Treatment-of-varicose-veins ( to be continued)
What are the main side effects?
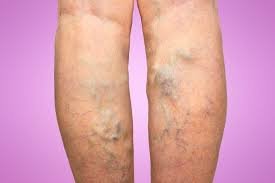
The best known side effects are heavy legs, feelings of size, weakness, the presence of painful veins, but also sometimes tingling, nocturnal spasms or irritability. Side effects are mostly worse at the end of the day (especially assuming you've been walking), throughout the year after exposure to heat, or after delayed sitting (distance travel for example). The hormonal cycle (shortly before menstruation) and pregnancies can also highlight side effects due to the increased levels of chemicals they cause. Finally, the side effects are however worked by lifting the legs, walking, physical activity and the cold (cold shower on the legs for example). You should know that 20 to 25% of patients with varicose veins experience no suffering other than the way the varicose veins appear, whether or not they are exceptionally large. These are often people who have a huge amount of regular work (walking, sport). If not treated, venous blockage can cause edema (expansion of the feet, lower legs and sometimes calves) with, over time, the presence of skin damage, then, at At this point, the skin becomes cardboardy, pigmented and delicate. conducted in the most serious cases up to skin ulcers. The most successive confusion that can appear at the stage of basic varicose veins is superficial phlebitis or "paraphlebitis", due to the presence of coagulation in the vein which is not intense in case it remains superficial, but compromising in the case where it extends deeply (deep phlebitis with risk of pneumonic embolism). What are the risk factors? The main risk factor is heredity. Varicose veins are often an innate problem. Did you at least know that when one of your two guardians has varicose veins, you have a 1 in 2 chance of having them and that if both guardians are affected, you have a 75% chance of having varicose veins. during your life? Heredity therefore plays a central role in the development of varicose veins. Additional risk factors are: aging, a stationary lifestyle or lack of real daily activity, trampling at work or in daily life, weight gain, pregnancy and habitual availability of warmth. How can we limit these risk factors? The elements that help combat these risk factors are real work, the act of play, with the most remunerative exercises being walking, swimming and cycling. Wearing pressure socks or stockings limits the impact of sometimes inevitable trampling. Weight control and escape from habitual or potentially prolonged hot opening remains important. What are the main side effects? The best known side effects are heavy legs, feelings of size, weariness, the presence of difficult veins, but also occasional tingling, nocturnal spasms or irritability. Side effects are generally more severe at the end of the day (especially if you have been walking), in late spring after exposure to heat, or after delayed sitting (distance travel for example). The hormonal cycle (shortly before menstruation) and pregnancies can also complement side effects due to the increased levels of chemicals they cause. Finally, the side effects are however worked by lifting the legs, walking, physical activity and cold (cold shower on the legs for example). You should know that 20 to 25% of patients with varicose veins have no drawbacks other than the way the varicose veins appear, whether or not they are exceptionally large. These are often people who have a critical normal active job (walking, sport). If not treated, a venous blockage can cause edema (hypertrophy of the feet, lower legs and sometimes calves) with, over time, the presence of skin damage, then skin lesions. . becomes cardboardy, pigmented and delicate. conducted in the most serious cases up to skin ulcers. The most common confusion that can appear at the stage of simple varicose veins is superficial phlebitis or "paraphlebitis", due to the presence of coagulation in the vein which is not intense if it remains superficial, but compromising on the par by chance, it extends deep (deep phlebitis with risk of pneumonic embolism).
What are the risk factors?
he main factor in the risk is the hérédité. These variables may be a genetic problem. Save the money you have for your tutors in a variety of ways, you have 1 chance on the next day and if the tuteurs touch them, you have a 75% chance of a variety in your life. vie. vie? The hérédité is next to a central rôle in the variable amélioration. The additional risk factors are: The video, in a stationary mode, or in the absence of daily activity, the device on the road or in the old video, the price of poids, the gross and normal overhead. Comment What are the risk factors? The elements that allow the shutter to control these risk factors on the real traffic, the operation of the day, the operations of most of the uses on the march, the nationalization and the location. The port of the chaussettes or the base of the pressure limit the impact of the Piétinements parfois inévitables. The control of the poids and the aversion for the output of the standard shade or enhanced prolongation of remaining important items.