Unraveling the Mysteries of Blockchains: A Guide to the Future of Technology
In recent years, the term "blockchain" has become increasingly ubiquitous, hailed as a game-changer across various industries. But what exactly is a blockchain, and why is it generating so much excitement? In this blog post, we'll embark on a journey to explore the intricacies of blockchain technology, uncovering its inner workings, potential applications, and the transformative impact it promises to have on our world.
Decoding Blockchain Technology
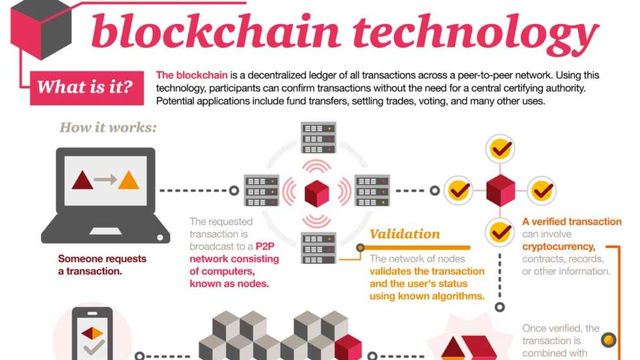
At its core, a blockchain is a decentralized and immutable ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a secure and tamper-proof chain of blocks. This distributed nature ensures transparency, security, and trust without the need for intermediaries or central authorities.
Key Components of Blockchains
Decentralization
Blockchains operate on a peer-to-peer network of nodes, eliminating the need for a central authority to validate transactions. This decentralization democratizes control, ensuring that no single entity has undue influence over the network.Transparency
Every transaction recorded on a blockchain is visible to all participants, fostering transparency and accountability. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and corruption, as transactions can be independently verified by anyone on the network.Immutability
Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or deleted. This immutability ensures the integrity and permanence of the data stored on the blockchain, making it an ideal solution for applications requiring tamper-proof records.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain technology is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies leverage blockchain technology to enable secure, peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries like banks or payment processors.Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. These contracts automatically execute when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and facilitating trustless transactions across a variety of industries.Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology can revolutionize supply chain management by providing transparency and traceability throughout the entire supply chain. By recording each step of the process on a blockchain, companies can improve efficiency, reduce fraud, and ensure the authenticity of their products.Identity Management
Blockchain-based identity management systems offer a secure and decentralized solution for managing digital identities. By storing identity information on a blockchain, individuals can maintain control over their personal data and securely authenticate their identities without relying on centralized authorities.