What is Bitcoin Lightning Network? And How Does It Work?

The two major hitches that cripple the platforms handling transactions in fiat currencies are the slow transactions and the high transaction fees charged in the process. Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies in general were created to offer a solution to these problems.
However, anyone who is familiar with bitcoin transactions would know that the reverse is the case. In regards to the time it takes to process a single transaction, other payment systems that utilize conventional money like PayPal, Visa and MasterCard can process hundreds of transactions in split seconds.
Accordingly, the bitcoin system was expected to handle ten thousands of transactions in an equivalent amount of time. On the contrary, using bitcoin, it could take anytime from minutes to hours, worst case scenario, days for a single transaction to go through.
Now, when a bitcoin user initiates a transaction, the payment is verified and recorded on the blockchain database through a process called mining. Miners are paid a certain amount of fees charged to the initiator of the transaction as transaction fees. There is no fixed charge set for a transaction, rather it fluctuates with the volatility of the coin. Yet, the cost of transactions are so ridiculously high and the system is basically inefficient.
Let’s assume a user wants to pay for a box of pizza using bitcoins, putting into consideration the fact that it may take at least several minutes or hours for the system to process the payment and the fact that the cost of transaction may be higher than the actual price of the pizza, how functional and practical is the bitcoin system in the every day life of a regular individual? The Bitcoin Lightning Network was designed to address these problems.
What is Bitcoin Lightning Network
Simply put, Bitcoin Lightning Network is a system of payment that enables Bitcoin users to exchange money off-chain i.e. without the involvement of the bitcoin blockchain. The lightning network operates a few complex algorithm to process transactions at 'lightning' fast speed with minimal transaction fees all without disrupting the inbuilt decentralized network of the system. The system was developed by Thaddeus Dryja and Joseph Poon and it is still in testing phase of the development process.
How the Bitcoin Lightning Network works
A node, in the context of the blockchain technology, refers to a computer connected to a network. First of, to use the lightning network, every user must be a node, i.e. have at least one connection to another node. Below is a breakdown of all the unique features and tools that make up the Bitcoin lightning network.
Multisignature wallets

Technically, the Bitcoin lightning network is a multisignature cryptocurrency wallet. So what is a multisignature wallet? A multisignature wallet is a type of cryptocurrency wallet that requires more than one private key to authorize a transaction. Regular cryptocurrency wallets have just one private key and one public key and are managed by a single user.
Multi-sig wallets allow for more than one user. In this case, a user can create a multi-sig address and choose a number of people known as co-payers to operate and manage the wallet with. Before a payment can be completed by one user on a multi-sig wallet, other co-payers would have to authorize the transaction before the money can be withdrawn from the wallet. Basically, think of a multi-sig wallet like a joint bank account where all signatories will have to sign off on a transaction before it is authenticated.
In multisignature wallets, the private key is be distributed across different wallets, devices and can even be operated from a different location. In a case where one wallet is compromised, the bitcoins are still safe and a hacker would need to private keys of every co-payer in the wallet to access the funds, thus a multi-sig wallet is very efficient and secure.
The funds in a Bitcoin lightning network are held in a multi-sig wallet, co-payers make their respective deposits to this account, transactions and updated account balances are recorded here as well. The wallet is accessible to all co-payers on the network connection.
Payment channels
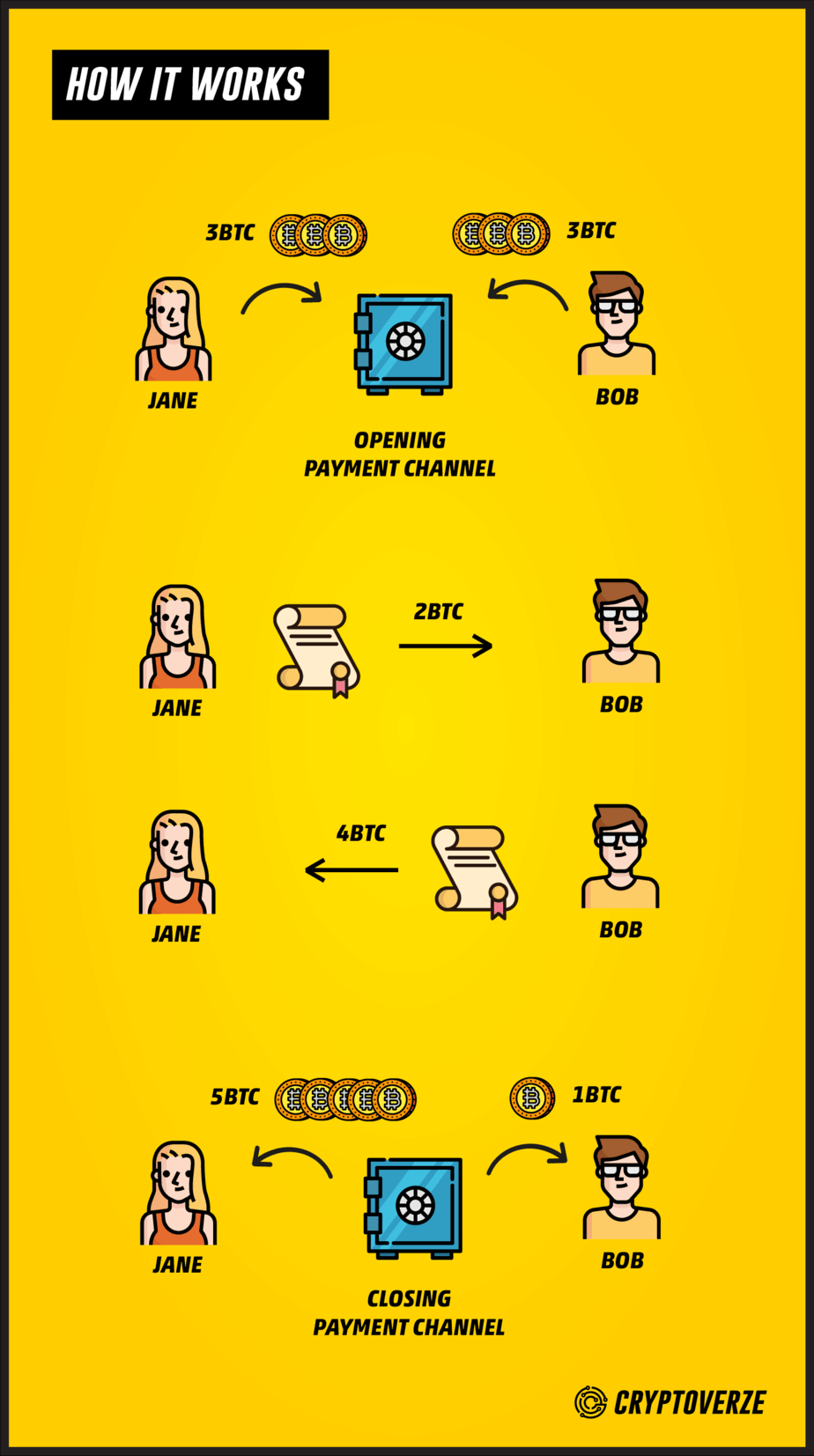
Like previously stated every user must be a node to use the Bitcoin lightning network. So how does the connection operate? Here's an example.
First of all let us assume there are two nodes on the network who are in business together and need to constantly make transactions with one another. We will call the users Jane & Bob
Jane creates a payment channel - the multi-sig wallet - and chooses Bob as co-payer to share the wallet with.
Lets assume Bob and Jane deposit 3 BTC respectively in the multi-sig wallet, the Lightning Network uses a smart contracts protocol to keep track what belongs to who in the connection and each party can only access their own bitcoins in the wallet.
This process (creating a payment channel) is called opening transaction, it is an on-chain activity and as such it is recorded on the main bitcoin blockchain.
Also, details of the payment channel - the wallet address and opening balances are recorded on the blockchain too.
From this point, transactions within the payment channel are conducted off-chain within the Lightning Network. These transactions are called commitment transactions.
If Jane sends 2 BTC to Bob, she transfers a promise of ownership for 2 of her Bitcoins in the payment channel/multisig wallet to Bob. By the same token, If Bob decided to then sends 4 BTC to Jane, he transfer a promise of ownership for 4 of his Bitcoins in the payment channel/multisig wallet to Jane.
In essence, the lightning network doesn't actually send money, it just updates the balances on how much a user on the network can access.
Since the transaction is conducted off chain, a lot of time is saved as there will be no need for miners to verify the transaction as it is not recorded on the blockchain.
Additionally, no transaction fees are charged to Jane as no mining was done.
Whenever Jane and Bob are through with the business and do not expect to conduct further transactions with one another, they can choose to close the payment channel by signing a closing transaction with their respective private keys to broadcast the closing balances to the main bitcoin blockchain.
The closing of the payment channel takes place on chain and is recorded on the blockchain database. Whatever funds are left to each user is refunded to their respective individual wallets.
Essentially, the only transactions broadcast to the blockchain are the opening and closing of a payment channel and when a user credits their lightning account on the multi-sig wallet. Every other transaction is conducted off-chain. For one time transactions between users, creating a payment channel is ineffectual. Transactions can be bounced along between as many nodes as required via indirect channelling routes. As long as there is a network of nodes that connects to the recipient, there is no need to create a payment channel to send funds to someone.

For example, if Jane wants to sent 2 BTC to Steven, instead of opening a new payment channel with Steven, she can use the payment channel that was previously established between Bob and Steven to achieve that. Bob will transfer a promise of ownership for 2 BTC to Steven and in turn Jane will transfer a promise of ownership for 2 BTC to Bob via the Jane-Bob payment channel to reimburse the amount.
With a network of payment channels as such, millions of instant transactions are able to take place with minimal amount of transaction fees involved.
Hash Time
Hash Time Locked Contract (HTLC) is a technology used to lock bitcoin in a multisignature wallet to prevent cheating and malicious transactions through payment channels on the network.
Since the Lightning Network is essentially based on commitment transactions, HTLC ensures that each party in the network holds up their end of the bargain and in the failure to do so, after a stipulated amount of time dictated by the contract, the bitcoins in the wallet are redeemed to their respective owners. HTLC keeps the parties honest and accountable in their transactions.
Other than reaching the timeout period, the money can also be unlocked and returned to either party’s individual wallets if both parties sign the closing transactions together.
Lightning Network Fees
Realistically, every user can not have a connection with everyone they intend to send money to and set up a payment channel for every transaction is not practicable. In this case, a user can use a hub of connected nodes to send the funds.
The Lightning Network charges transaction fees to the sender, minimal fees compared to the transaction fees in a regular bitcoin system. The fees are paid to other nodes on the multichannel payment network.
The money serves as incentives for users to keep nodes active and functional to pass transactions through. Additionally, there are also transaction fees charged at the opening and closing of payment channels as these transactions are verified by miners and recorded on the bitcoin blockchain.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Bitcoin Lightning Network
Advantages of Bitcoin Lightning Network
- Transactions are processed instantly, the account balances of the nodes are just updated and the money is immediately accessible to the new owner.
- Transaction fees are a mere fraction of the transaction cost, hence, users do not have to worry about being charged fees higher than the original amount in the transaction.
- Commitment transactions are not recorded on the blockchain so once a payment channel is closed, the transactions can not be traced back to the users. This is particularly useful for people who wish to maintain anonymous during transactions.
Disadvantages of Bitcoin Lightning Network
- Lightning Network is not suitable for making bulk payment, the intermediate nodes in the multichannel payment network may not be loaded with money to move the funds along and in that case, the transaction hits a dead end.
- Recipients cannot receive money unless their node is connected and online at the time of transaction.
- Certain nodes may decide to centralise the payment channel by loading their wallets with bitcoins for the primary purpose of handling transactions on the channel. A centralized network is inevitably bound to disable the system in some way.
Conclusion
The Bitcoin Lightning Network software is still undergoing development and is expected to grow and become more widely adopted in the payment system. Lightning Network is without doubt, a vital extensibility tool if Bitcoin must be established as a workable means of payment in the near future.
Source:
What is Bitcoin Lightning Network? And How Does It Work?
Source:
What is Bitcoin Lightning Network? And How Does It Work?