Blockchain for Beginners: Everything You Need to Know to Understand the Technology Behind Bitcoin

I’ll briefly explain what blockchain is and why it’s important. Blockchain is a revolutionary technology transforming multiple industries, and understanding its fundamentals can help anyone better grasp the future of digital transactions.
What is Blockchain?
I’ll define blockchain in simple terms. Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger where transaction data is stored securely, immutably, and transparently. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain is decentralized and consists of "blocks" that hold information.
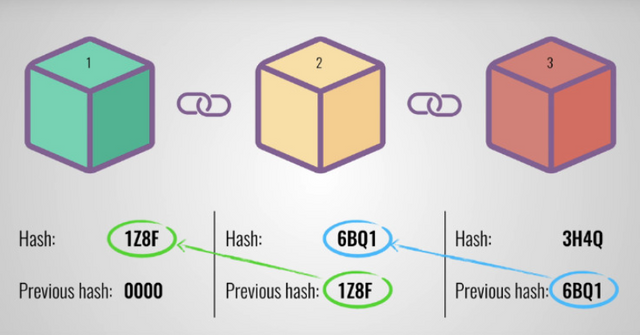
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain functions as a shared digital ledger, or "chain of blocks," in which transactions are grouped into blocks. Each block contains:
Transaction Information: Data about verified transactions, such as who is sending and who is receiving.
A Unique Hash: A code that uniquely identifies the block.
The Hash of the Previous Block: Connects the current block to the previous block, forming an immutable chain.
Process of How Blockchain Works:
Transactions: Someone initiates a transaction on the network.
Verification: The transaction is sent to a network of computers (nodes) that verify it.
Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is grouped into a new block with other transactions.
Add to the Chain: The block is permanently added to the chain and is connected to the previous block through the hashes.
.webp)
What does decentralization mean?
Unlike centralized systems, where a single entity (like a bank or a company) controls everything, blockchain operates on a network of computers called nodes. In this decentralized system, each node has a complete copy of the transaction record. This means there is no single point of control.
Advantages of Decentralization
Security: If one node fails or is attacked, the network continues to function because other nodes maintain the information. This makes it much harder for hackers to manipulate the system.
Transparency: All transactions are visible to all nodes in the network. This allows anyone to verify the transactions, increasing trust in the system.
No intermediaries: There is no need for a central entity to process transactions, which can reduce costs and make transactions faster.

What is block mining
Block mining is the process by which new transactions are validated and added to the blockchain, as well as the creation of new units of cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin. Here I will explain in more detail
Transaction Validation: When someone makes a cryptocurrency transaction, it is grouped with others into a block. Miners compete to validate this block, ensuring that all transactions are legitimate and comply with the rules of the blockchain protocol.
Solving Complex Problems: To validate a block, miners must solve a complex mathematical problem that requires significant computational power. This process is called proof of work. The first one to solve the problem has the right to add the block to the chain and receive a reward.
Reward: As an incentive for their work, the miner who validates a block receives a reward in the form of cryptocurrency, in addition to the transaction fees associated with the transactions in the block. This reward is crucial for the issuance of new coins and for maintaining the security of the network.
Network Security: Mining helps maintain the security and integrity of the blockchain. The more miners participate, the harder it becomes for an attacker to modify the information on the blockchain, as they would need to control more than 50% of the network's computational power.

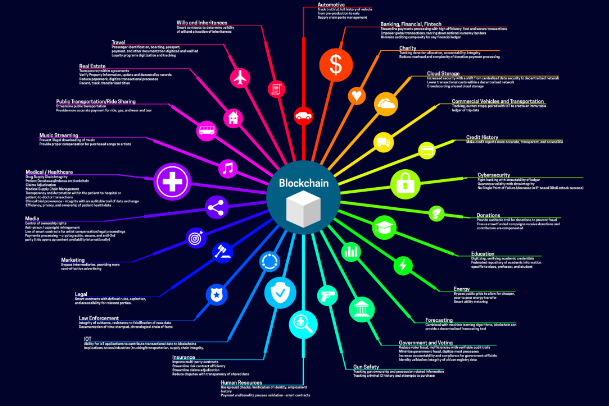
Examples of Blockchain Use
Logistics: Blockchain is used to track shipments and manage the supply chain. By recording each step of the process in an immutable ledger, companies can increase transparency and efficiency, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. This allows consumers to verify the authenticity of products and their origin.
Healthcare Sector: In the healthcare field, blockchain is employed to protect patient data and ensure the privacy of medical information. Storing medical records on a blockchain allows only authorized parties to access them, improving security and facilitating interoperability between different health systems.
Electronic Voting: Blockchain can be used for online voting systems, where each vote is recorded in a block. This increases transparency and security in the electoral process, as votes cannot be altered and can be easily audited.
Digital Identity: Blockchain enables the creation of secure and decentralized digital identity systems. This helps individuals maintain control over their personal information and verify their identity without relying on a third party, such as a government entity or a company.
Intellectual Property: In the field of intellectual property, blockchain can be used to register and manage copyrights and patents. This facilitates proof of ownership and helps protect creative works from piracy and unauthorized use.
Finance and Smart Contracts: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is used in the financial sector to execute smart contracts, which are programmable agreements that automatically execute when certain conditions are met. This can simplify processes such as loans, insurance, and commercial transactions.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of blockchain and its potential to transform various industries beyond the realm of cryptocurrencies
Conclusion: The Future of Blockchain
Blockchain technology has immense potential to transform various industries in the future. Its ability to enhance security, transparency, and efficiency makes it a valuable tool that can revolutionize sectors such as healthcare, finance, logistics, and more. As we move toward an increasingly digital world, understanding and harnessing the power of blockchain will be essential for businesses and individuals.
I encourage you to continue learning about this innovative technology. Blockchain is not only changing the way we conduct transactions, but it is also redefining trust and collaboration in society. Stay informed and explore the numerous applications that this technology can offer in the near future. The future of blockchain is bright, and you can be a part of it!
