Block Chain Community and Its Governance: Reflections on Legitimacy and Narrativity

The bifurcation of BCH leads to community splitting and public outcry. A joke from BM leads to panic in EOS community. Why can a small number of people or companies always have a huge impact on the block chain that has been labelled "de-centralized", or even lead to the breakdown of consensus? What is the connotation of decentralized governance of block chains? So-called de-centralized governance is human governance chain, or chain governance person, or chain governance chain, or human governance person? This paper explores the connotation of decentralized governance from multiple perspectives, providing a thinking perspective for the current "hot spots" in the currency circle.
Block chain governance is a very confusing topic. First, we don't always know what we are talking about. Even if we know, the cross-cutting issues of technology, culture and political philosophy will become complex. I hope this article can relax us a little and help clarify the strong relationship.
In determining the scope of discussion on block chains and governance, we first have to answer two questions: (1) What is the object of governance? (2) What is the content of governance? In other words, when discussing block chains and governance, there are generally four points:
(1) Man's governance of block chains (e.g. EIPs, BIPs and bifurcation);
(2) Block chains govern people (e.g. through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) or incentives);
(3) The governance of block chains by block chains (e.g. restrictions and permissions on chains);
(4) Governance of people (users or developers of block chains) by people (the main competent department of government).
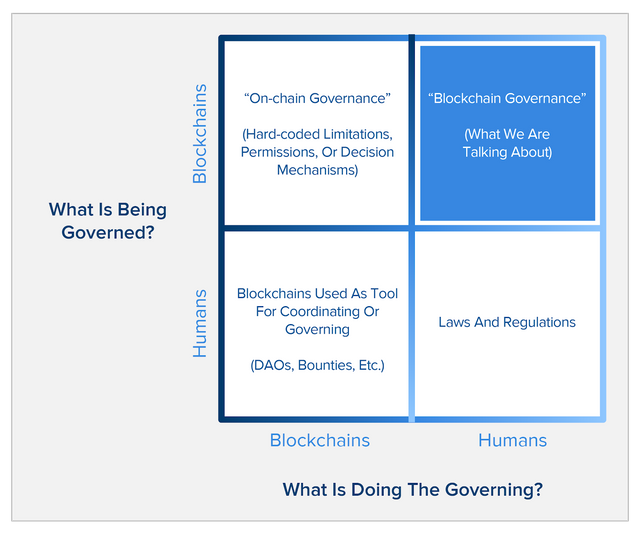
These four quadrants have some interesting and important issues, but it needs to be clear that the main concern of this paper is how human beings make decisions affecting block chains through such mechanisms as code updating and bifurcation (hereinafter referred to as "block chain governance").
Relevant decision-making of block chain governance is very important, because it can affect the way block chains work, use and the type of community around them, and then have a wide impact on society, and ultimately affect everyone.
1. Legitimacy or...
Let's jump out of the current topic for a moment and think about the specific meaning of legitimacy that Vlad Zamfir mentioned in his recent article Blockchain Governance 101.
Zamfir defines block chain governance as follows: a group of stakeholders jointly decide what measures to take on block chain: developers write and update block chain software, node operators decide whether to operate and update the above software, and owners of "trademarks" (e.g., people or organizations claim that "block chain is ETH" "Or" Block Chain is BTC ". In most cases, the above-mentioned parties are not appointed by any organization. Their collaboration determines the evolution direction of block chain software. The unity or division of the developer community or user community will form different ideological directions.
In Zamfir's view, legitimacy is an attribute of the coordinating mechanisms of these collaborators when their outcomes may be respected.
I believe that a decision-making, decision-making process or coordination mechanism is "legitimate" provided that all participants in governance know that the decision will be executed or that the decision-making process or coordination mechanism will be used. [2]
In addition, Zamfir believes that:
f a coordination mechanism is legitimate, people will behave (reasonably) as if they would use it. When a decision is legitimate, people don't have to worry about whether others will implement it, they can trust them. On the other hand, if it is illegal, they will act as if people will not use it. I believe that the establishment of legitimate decisions, decision-making processes and coordination mechanisms is a clear and elegant way to solve coordination problems. [2]
In addition, Zamfir observes that this legitimacy comes from a variety of sources. For example, advocates of block chains in autonomous regions want to limit the impact of people on the future governance process of block chains, and they want the block chains themselves to be the only source of legitimacy. Otherwise, it can be imagined that the governance process is controlled by various groups in the real world, such as companies, developers or government agencies. As a result, these groups will "monopolize" legitimacy under the existing block chain environment.
All of these raise interesting and difficult questions. But let me pause for a moment for semantic sophistry.
2, authority
When Zamfir talked about legitimacy, he put forward an important theme for the governance of block chains, and his analysis was clear. But we don't think "legitimacy" is the best word, and "authority" may be more appropriate.
It needs to be clear that this is a purely semantic argument, not a critique of Zamfir's logic. But sometimes semantics is very important, and we think that's one of them. Let's explain.
In the literature on political legitimacy, there are generally two schools of thought: one is descriptive, the other is normative. According to the descriptive theory of legitimacy, legitimacy refers to people's beliefs about where power exists and how it comes into being. On the other hand, the normative theory of legitimacy deals with the legitimacy of power. They distinguish between de facto authority and legitimate or legal authority.
Zamfir's concept of legitimacy is purely descriptive, and his insights are still important because they relate to how members of the block chain community position authority and how they make authoritative decisions. I just think there's a better word to describe it. Why not call it "authority"?
Look at this key article from Zamfir, replacing "legitimacy" with "authority". In my opinion, its meaning is clear and unchangeable:
If a coordination mechanism is authoritative, people will behave (reasonably) as if they would use it. When a decision is authoritative, they don't have to worry about whether others will implement it, they can trust them. On the other hand, if it is not authoritative, they will act as if people will not use it. In my opinion, the establishment of authoritative decision-making, decision-making process and coordination mechanism is a clear and elegant way to solve coordination problems. [2]
But we got off the point. The importance of semantic points is merely to emphasize the need for dialogue on normative legitimacy in block chain governance.
In block-chain communities, normative legitimacy is as important as in national states or other regulatory entities, such as companies or tribes. For example: suppose a cigar-chewing commander-in-chief appeared on state television to announce the success of a violent coup, declaring himself head of state, and then issuing credible, threatening orders to fearful people. These orders are likely to be followed by all or most people. They are authoritative, but not legitimate, because the value of the community is reflected in a certain decision-making process [1], which is ignored by the commander-in-chief. Society will not accept the legitimacy of his decision-making, because the decision-making is not made through the appropriate way to reflect social values (such as democratic elections). While rejecting the legitimacy of the commander-in-chief's decision, the members of the community accept the authority of decision-making, but the difference in their minds is an integral part of this special community. It makes the community a community, not just a group of people blindly obeying the orders of the loudest or most representative community leaders.
I hope readers can understand why this is worth discussing. For block chain communities, if there is no normative content of legitimacy, then block chain communities have no meaning, they are not real communities.
3. What is the community of the block chain?
Yuval Harari has an accurate and interesting view of the community. He believes that the community is a group of people who believe in the stories they share. Shared stories allow people to work with people they don't know and create a community that transcends family and friends. For example, we generally don't trust strangers, but if we know that he or she believes in the same religious or moral story as we do, everything will change. We can trust him or her and cooperate with each other without fear of any malice.
Block chains are technologies that allow people to cooperate with each other without mutual trust and experience --- without sharing stories, in other words, they make it possible to cooperate without communities. And that's confusing, because this kind of collaboration, which enhances trust and opens up the traditional boundaries of communities, falls within the quadrant at the bottom left of the picture above. It's interesting and important. But this has nothing to do with what we call "block chain governance", which involves the upper right quadrant.
Ultimately, the block chain is embedded in the actual human community. These communities are remote, controversial and difficult to define, but they do exist. They are composed of common stories and values, which provide a basis for the legitimacy of block chain governance decisions.
Now let's look at three very prominent examples of mainstream encrypted assets.
4. Contrast among BTC, ETH and ZEC
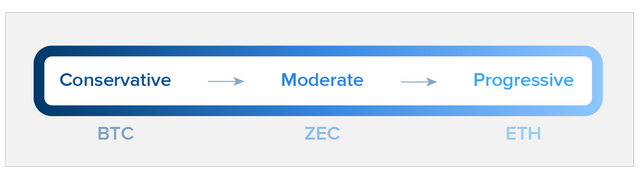
The BTC community is highly conservative (Figure 2), and the description of the use of block chains is very limited (basically focusing on the idea of replacing legal tenders). Few groups have significant governance impact. One of Bitcoin's business cards is that it runs almost automatically, uninterruptedly and with high capacity, longer than any other block chain. Therefore, revisions are treated with caution because they weaken the overall narrative.
The Bitcoin community has repeatedly shown that it attaches great importance to the conservative nature of technological improvement, and if this spirit is challenged because "most people" see it as a short-term improvement (studying Bitcoin's history against coin bifurcation and learning more about it), they will strive to promote it.
By contrast, Ethereum's community is more flexible and open. It contains the idea that its block chains can and should provide completely different uses for different people. Individuals can use the main public chains to generate loosely coupled applications.
In addition, its narrative focuses less on the concept of alternative currency and more on the concept of decentralized institutions. The Bitcoin community doesn't seem to care whether it will spawn a new kind of rich rule, while the Ethereum community is more like a "big tent" with more room to realize the dream of equality (as long as you respect the spirit of progress).
Their community is based on improving and expanding the ETH Layer 1 code base. In order to achieve the ultimate goal of the POS consensus mechanism, they launched a very ambitious roadmap. The more progressive your community is, the more opportunities you will eventually offer to its members. For example, ETH and its large-scale developer community/funnel are likely to be driven by funds raised by ICO in late 2017 and early 2018. )

Figure 3: As the community grows, mobility becomes stronger and stronger. It is becoming more and more important to have a funnel that can attract new talent.
More innovative and "fast-moving" encrypted currencies will be more inclined to progressive currencies, thanks in particular to their large market capitalization and high liquidity assets (which means that the community will not be affected by underallocation/reinvestment).
ZEC is between these two extremes. As a relatively new asset born in October 2016, compared with BTC and ETH, ZEC still has a lot to improve.
It also provides credibility for the theory that the newer your major public-chain assets are (considered wise and worthwhile by the technology community), the more your community needs to improve slightly than most of the existing traditional communities in order to "catch up" with liquidity and get a proper foothold in integrating existing services. Point. Although ZEC is separated from BTC's original code base and uses UTXO set, ZCash must maintain a certain degree of conservatism compared with the unparalleled speed of technological innovation adhered to by Taifang Intelligent Contract, Account-based and token-based model.
With the establishment of ZEC, ZEC Foundation and other profitable/non-profit entities, ZEC is slowly building a strong foundation on which communities can rely for a long time, while building a spirit and a story around quality and safety.
The public parameters of ZEC zero-knowledge proof are generated by real people on a (maximum transparent) ritual. Therefore, to believe the inviolability of ZEC encryption, it is necessary to have non-zero trust in the integrity of the process.
In addition, ZEC updates are highly transparent and open to user participation. Each subsequent hard branch will increase the number of active participants, and with each iteration of MPC rituals, the degree of decentralization will be further enhanced. These are all signs of openness. At the same time, ZEC creates a completely hidden environment in which users can participate in good or bad things without being discovered. ZEC distinguishes itself from BTC and ETH through this feature.
In this respect, it attracts radical egoists and thus has a user base that advocates value agnosticism. ZEC continues to explore interesting tensions between the closure and openness of its communities.
Their goal is to maintain a more moderate but still conservative pace of change, while refusing to add any features deemed unnecessary by the underlying technicians.
First, by developing integrated security practices, focusing on scientific peer review/code review, and slowly adding financial support to alternative full-node customers, they can lead the future of assets in the right direction, while distinguishing themselves from existing BTCs, which are very Privacy-oriented and long-term growth.
Their team even realized that one day their internal community might choose to branch itself to improve its infrastructure for more needed application scenarios or other important additions that would make the community more resilient. With the successful release of Sapling, the ZEC community has just completed another hard bifurcation of the plan, and has laid the foundation for further improvements in Level 1 in next year's "Blossom" upgrade.
Finally, we believe that a mobile and open governance style is conducive to the growth of block chain communities. Making more people have a place at the negotiating table --- and a role in narrative formation -- "expands" the funnels of community members. For example, both BTC and ETH have caused huge speculation in the past few years. But ETH has done more to transform this speculative energy into a real, thriving community, mainly through ETH Foundation, consensus system and other organizations, as well as meaningful developer communities such as EthMagic. ZEC is also moving in a similar direction. Compared with TC, ZEC is more progressive.
5. Conclusion
Looking ahead, we look forward to the open and mobile governance of block chain communities, as well as the conversion of speculative energy into specific development opportunities. Perhaps most importantly, we will look for a community linked by a compelling and inspiring story.
The low-level technical semantics of each asset based primarily on block chains are of course very important - however, a common narrative that people can understand and respond to is equally important and vital to the life and growth of a new community.
by:bitaves
Thank you so much for sharing this amazing post with us!
Have you heard about Partiko? It’s a really convenient mobile app for Steem! With Partiko, you can easily see what’s going on in the Steem community, make posts and comments (no beneficiary cut forever!), and always stayed connected with your followers via push notification!
Partiko also rewards you with Partiko Points (3000 Partiko Point bonus when you first use it!), and Partiko Points can be converted into Steem tokens. You can earn Partiko Points easily by making posts and comments using Partiko.
We also noticed that your Steem Power is low. We will be very happy to delegate 15 Steem Power to you once you have made a post using Partiko! With more Steem Power, you can make more posts and comments, and earn more rewards!
If that all sounds interesting, you can:
Thank you so much for reading this message!
Congratulations @happlysky! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @happlysky! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!