Multivac - project about which the whole world will speak
About project
New generation public blockchain project for decentralized industrial-scale applications. MultiVAC is based on robust shard technology (“fragments”), which allows unlimited and sustainable scalability to be used and offers a new approach to solving the blockchain scalability problem.
The platform includes the world's first model of shards, based on verified random functions (VRF), and applies it to transactions, computational processes and data storage.

Development team
The project has a talented Chinese team of specialists, almost all of whom have academic degrees and practical work experience. The only thing that is a little alarming is the fact that some of them are currently combining work on MultiVAC with a full-time job in other companies. A team of 22 people works on the implementation of the idea, including:
- Tong Xiao (PhD in statistics at Harvard University, a researcher specializing in probability, machine learning and big data, is engaged in research and development of quantitative trading strategies in leading hedge funds).
- Li Ge (PhD in mathematics at the University of Sydney, an expert in group theory and cryptography, is a quantitative strategist at leading international hedge funds).
- Sun Hong (PhD at Microsoft Research Asia Research University and Tianjin University, a postdoctoral fellow at the Microsoft Asia Institute and an expert in artificial intelligence (AI), is a research fellow at Microsoft Research in the USA).
- Zhang Minqi (Ph.D. in Computational Science at Nanyang Technological University, an expert on the application of modern topology and applied mathematics in computational science).
Main features of the project
MultiVAC is a newcomer to projects using shard technology in the blockchain industry. By focusing on sharding (like Zilliqa , Quarkchain and Emotiq), the authors of the idea set the task of creating a high-speed network for decentralized applications (dApps).
In order to distance themselves from Zilliqa and Emotiq, they chose to introduce the technology of verified random functions (VRF) for the consensus mechanism and the choice of shards. Projects like Dfinity and Ontology introduce similar randomized methods to select block creators. The MultiVAC accounting method involves the use of UXO, similar to that used in the Bitcoin blockchain.
This will allow developers to have the opportunity of a flexible combination of compromises within the framework of the CAP theorem, namely, to achieve consistency, accessibility and admissibility of sections. Simply put, decentralized computing on a large scale is currently an unsolved problem in the field of informatics. Decentralized networks can be maximized along the two corners of the triangle with consistency, accessibility, and splitting, representing edges. The authors of MultiVAC are well aware of these tradeoffs and allow developers to choose the parameters necessary for their use.
The Web 3.0 technology stack hopes to compete and outrun the existing Internet through scalable distributed networks. Public blockchains such as Ethereum are working on solutions to achieve second-level scalability. Sharding networks, such as the Zilliqa, make some security concessions in favor of higher scalability.
For example, EOS, after the recent launch of its network, was implemented with “sufficient” decentralization and 21 nodes responsible for creating new units in order to create a high-performance system.
VRF with Sharding
They are pseudo-random functions that allow the user to generate evidence in which all verifiers can quickly pass the test for the fastest possible implementation of the main function.
Shards are just subgroups of the main network. For example, if the entire network consists of two "fragments", then when connecting nodes to the network, they must choose between them. In the MultiVAC network, VRF is used to bind a node to one of the shards.
The project also uses another term - “underlying mechanic”. This is a random number that is generated in the main chain and then encrypted (hashed) using the private key of the unassigned node. The end result is a pseudo-random number, which is then assigned to the shard in accordance with the probability table.
Consensus inside shards
Consensus allows you to conclude an agreement on the status of a distributed book without the participation of a third party. Depending on the algorithm used, different thresholds for network reliability are needed to achieve consensus. There are many different consensus schemes and variations of the mentioned schemes.
To achieve consensus on work, the proportion of “honest” nodes within the shard must be greater than or equal to the established safety standard. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the general state of synchronization of the network. Naturally, the nodes fall into an asynchronous state during benevolent or malicious actions (for example, during a DDOS attack). Thresholds of consensus must also take into account security issues and the proportion of synchronized nodes.
The MultiVAC network defines priority algorithms that prevent the use of forks. The technical documentation notes that each fragment can use one of the following algorithms: PBFT (Zilliqa), asynchronous BFT or BA⋆ (Algorand).
Fragment sync
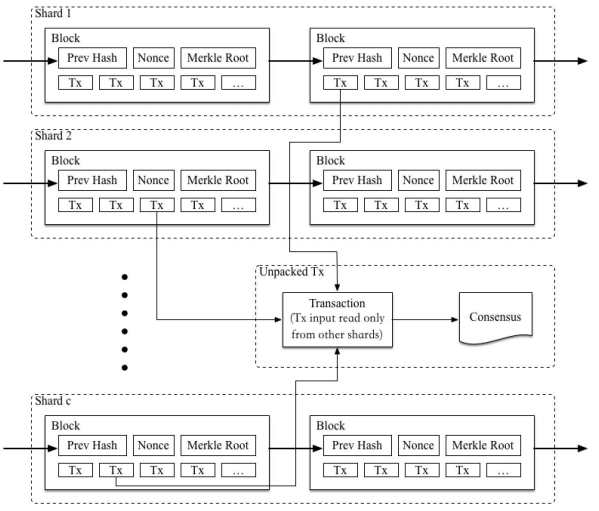
Currently, all projects using shard technology are faced with the same problem - not only synchronization of transactions between fragments (between nodes within one fragment), but also other fragments in the network.
In Zilliqa, a global book is used, divided by each fragment. To achieve a sufficient level of security in this case will require about 600 nodes. The authors of MultiVAC have chosen a simpler solution. This mechanism is activated only when calculating the account. The transaction will be in a register within a particular shard, of which the account is a part. At the programming level, this approach simplifies the entire process, without compromising security while improving scalability.
Shard Spamming Protective Mechanism
Shards can be considered as a subset of the common network. The strength of a distributed network lies in its ability to absorb DDOS or 51% attacks with a sufficient number of nodes. Shards in MultiVAC have far fewer nodes than other similar projects, so this network is at increased risk of attacks.
To prevent them, the developers decided to use dynamic shard setting. In this case, miners are assigned randomly for different fragments. The random assignment mechanism is also intended to increase the level of security by preventing coordination among attackers.
Proof of instruction (PoIE)
This is the universal algorithm of the MultiVAC virtual machine for checking the fair calculation of smart contracts. The platform design focuses on ensuring that each node with an intelligent contract is costly in terms of computing.
PoIE forces miners to not only hash, but also randomly read large amounts of data from memory. This burden reduces the possibility of attempts to dominate the network of specialized large mining companies and computer centers using powerful equipment such as ASIC.
In the case of attempts to influence the network during the mining process, miners will incur higher computational power costs, which will make any attempts of malicious actions economically unprofitable.
Decentralized applications
Modern dApps come in many shapes and sizes. Some require a high level of security, while others need a high-speed network. Block chains today have a number of compromises, and none of them satisfy all the requirements of each dApp.
So, Ethereum refused to focus on speed, choosing an optimization path for decentralization and security. EOS has taken a step towards centralization for high speed. In contrast, the creators of MultiVAC have defined clear boundaries within which they intend to offer their conditions to the dApp developers.
For use cases requiring a high level of security, dApp will be able to select a shard with a large number of nodes. If high bandwidth is in the first place, the application can work with a less decentralized shard (containing fewer nodes).
Official project links:
Website: https://www.mtv.ac/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/MultiVAC_Global
Telegram: https://t.me/MTVCommunity
Medium: https://medium.com/multivac-foundation
Hello @koliakavitalii! This is a friendly reminder that you have 3000 Partiko Points unclaimed in your Partiko account!
Partiko is a fast and beautiful mobile app for Steem, and it’s the most popular Steem mobile app out there! Download Partiko using the link below and login using SteemConnect to claim your 3000 Partiko points! You can easily convert them into Steem token!
https://partiko.app/referral/partiko
Congratulations @koliakavitalii! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!
Congratulations @koliakavitalii! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!