor marker:
The β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin is also secreted by some cancers such as choriocarcinoma, germ cell tumors, formation of hydatidiform mole, teratoma with elements of choriocarcinoma (is rare), and islets of tumor cells.
For this reason, a positive result in men can be a cancer test. The normal range for men is 0-5 IU / ml, although you should not suspect that there is cancer if the level is less than 30 IU / ml.
2.- Fertility treatments:
HCG is widely used as parenteral medication in fertility treatments instead of luteinizing hormone. In the presence of one or more mature ovarian follicles, ovulation can be activated by the administration of hCG. As ovulation will occur about 36-48 hours after the injection of hCG, procedures can be programmed to take advantage of this time sequence. Therefore, patients who undergo in vitro fertilization, in general, receive hCG to trigger ovulation, but have their eggs recovered in about 36 hours after injection (a few hours before what the ovules would normally be released in the ovary).
The administration of hCG is also used, in certain circumstances, to increase the production of progesterone.
In the male, hCG injections are used to stimulate the Leydig cells that synthesize testosterone. Intratesticular testosterone is necessary for spermatogenesis in Sertoli cells. The typical uses of hCG in men are hypogonadism and fertility treatments.
During the first months of pregnancy, the transmission of HIV-1 from the woman to the fetus is extremely rare. It has been suggested that this is due to the high concentration of hCG, and that the beta subunit of this protein is active against HIV-1.
3.- Weight loss:
A controversial use of hCG is as an adjunct to an ultra-low-calorie diet developed by the British endocrinologist ATW Simeons. This technique would allow losing fat with a very low calorie diet without losing muscle tissue, thus fighting obesity. However, the use of hCG to lose weight is considered inefficient and insecure by the scientific community.
4.- Use of HCG in combination with anabolic steroids:
In the world of drugs that increase sports performance, HCG is increasingly used in combination with several cycles of anabolic androgenic steroids (EAA).
In men, HCG mimics luteinizing hormone and helps restore and maintain the production of testosterone in the testes. Because of this, HCG is commonly used during and after steroid cycles to maintain and restore testicular size, as well as the production of endogenous testosterone.
However, if HCG is used for too long and at too high a dose (with the consequent increase in natural testosterone), it will eventually inhibit its own production through negative feedback on the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
I hope it will be useful for the steemit community.
Contribution @ nashilda17