Marketplace - how it works

Marketplace is a platform where a buyer is able to compare and purchase goods from several sellers at once. The Marketplace acts as an intermediary between a consumer and those who offer their products or services. As a rule, multiple types of goods are sold on such platforms, for example, a user will not find exclusively household appliances there.
Today, there are more than 40 marketplaces in the world with a capitalization of over $1 billion. There are the Lyft taxi aggregator (capitalization is $5.5 billion), the German delivery service Delivery Hero ($2.9 billion), the French search service Blablacar (capitalization $1,6 billion), Amazon and Alibaba Group in the list of high-profile names. On the Alibaba.com platform, hundreds of thousands of transactions are executed per month, while the Amazon retail market model provides 52% of the assortment, 46% of the revenue and 90% of the company's total margin.
The idea of the marketplace got a new twist of development in the 2000s after the release of Chris Anderson's book “The Long Tail: Why the Future of Business is Selling Less of More”. The book confirmed that the key to increasing sales is a wide range in the first place. That is, the more goods of different categories will be offered by a store, the higher the chance is that a buyer will buy something.
The popularity of the marketplace is easy to explain: they are able to accommodate countless products, provide convenient conditions for purchase, and provide the necessary guarantees and high-quality products. All these options are very attractive for a buyer: a user does not need to look through dozens of sites or go to the shopping center, he/she is able to buy everything on one electronic platform.
The marketplace model is relevant for a large number of industries, as this is a simple way to expand the range without increasing costs. World practice shows that most of the companies that join marketplaces are e-commerce players, large retailers, postal and logistics operators, financial organizations, and IT companies.
Each industry has its own goals and expectations from the transition to this model. Someone has exhausted available resources, but wants to ensure the further growth of business. Someone is frankly experiencing problems and understands that the marketplace is the only way to stability. Someone has just decided to expand channels of interaction with audience.
Any company that has resources can consider the transition to the marketplace today: sales outlets, logistical capabilities, a large client base, etc. are able to do it today. In general, we can say that this model is our future.
The obvious way to earn money for the marketplace is the commission for orders. But in some cases this is not the only source of income. Let’s consider the example of the Allyouneed.com marketplace, created by the DHL logistics operator. The benefits that DHL receives are expressed not only in monetary terms, but also in the fact that the operator himself delivers all goods, utilizing the logistics business line of the company.
Postal companies are also interested in creating marketplaces. And this is not surprising, because they have a number of competitive advantages: the presence of a developed logistics and payment infrastructure, as well as time-tested schemes of work in post offices. Now, for example, the project of launching the marketplace by Austrian post office is being prepared.
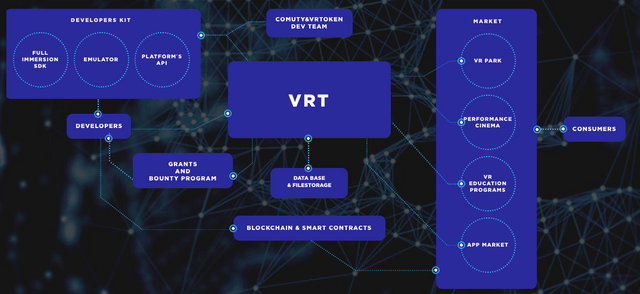
There are three stakeholders in this marketplace business model: buyers, third-party suppliers of goods and services (merchants) and the operator company that implemented the marketplace.
The benefit to a consumer is obvious: he/she can quickly and conveniently obtain a specific offer on transparent and, in most cases, uniform conditions for the entire range at one site. All the goods basket necessary for a buyer is listed on one site, and all the problems that arise can be solved on the principle of a "single window" (without contacting each of the suppliers directly).
The benefit that integration into the marketplace brings to suppliers is that they get access to a wide audience. Such a platform helps to create a new business or stay afloat for various market players.
Marketplaces, according to statistics, are visited more often than sites of niche players. It is also important that merchants can take part in consumer research conducted by the site owner and, thus, better understand the portrait of their client and evaluate his/her purchasing power. As mentioned earlier, the companies that implement the marketplace model can earn by receiving a commission from each transaction, as well as selling their goods or selling their own services, as the case with logistics companies is. Also, the implementation of such a model allows companies to either utilize their core business, or give it a new development, new growth points.
In addition to this, there is a wide range of commercial services that can bring additional profit to the marketplace, for example, the provision of premium services for merchants - targeted mailings, promo-placement, listing in search results and much more.
Blockchain technology is growing at an incredibly rapid pace. With the development of blockchain technology, the potential impact that a blockchain will have on the market is being considered. For example, the OpenBazaar project does not have an intermediary: the platform directly connects buyers and sellers. Thus, since there is no one in the middle of the transaction, there are no fees and no restrictions on what goods can be listed and sold. OpenBazaar implements the blockchain to return "power" to ordinary users, bypassing all intermediaries.
The main goal of the VRT (VR technologies) platform is the creation of a decentralized VR marketplace with convenient SDK and APIs that allow attracting a wide range of developers to the creation of VR content, not limited to one type of device or company policy.
Since the platform will be based on the blockchain technology, the project economy will be transparent and open to all market participants. This will result in a more equitable distribution of funds between the creators of the content and the site for its placement, as a result, the cost of the final product will become more affordable for consumers.
In addition, VRT will be regulated by the community itself, which will independently choose the priority directions for the development of the system. The platform will encourage the creation of content that is really interesting for users, but not for a narrow circle of owners, as it happens in centralized services nowadays. The problems of artificial vote wrapping and paid releases will become our past, and the best ratings will be gained by the content, which the participants of the system will really vote for.
Cutting a long story short, when launching the marketplace, a person should remember that it is a long process. If social services can make a leap from creating a product to selling a company within six months (this is the way that MSQRD took - the startup was absorbed by Facebook), then the founders of the aggregators are doomed to a long and painstaking alignment of the system. At the same time, the potential for financial growth of companies that automate entire niches is huge. It certainly depends on the volume of the target market. However, the founders of popular marketplaces do not always approach the calculation of such indicators with due diligence - it is unlikely that the founders of Airbnb drew the growth charts of the niche of renting accommodation for travelers by renting a mattress in a room in San Francisco in 2007.