Bitcoin Private Keys: Everything You Need To Know

What if you lost all of your bitcoins tomorrow? What would you do?
Let me stress this point:
“If you don’t own your private key, you don’t own your bitcoins.”
Yes, you read that right
Even the most knowledgeable man on Bitcoin says:
“The private key must remain secret at all times because revealing it to third parties is equivalent to giving them control over the bitcoins secured by that key. The private key must also be backed up and protected from accidental loss, because if it’s lost it cannot be recovered and the funds secured by it are forever lost, too.”
― Andreas M. Antonopoulos, Mastering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital Cryptocurrencies
What is a Private Address (or key)?
A private key is a secret, alphanumeric password/number used to spend/send your bitcoins to another Bitcoin address. It is a 256-bit long number which is picked randomly as soon as you make a wallet.
The degree of randomness and uniqueness is well defined by cryptographic functions for security purposes.
This is how the Bitcoin private key looks (it always starts with 5):
5Kb8kLf9zgWQnogidDA76MzPL6TsZZY36hWXMssSzNydYXYB9KF
What is a Public Address (or key)?
This is another alphanumeric address/number which is derived from private keys only by using cryptographic math functions.
It is impossible to reverse engineer and reach the private key from which it was generated.
This is the address used to publicly receive bitcoins.
This how the Bitcoin public address looks (it always starts with 1):
1EHNa6Q4Jz2uvNExL497mE43ikXhwF6kZm
This address is always seen and broadcasted for receiving bitcoins. Users can make as many public addresses as they want to receive bitcoins.
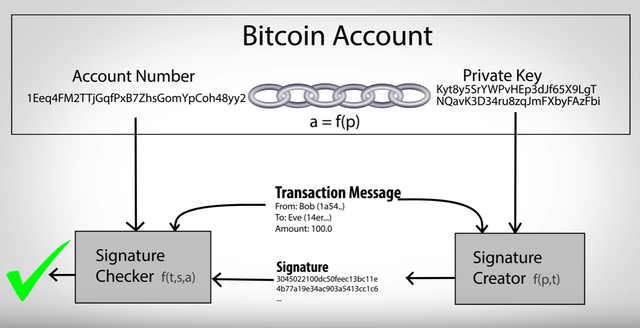
What are Bitcoin private keys used for?
Private keys are used for making irreversible transactions. Yes, irreversible!
They are the key to spending and sending your bitcoins to anyone and anywhere. This irreversibility is guaranteed by mathematical signatures which are linked to each transaction whenever we use the private keys to send bitcoins.
And for each transaction, these signatures are unique, even though they are generated from the same private keys. This feature makes them impossible to copy. The user can confidently use the same private key again and again.
Moreover, the signatures are mathematically related to Bitcoin addresses. This math relation helps in confirming that the signatures are only of that particular account holder who wants to transfer bitcoins.
How do we keep private keys safe?
It is OK if you didn’t understand the above technical stuff.
You can still use Bitcoin as long as you keep your private keys safe.
These digital keys are crucial in the ownership of bitcoins. These keys are not stored on the Bitcoin network but are created and stored by the file/software (a.k.a. wallet).
A wallet stores these keys. There are a lot of types of wallets out there and some allow the private keys to be stored and guarded by the user.
Some keep the key safe on behalf of the user.
I have explored each type of safety measure for you so that you can choose the most effective wallet according to your needs.
Web and Mobile Wallets
Most of the web and mobile wallet software services in the Bitcoin market store your private key on your behalf on their servers.
They get stored in an encrypted form which only you can decrypt.
Android Wallets:
MyCelium
Jaxx
Coinomi
SamouraiWallet
iOS Wallets:
Breadwallet
CoPay
AirBitz
In this kind of wallet, your keys are held by someone else, and if that gets hacked or stolen, your bitcoins are gone. That is why you need to take extra safety measures when dealing with these services.
However, there are really great wallets like MyCelium, which I personally use because of its additional security features and compatibility with hardware wallets.
Desktop Wallets
Desktop wallets are relatively safe. In such wallets, once you install them on your desktop, you will get your Bitcoin address and private key in a downloadable and importable file.
These importable keys can be made password protected and stored on a memory stick or hard drive.
But once you lose the file of the private key, you will lose the bitcoins.
I am going to discuss each one of these in detail in upcoming articles.
Here are a few desktop Bitcoin wallets:

Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are basically an electronic invention made to store your private keys offline away from the vulnerable online environment so that they can’t be hacked.
Some hardware wallets come with security grid cards similar to some debit cards in order to verify the transaction. Some even have a little digital screen to verify your transactions.
They are temper proof and come with a limited user interface. In case your device is destroyed, as long as you have a backup code, you can retrieve your keys and bitcoins.
Some of the popular hardware wallets are:
Trezor:
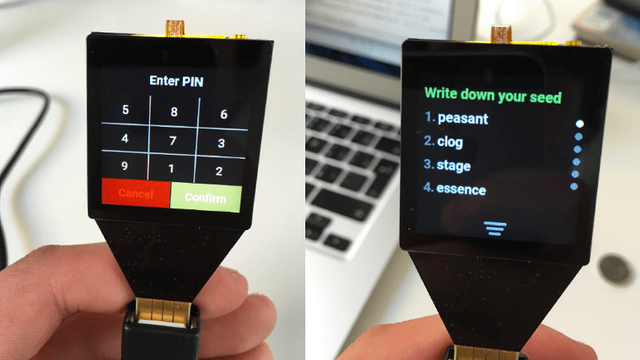
Trezor was the first hardware wallet to be launched since the invention of Bitcoin. It is a small device which can be connected via a USB cable to your personal computer. Its fundamental purpose is to store the private keys offline and sign transactions.
Ledger Nano S:

Ledger Nano S can be used even on a computer that is infected with malware. It has two buttons which are needed to be pressed together to sign and confirm a transaction, making impossible for a hacker to use.
Ledger Nano S also requires the user to create a PIN code on setup. The PIN code helps prevent the loss of bitcoins in case your Nano S gets lost.
It supports Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other popular altcoins, and connects with other software wallets like MyCelium. Here are few videos to learn more about Ledger Nano S:
Paper Wallets (Cold Storage)
Paper wallets are simply Bitcoin private keys printed on a piece of paper. It can have the Bitcoin public address also printed on it, but not necessarily. Paper wallets are an effective way of storing Bitcoin private keys offline.
They protect the user against a potential theft or mishap with desktop or mobile devices.
These kinds of wallets are also called “cold storage” because the keys are generated offline and never stored online or on a computer.
You can make your paper wallet from bitaddress.org, which is an HTML page specifically for this purpose only.
You can save the HTML page offline and remain disconnected from the internet to generate the keys. They can be printed on paper or stored as a soft copy on a USB or hard drive. Read my previous guide on how to make a Bitcoin paper wallet.
Conclusion
In a Bitcoin wallet, the most important thing is your private key because it will prove that the bitcoins you claim as your own are actually yours.
READ MORE: https://coinsutra.com/bitcoin-private-key/
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://coinsutra.com/bitcoin-private-key/
Please upvote: https://steemit.com/free/@bible.com/4qcr2i
Coins mentioned in post: