Controlling Big Data? Blockchain Can Help With That...

Remember when “Big Data” was the technical buzz word of the 2000s for everyone who wanted funding, a job, or research grants?
Although the term was slightly over-used, Big Data is forever growing in importance. From the NSA’s super computers to recording Likes on Facebook, everything is documented and nothing is lost, maybe scrubbed like S.O.S. emails, but never lost.
With such vast data demands from businesses, consumers, and governments, how can blockchain technology help with the 5 V’s of Big Data? Well, blockchain tech is relevant for at least 3 of the 5:
- Velocity
- Variety
- Veracity
The other two, Volume and Value, must be addressed first.
Volume:
Today, studies show we generate about 2.5 quintillion bytes of data daily. And stats gathered by NewGen Apps :
- By 2020 the new information generated per second for every human being will approximate amount to 1.7 megabytes.
- By 2020, the accumulated volume of big data will increase from 4.4 zettabytes to roughly 44 zettabytes or 44 trillion GB.
- Originally, data scientists maintained that the volume of data would double every two years thus reaching the 40 ZB point by 2020. That number was later bumped to 44ZB when the impact of IoT was brought into consideration.
- The rate at which data is created is increased exponentially. For instance, 40,000 search queries are performed per second (on Google alone), which makes it 3.46 million searches per day and 1.2 trillion every year.
Are you seeing the rise of huge data centers in and around metropolitan cities? Municipalities set aside land and bid for their city to host data center businesses. Such as Phoenix’s H5 Data Centers dedicated to hosting co-location space for cloud servicing centers.

Many cities are touting space to court the newest member of the “warehouse district”. I don’t believe Volume is a problem for Big Data, the real estate deals are sweet for landlords. With servers quietly humming, no worries of the dreaded triple T of real estate (trash, toilets, & needy tenants).
Value:
Webopedia defines Big Data as a massive volume of both structured and unstructured data. Data so large, it is difficult to process and extract full value. Data from corporate systems, internet of things (IoT) and unstructured sources can be processed by tools like Spark which help make sense of the data.
Big Data is an incredibly profitable business, with revenues expected to grow to $203 billion by 2020.

Beyond the storage and service providers, industry examples of potential gain from Statisa:
- Recent studies indicate that by improving the integration of big data, healthcare could save up to $300 billion a year— these boils down to reducing costs by $1000 a year for each person that has access to the facility.
- A nominal 10% upsurge in data accessibility can result in more than $65 million increase in the net income, for a typical Fortune 1000 company.
- Retailers who choose to leverage the full potential of big data analytics can optimize their operating margins by approximately 60%.
- Out of the 85% companies who are trying to be data-driven, only 37% have been successful in their initiatives.
- As of this moment, only 0.5% of all accessible data is analyzed and used.
Data intelligence services and Big Data tools are emerging to help organizations delve deeper and uncover “hidden” patterns. There may emerge decentralized apps and open source programs that perform on par with products offered now. A protocol working to organized unstructured data is MarketProtocol.
MARKET Protocol has been created to provide a secure, flexible, open source foundation for decentralized trading on the Ethereum blockchain. We provide the pieces necessary to create a decentralized exchange, including the requisite clearing and collateral pool infrastructure, enabling third parties to build applications for trading.
Also, decentralized platforms can interface with traditional aggregators; such as Google recently including Ethereum datasets in BigQuery for analytics.
So, how else can blockchain technologies help advance Big Data?
Variety
Variety is the format data inputs and outputs moving through an organization.
Before, information could be controlled in well structured intranet formats, but now unstructured streams are the norm.
From a consumer vantage, envision the way we interface, store and retrieve data. Notably, video, which for many platforms was a big no-no. Now, Facebook, Twitter, and many other platforms welcome video, audio, and other file types just as readily as text.
Standardization did help with security and ensure no malicious files entered a controlled environment. However, it’s not realistic to keep your email server in “Plain Text” mode forever.
With the advent of blockchain, known and trusted sources are secured and encrypted, so expected information is transmitted with no extra baggage or manipulation. Now, managers can be agnostic to the files and streaming data due to blockchain security. Even the vast amounts of unstructured data can be retained and undegraded forever.
Velocity
Velocity is increasing, can blockchain keep up?
Within 2018, 3rd generation blockchain technologies emerged and are maturing, such as EOS, Nebulas, ARK, Ontology, AION etc. Will these technologies scale to the Transactions Per Second necessary for business use-case?
Yes.
With the advent of multi-thread parallelism, Byzantine consensus, sharding, and even Distributed Ledger Technology, speeds are increasing.
Even gen 2 blockchains introduced a new form of transacting with greater speeds, the token. Tokens and smart contracts track the end to end job and details about each job. These micro data packets can not only increase velocity of data via software protocols, but also the need for end-user data screening and verification is no longer needed. Legacy filtering and middle-men facilitation are no longer necessary with blockchain, and thus, an increase in data velocity.
Veracity.

Data accuracy increases trust levels to use the data for analysis. With no single point of failure, the immutable blockchain will ensure no data is loss, degraded, or corrupted. Time is not a factor, so analysis can be performed on current data just as readily as when data is over 50 years old.
Veracity also involves data origins. Logistics is the first industry to realize this value. Raw materials and widgets are tracked from origination, through manufacturing, processing, wholesale chains, distribution, retail and to the end-user. The hardware, tags and sensors currently exist, all that was needed was an immutable ledger to document each step of production, handling, storage, and sale.
Blockchain platforms will fulfill the secure supply chain mandate and become the trusted source of data upload, management, and retrieval.
The next step, Oracles:
Why Oracles are need for full blockchain integration? Oracles will assist with integration of legacy information systems from centralized servers and new information feeds into blockchain protocols. Information from the physical world is essential to build a distributed (decentralized) economy.
One project focusing on the connectivity problem is ChainLink. According to their website, “ChainLink connects Smart Contracts to any/all external systems and APIs”.
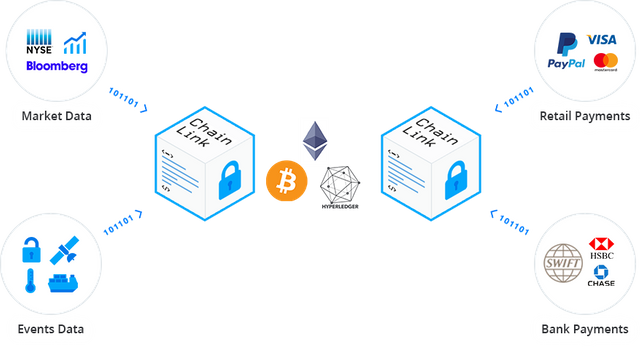
Thomas Reuters launched its Knowledge Graph Feed, allowing Financial Services customers to accelerate their AI and Digital Strategies. Disparate data from multiple industries sources could be connected to ChainLink and fed into a blockchain platform. Information can now be fed outside garden walls with encrypted security and dispersed freely on a dedicated immutable blockchain.
Graph network of 2 billion relationships brings to life a comprehensive view of the financial ecosystem so that users can uncover new, unexpected or difficult to find insights from connected data.
Aeternity is another project seeking to solve the problems with current blockchains. Within their own FAQs aeternity describes themselves as more than a tech project but a movement that aims to propose alternatives to the existing governance, economic and financial intermediaries. In addition to their unique blockchain tech solutions of smart contracts, consensus, and state channels, they also tout value propositions of privacy, security, and low costs.
Aeternity also incorporates oracles, and state their importance as follows:
How can an oracle be helpful?
What if the fulfillment of a smart contract depends on weather conditions, a share price, or other public information from the real world? Oracles can provide tamper-proof data upon which contracts can act. Election results, the prices of assets such as gold, weather conditions and many other real-world data play a crucial role for many business applications.
The End-Goal of Big Data Utilization:
Once data is freely flowing within the multitude of blockchains and interoperability between the blockchains is fully implemented (another article for another day), we will see a new paradigm of empowering the individual to interface with networks outside the traditional organizations of small, medium and big businesses. Governments at every level must rethink how it interfaces with citizens and enterprises. New decentralized market models, new forms of transmitting value, new governance models for coops and associations will encourage network effects for everyone on the planet with access to computing (smartphone), energy (green self-generated), and bandwidth (internet).
Old markets will continue to operate, and many will choose to continue to do business as usual. However, the economic models, for most industries, will enter into a new evolution of something we were never able to achieve before.
The blockchain economy is a unique combination of globalism while staying true to free market principles, even to the point of extreme laissez-faire. Entities are free to organize their governance within each blockchain infrastructure and create its unique tokenomics; all while enabling the sovereign rights of the individual to privacy and free association without intrusion from a forceful government. The abundance created can benefit people in developed nations in equal proportions to those in "developing nations". The 5.8 billion can leap-frog from institutional poverty to fully expressing their talents and directly reaping the fruits.