ALL ABOUT CHINA:INFORMATION OF CHINA FACTS,GEOGRAPHY, GOVERNMENT, CULTURE & HISTORY

http://chinatourpro.com/all-about-china-information-of-china-facts-geography-government-culture-history/
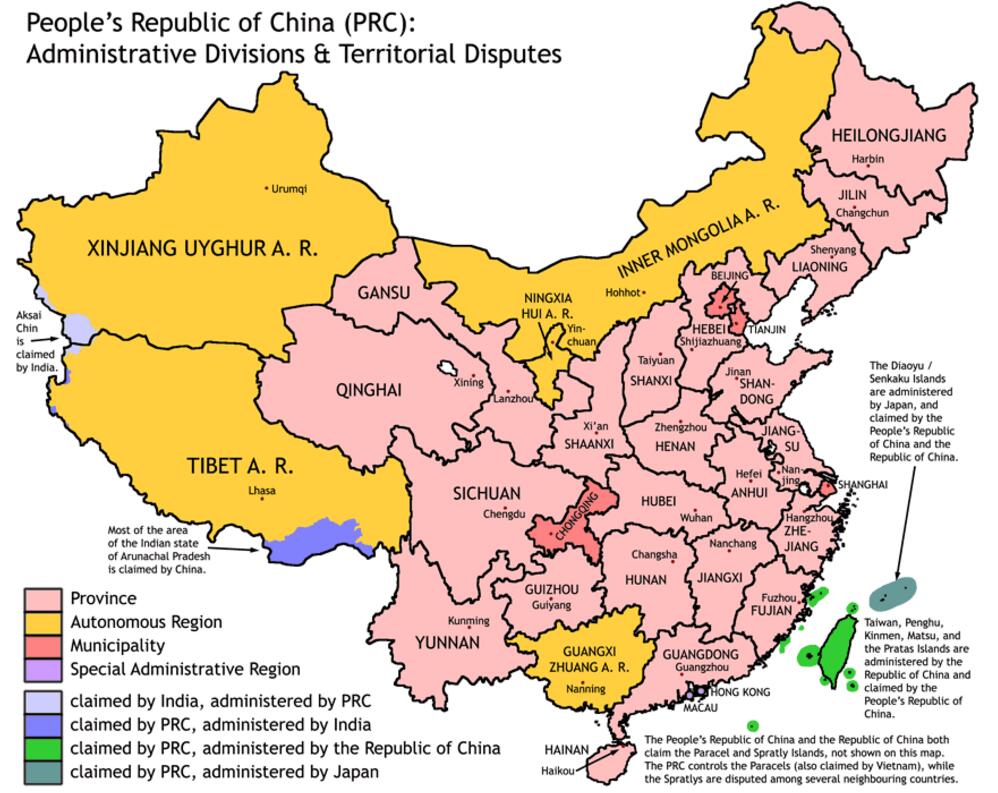
The People’s Republic of China located in eastern Asia, the Pacific West Bank, is a socialist country. China was established in October 1, 1949, five-star red flag is the national flag, “Volunteers March” is the national anthem. The national emblem includes the national flag, Tiananmen Square, gears and wheat ears. China’s capital is Beijing. China have 23 provinces, 5 autonomous region, 4 municipality directly under the Central Government and 2 special administrative regions. It is a united multi-ethnic country with 56 nationalities . The Han nationality accounts for 91.51% of the total population.

china-national-flag
The People’s Republic of China has a land area of about 9.6 million square kilometers, the mainland coastline of more than 18,000 km, the island coastline more than 14,000 km, the water area of about more than 470 million square kilometers. Sea area has more than 7600 islands, of which the largest island is Taiwan with an area of 35798 square kilometers. Land border with 14 countries, and 6 countries adjacent to the sea.
China is one of the four ancient civilizations, has a long history and culture, is the world’s third largest country, the world’s largest population country, is a permanent member of the UN Security Council. China is the world’s second largest economy, the world’s largest trading country, the world’s largest foreign exchange reserves country, the world’s largest steel producer and the world’s largest agricultural country, the world’s largest grain output country. The second largest country to attract foreign investment, and an important member of many international organizations.The People’s Republic of China has the most abundant world cultural heritage and natural cultural attractions, is one of the world’s top tourism countries.
Chinese civilization is based on ‘Huaxia’ civilization as a source of Chinese culture. Chinese people call themselves the descendants of the dragon and the ‘Yan Emperor and the Yellow Emperor’ descendants.China is one of the four ancient civilizations of the world, has a long history. Since about 5000 years ago, the Central Plains region began to form a settlement organization and then the state, after several national blending and dynasties change, formed a multi-ethnic unified state. After the 1911 Revolution in the early 20th century, the monarchical government withdrew from the stage of history and the republican government was established. After the founding of the People’s Republic of China in 1949, the people’s congress system was established in mainland China.
The population of the Song Dynasty exceeded 100 million and the population of the Qing Dynasty exceeded 400 million. At present, the population of China has exceeded 1.3 billion.
Chinese culture has a long history and is rich and colorful. It is the cultural sovereign of the East Asian cultural circle. It occupies an important position in the world cultural system. Due to its geographical location and natural conditions, humanities and economy have their own characteristics. China has a variety of folk culture, traditional art forms of poetry, drama, calligraphy, painting and so on. Chinese New Year, Lantern Festival, Qingming Festival, Dragon Boat Festival, Mid-Autumn Festival and Chongyang Festival are important traditional festivals in China.
china-map
Major cities: Shanghai, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Wuhan, Taipei, Nanjing, Chengdu, Chongqing, Shenyang, Xi’an, etc.
Special Administrative Region: Hong Kong, Macao
National Day: October 1
National anthem: “Volunteers March”
Flag: five – star red flag
Country Code: CHN
Official language: Mandarin
Currency: RMB (HK $, MOP, NT)
Time zone: Dongba District (Beijing time)
The Political System: The People ‘s Congress System
National leaders: President Xi Jinping, Premier Li Keqiang, Chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress Zhang Dejiang
Population: 13.6782 million (2014)
Population density: 139.6 persons / km2 (2011)
Main ethnic groups: Han, Manchu, Mongolian, Hui, Uygur, Tibetan, Zhuang
Main Religions: Taoism, Buddhism, Protestant Christianity, Catholicism, Islam
Historical figures: Yan Emperor, the Yellow Emperor, Confucius, Sun Yat-sen and so on
Characteristics of scenic spots: the Great Wall, the Forbidden City, Terracotta Warriors and Horses
Characteristics of animals: dragon, phoenix, panda and so on
chinese-dragon
chinese-dragon
Cultural thought: hundreds of philosophers, Chinese clothing culture, Tang poetry and so on
Land area: 9,634,057 square kilometers,
Territorial sea: about 4.7 million square kilometers
Waters rate: 2.8%
GDP Total: 67.67 trillion yuan (2015) Per capita GDP: 52,000 yuan (2015)
International Telephone Code: +86 (Hong Kong: +852, Macau: +853, Taiwan: +886)
International domain name abbreviation: com, .cn (Hong Kong: .hk, Macau: .mo, Taiwan: .tw)
Road access: by the right driving (Hong Kong, Macao left driving)
Scenic spots: the Forbidden City, the Great Wall, Mount Tai, Terracotta Warriors and Horses
The ruling party: the Chinese Communist Party
The longest river: the Yangtze River
The largest lake: Qinghai Lake
Coastline: 1.8 million kilometers
Geography Most High: Mount Everest (8844.43 m)
The lowest point of geography: Turpan Aydin Lake depression (-154.31 m)
Central Bank: People ‘s Bank of China
Main festivals: Spring Festival, Ching Ming Festival, Dragon Boat Festival, Mid-Autumn Festival and so on
Institutions of higher learning: Peking University, Tsinghua University, Fudan University
Legal system: European legal system (Hong Kong is Anglo-American law system)
National Constitution: “The Constitution of the People’s Republic of China”
Territorial scope
Land territory: mainland China and its coastal islands, Taiwan and its subsidiaries. Dongsha Islands, Xisha Islands, Zhongsha Islands, the Nansha Islands and all other islands belonging to the People’s Republic of China (including the Diaoyu Islands, ‘Su rock’ reefs). Land territory is about 9.6 million square kilometers.
Marine land: the Bohai Sea and the vast majority of the Yellow Sea, East China Sea, South China Sea and exclusive economic zone, a total of about 4.7 million square kilometers, of which the South China Sea within the Jiugong line area of about 3 million square kilometers.
Land area: land area of 9.6 million square kilometers, accounting for about 1/15 of the world total land area, less than Russia (17.075 million square kilometers) and Canada (9.971 million square kilometers), ranking third in the world.
Land resources: mountain 3.2 million square kilometers, plateau 2.5 million square kilometers,basin 1.8 million square kilometers, plain 1.15 million square kilometers, hills 95 million square kilometers (as of 1997).
China terrain
China’s terrain is the west high east low, mountain, plateau and hills account for about 67% of land area, basins and plains account for about 33% of land area. Mountains are mostly east-west and northeast-southwest direction, there are Altai, Tianshan, Kunlun Mountains, Karakoram, Himalayas, Yinshan, Qinling, Nanling, Daxinganling, Changbai Mountain, Taihang Mountain, Wuyi Mountain, Taiwan Mountains and Hengduan Mountains . The western region has the world’s tallest Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, with an average elevation of 4,000 meters or more, known as “the roof of the world,” said. Mount Everest has an elevation of 8844.43 meters, is the world’s highest peak. Inner Mongolia, Xinjiang, the Loess Plateau, Sichuan Basin and the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, is China’s second-level terrain ladder. Daxinganling, Taihang Mountain, Wushan, Wuling Mountain, Xuefengshan to the coastline are mostly plains and hills, is the third-level ladder. The continental shelf to the south of the coastline is rich in seabed resources.
Millions of years ago, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau uplift, this major crustal movement formed China’s landscape. From the air overlooking the land of China, the terrain is like a ladder, from west to east, gradually declining. By the Indian plate and the impact of the Eurasian plate, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau continue to uplift, with an average elevation of 4,000 meters above, constitute the first step of the terrain of China. Plateau of the Himalayas peak of Mount Everest up to 8844.43 meters, is the world’s highest peak. Inner Mongolia Plateau, the Loess Plateau, the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and the Tarim Basin, Junggar Basin, Sichuan Basin, with an average elevation of 1000-2000 meters, constitute the second step of China’s terrain.
Daxinganling, Taihang Mountain, Wushan and Xuefeng Mountain, east to the Pacific coast is the third ladder, this ladder terrain dropped to 500 meters to 1000 meters below. And then east to the shallow continental shelf of China, which is the fourth-level ladder, mostly has less than 200 meters water depth.
China’s river
China’s rivers and lakes are numerous. These rivers, lakes are not only an important part of China’s geographical environment, but also rich in natural resources. China’s rivers and lakes region are unevenly distributed.China has many long-standing rivers. There are more than 1500 rivers which has a watershed area of more than 1000 square kilometers.
China’s lake
China has a total of more than 24,800 lakes. The distribution of lakes is very uneven. In general, the eastern monsoon region, especially the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, is China’s largest freshwater lake group; the western Qinghai-Tibet Plateau lakes are more concentrated, mostly inland saline lake.
China’s famous freshwater lake are Poyang Lake, Dongting Lake, Taihu Lake, Hongze Lake, Chaohu Lake and so on. Most of the lakes in the inner flow area are the end of the inner stream. The lake can only flow in. Because of the evaporation, the salty lake is formed, such as Qinghai Lake and Nam Co Lake.
China’s Temperature
Winter Temperature Distribution
Mohe in Heilongjiang temperature is below -30 ℃. Sanya in Hainan, the temperature is above 20 ℃. The warmth of the south and the coldness of the north are the characteristics of winter temperatures in China.
Summer Temperature Distribution
Most areas of China is more than 20 ℃, many parts of the South is 28 ℃ or more; Xinjiang Turpan Basin in July the average temperature is 32 ℃, which is China’s hot summer center. So the country is generally high temperature in summer.
China’s economy
Ancient China has a developed agricultural economy. Its economic scale in a very long period of time leaded the world. Due to the changes of the natural environment and the human factors such as war, the ancient Chinese economy usually had the same cycle as the rise and fall of dynasty.
After the Qing Dynasty, China clung to the agricultural economy, while the Western world in the same period took the lead in realizing the industrial revolution, the Chinese economy then lagged behind in the West. Since the Opium War, China’s original conservative agricultural economy has been challenged by the Western world.
China followed the process of developing industry in the West, and had developed smoothly since the establishment of the Republic of China National Government until the Sino-Japanese War.
Since the 1980s, the Deng Xiaoping government announced reform and opening up, began to implement the socialist market economy. China in recent years to 2010, GDP is more than 7.2 trillion US dollars. China has become the world’s second largest economy after the United States. China is still the fastest growing economy in the world, but per capita GDP is still at the middle level of the world (89th), and is increasingly constrained by resource and widening gap between the rich and the poor. Among the provinces of the People’s Republic of China, Guangdong is the province with the highest GDP, and Zhejiang is the province with the highest per capita income.
The economic ties between China, Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan are becoming more and more close in the process of globalization.
Chinese Language and Culture
Mandarin Chinese is the world’s most used language, is China’s official language. Chinese characters are the quintessence of China. Mandarin is based on the pronunciation of Beijing as the standard tone, based on the northern dialect, the classic modern vernacular works as a grammar specification. The Law of the People’s Republic of China on the Common Language and Language, promulgated on October 31, 2000, defines Putonghua(Mandarin ) as a national common language.
Chinese dialects are usually divided into seven dialects: the northern dialect, Wu dialect, Hunan dialect, Gan dialect, Hakka dialect, Guangdong dialect, Min dialect. The northern dialect is divided into northern Mandarin, northwest Mandarin, Southwest Mandarin, ‘down the river’ Mandarin.
Oracle is China’s earliest text, has more than 3,000 years of history. Some ethnic groups have also completely used Chinese characters, while Chinese characters are also common in all ethnic minorities of the text. Since the 1950s, the state has sorted out and simplified the existing Chinese characters. The State has formulated and published the standards of “the first batch of variant Chinese characters”, “simplified Chinese characters”, “simplified Chinese character list”, “modern Chinese common word table”, “modern Chinese universal word table” and other standards. October 31, 2000, China promulgated the “Law of the People’s Republic of China National Language” to determine the norms of Chinese characters for the national common text. Standardized Chinese characters refer to simplified words and simplified characters.
Before the founding of the People’s Republic, 21 ethnic minorities had their own words. After the founding of the People’s Republic of China, the government has for the Zhuang, Buyi, Yi, Miao, Hani, Lisu, Naxi, Dong, Wa, Li and other ethnic groups developed written program.
February 11, 1958, the first session of the Fifth National People ‘s Congress passed a resolution published “Chinese Pinyin program”. The state provides the Chinese Phonetic Alphabet as a tool for Chinese spelling and phonetic transcription.
China’s music
Since the Neolithic China invented the bone flute. Bone flute is the world’s earliest known wind instrument.Chinese traditional music is formed in the exchange and integration of Central Plains music, four-domain music and foreign music, including folk music, literati music, religious music, court music and other categories. Chinese traditional music has distinct characteristics. Commonly used instruments are Zheng, Qin, Xiao and so on.
Chinese traditional dance has a long history, reflecting the traditional Chinese culture, aesthetics, martial arts, acrobatics and drama.
Opera is a traditional stage art of China. It integrates many kinds of opera such as beijing opera, Yu opera, Hebei opera, Huangmei opera, Jinju opera and Huagu opera.
Chinese painting
Chinese painting mainly refers to the silk or rice paper painting, with a brush, soft pen or finger as a tool.Chinese painting can be divided according to the content of flowers and birds painting, landscape painting and figure painting.
Science and technology
China is one of the ancient civilizations. Ancient China had a different technological tradition from the West. Ancient China contributed a lot of inventions to the world, and developed unique and advanced achievements in astronomy, mathematics, medicine, machinery, metallurgy, ceramics, textile, architecture and so on.
Some inventions invented by China in advance of other countries include: four inventions (papermaking, printing, compass, gunpowder), seismograph, abacus, umbrella, toothbrush, stirrup, silk, Rugs, porcelain, oil wells, paper money, matches, lacquerware, kites, hot air balloons, fishing rods, fans, crossbows, docks, trebuchet and so on.
After entering the modern society, Chinese scientific research has been developing continuously. The successful launch of the Shenzhou-series spacecraft in 2003 marked the country’s ability to send people into space alone.
China’s religion
It is generally believed that Taoism is a religion founded in China. Spring and Autumn Period (about the sixth century BC), Laozi founded Tao School.Qin and Han Dynasties Fangxian School, Huanglao School appears. To the Eastern Han Dynasty, Zhang Daoling founded ‘zheng yi meng wei ‘ School,marking the formal formation of Taoism.
The Eastern Han Dynasty Ming Emperor Yongping years, the Han emperor sent envoys to Tianzhu(India today) for Buddhist scriptures. Since then Buddhism has entered China. Wei Jin Southern and Northern Dynasties, due to social unrest, people began to widely seek spiritual beliefs, Buddhism began to flourish. Because Taoism, Buddhism and Confucianism influence each other, the Chinese religious tradition of the unity of the three religions formed.
Chinese Islam originated from Muhammad’s uncle who led the mission to China and built one of the world’s oldest mosque ‘Huai saint’ temple. During the Song dynasty, Chinese Muslims controlled import and export trade and gradually gained influence in the regime. Zheng He is a famous Muslim. During the Ming dynasty, the descendants of early Muslim immigrants were integrated into Chinese society in terms of language, names and customs, and Nanjing became an important center for Islamic learning. Islam is the main population of the Hui, Uygur, Kazak, Kirgiz, Tatar, Uzbek, Tajik, Dongxiang, Sala and other 10 ethnic groups.
The introduction of Christianity to China was in Tang Dynasty. In the Yuan Dynasty, Catholic was introduced into China. These religions became localized to accommodate Confucian society. In the Qing Dynasty, because the Holy See forbidden Chinese worshipers offering sacrifices to ancestors, the Qing government banned Catholic activities in China in YongZheng years. In 1840 the West opened the door of China by gunboat, a large number of missionaries came to China, and opened a number of education, medical and other institutions.
Chinese apparel
The Han Chinese clothing(Hanfu), also known as China’s national dress, Han clothing, Tang clothing. From the Yellow Emperor ascended the throne (about 2698 BC) to the late Ming Dynasty (the middle of the 17th century AD) in the past 4,000 years, the Han Chinese clothing is a unique cultural characteristics of the traditional national costumes. Chinese clothing is the world’s oldest national costumes, is the Han national heritage of 4,000 years of traditional national costumes. Based on the Confucian classics “Book of Songs”, “Shangshu”, “Zhou Li”, “Book of Rites”, “Book of Changes”, “Spring and Autumn” and other historical collections, the Han Chinese clothing inherited Chinese ritual culture and influenced the whole Chinese cultural circle .
Japan, North Korea, Vietnam have promulgated the law to follow the Chinese crown clothing system. In the Qing Dynasty in 1645, the Qing Dynasty Emperor Duoergun issued a shaving order, requiring all people must shave and change clothes, so in the next few hundred years the Han man basically switched to the original Manchu costumes. Modern Chinese dress gradually converge with Western countries. China’s ethnic minorities often have their own unique national costumes.
Chinese traditional festivals
Chinese New Year: Lunar New Year first day
Lantern Festival: the first lunar month fifteen
Head teeth: Lunar New Year in February two
Cold Food Festival: Ching Ming Festival the day before
Ching Ming Festival: 108 days after the winter solstice
Dragon Boat Festival: fifth day of the fifth lunar month
Tanabata: seventh day of the seventh lunar month
Zhongyuan Festival: Lunar July fifteen
Mid – Autumn Festival: Lunar August 15
The Double Ninth Festival: September 9th
Winter Solstice: solar term winter solstice
Laba Festival: eighth day of the eighth lunar month
The end of the tooth: the lunar month of the twelfth lunar month
Sacrifice stove: the twelfth lunar month
New Year ‘s Eve: the last day of December
diet
China is the hometown of tea, Chinese tea culture has a long history, broad and profound.
China is the ancient country of making wine.Pre – Qin period appeared wine. In Han Dynasty wine technology was developed . The red wine was introduced in the Eastern Han Dynasty. Chinese wine culture has a long history. Wine is not only used for worship, Union, celebration and other official activities, but also for civil funeral rituals, get-together and other occasions.
Chinese food has gone through thousands of years of development history. It consists of ancient palace dishes, official dishes and different flavors of local cuisine. Famous cuisines are Shandong cuisine, Sichuan cuisine, Cantonese cuisine, Fujian cuisine, Su Cai cuisine, Zhejiang cuisine, Hunan cuisine, Anhui cuisine and so on. Chinese food is mostly processed into small pieces. Chinese used chopsticks to eat.
An Overview of Chinese History
Ancient times and slave society (1.7 million years ago – 476 BC)
China is one of the earliest developed countries in the world, with nearly 4,000 years of written history.
Found in Yunnan Yuanmou ape-man fossils indicate that 1.7 million years ago, “Yuanmou people” is the earliest primitive human known in China. 60 million years ago living in Beijing Zhoukoudian area, “Beijing Man” can walk upright, to create, use simple tools, and know the fire.In Yuyao, Zhejiang Hemudu and Xian Banpo sites, people found the cultivation of rice and miliary and agricultural tools which was used six or seven thousand years ago.
The Xia Dynasty began in about 2070 BC. The central area of the Xia Dynasty, in today’s western Henan Province and southern Shanxi area, its influence and influence has reached the Yellow River north and south, and began to enter the slave society .. After the fall of the Xia Dynasty, the Shang Dynasty, the Western Zhou Dynasty deepened the slavery.Then, “Spring and Autumn” era began. This period is the slave society to the feudal society transition.
About 5000 years ago, the Chinese people know the technology of smelting copper. More than 3,000 years ago, the Shang Dynasty, the Chinese began to use iron, began making white pottery and painted pottery. Silk weaving production is also quite developed, mastered the world’s first jacquard silk weaving technology. During the Spring and Autumn Period, the steelmaking technology had already appeared, and the thought and scholar of the Spring and Autumn and Warring States period was unprecedentedly active, and the famous philosopher Lao Tzu, Confucius, Mencius and military scientist Sun Wu, who had far-reaching influence on later generations, emerged.
Qin Shi Huang (the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty) (BC 259-210 BC) and his empire
In 221 BC, Qin Shihuang Ying Zheng ended more than 250 years of the Warring States period. He established the first unified, centralized and multi-national feudal state in the history of China – Qin. Qin Shihuang unified the text, united the weights and measures, unified the currency, developed the county system .He developed China’s feudal state framework . In more than 10 years, he organized more than 300,000 people in the north of China to built a Great Wall stretching 5,000 km, and during his lifetime began to build his large graves .In 1974, Qin Shi Huang’s terracotta shocked the world .8000 life-size pottery Figurines, ceramic horses and chariots unearthed, known as “the world’s eighth largest miracle.”
Han Dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD) and the “Silk Road”
206 BC, Liu Bang established a strong Han Dynasty.Agriculture, handicrafts, business has been greatly developed. The population of the Han Dynasty reached 50 million. During the reign of Martial Emperor Liu Che (140-187 BC), the most powerful period of the Han Dynasty, he extended the actual control of the Central Government from the Central Plains to the Western Regions (now Xinjiang and Central Asia). The envoy Zhang Qian made two trips to the Western Regions, opening the road from Chang’an (now Xi’an in Shaanxi Province) to the east coast of the Mediterranean via Xinjiang and Central Asia, known as the “Silk Road”. With the close contact between the East and the West, Buddhism was introduced to China in the first century AD. AD 105, officials Cai Lun invented the paper, so that the human writing material has undergone fundamental changes.
The prosperity of the Tang Dynasty (618-907)
After the Han Dynasty, Li Yuan established Tang Dynasty in 618. Emperor Tang Taizong Li Shimin, the son of Li Yuan (626-649 reign), implemented a series of enlightened policies. Agricultural, handicraft and commercial, textile, dyeing, ceramics, smelting, shipbuilding and other technologies have been further developed. National water and land transportation criss-crossing. In the seventies, China’s power not only firmly rooted in the Tarim Basin, Junggar Basin, Ili River Basin , but also extended to many of the city-states in Central Asia. China and Japan, Korea, India, Persia, Arabia and many other countries have developed a wide range of economic and cultural ties.
Song, Yuan, Ming and Qing (960-1911)
After the demise of the Tang Dynasty, it experienced a period of frequent wars in the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, and the Song Dynasty (960-1279) was established by the Late Zhou General Zhao Kuangyin in 960 AD. In the Southern Song Dynasty, the regime moved to the south, and the advanced economy and culture of the North were extended to the south, which promoted the economic development of the region.
In 1206, Genghis Khan established the Mongol Khanate, whose grandson Kublai Khan took over the Central Plains in 1271 and established the Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368). Kublai put an end to the chaos of centuries of multi-regimes, unifying China (including Xinjiang, Tibet and Yunnan). Papermaking, printing, compass, gunpowder which are the “four great inventions” of the ancient Chinese science and technology , in the Song and Yuan Dynasties have been introduced to the rest of the world, made great contributions to world civilization.
In 1368, the Ming emperor Zhu Yuanzhang established the Ming Dynasty (1368-1644) in Nanjing, and his son Zhu Di (1360-1424) ascended the throne and began to build the city and palace of Beijing on a large scale and moved the capital to Beijing in 1421. 1405 To 1433, he sent eunuch Zheng He conducted seven large-scale maritime voyage, through the Southeast Asian countries, the Indian Ocean, the Persian Gulf, the Maldives Islands, as far as the east coast of Africa to Somalia and Kenya, was the world’s largest, Farthest offshore adventure at that time.
In the late Ming Dynasty, the Manchu people in the northeastern part of China rose rapidly, establishing the Qing Dynasty (1644-1911) in 1644. The most famous Emperor Kangxi of the Qing Dynasty (1661-1722) reunified Taiwan, He also strengthened the jurisdiction of Tibet. Under his rule, China covers an area of more than 11 million square kilometers.
Modern (1840 – 1919)
At the beginning of the nineteenth century, the Qing dynasty declined rapidly, and the British imported opium into China during this period. The Qing government tried to ban opium. Britain to protect the opium trade, in 1840 launched a war of aggression against China, the Qing government finally signed the “Treaty of Nanking” with the British government. After the Opium War, Britain, the United States, France, Russia, Japan and other countries continue to force the Qing government signed various unequal treaties, since then, China gradually reduced to semi-colonial and semi-feudal society.
In 1911 Sun Yat-sen led the Revolution, overthrew the Qing Dynasty 200 years of rule, ended the more than 2000 years feudal monarchy. The Republic of China was established. This is one of the greatest events in modern Chinese history.
The New Democratic Revolution (1919-1949)
The May Fourth Movement, which took place in 1919, was considered the source of many important events in modern Chinese history. The immediate cause was the unequal terms imposed on China after the First World War. Strong patriotism led to this protest movement, initiated by students and then developed into all parts of the country. It also triggered a variety of new ideas into China, one of the most noteworthy is the spread of Marxism-Leninism in China. In 1921, Mao Zedong and other 12 people on behalf of the communist group in Shanghai held its first national congress. The Chinese Communist Party was born.
In the process of leading the Chinese people to carry out the new-democratic revolution, the Chinese Communist Party experienced the Northern Expedition (1924-1927), the Agrarian Revolutionary War (1927-1937), the War of Resistance Against Japan (1937-1945) and the National Liberation War (1945- 1949) four historical stages. During the War of Resistance Against Japan, the Chinese Communist Party and the Kuomintang worked together to fight the invaders and won the war. In 1945, the Kuomintang launched a civil war. After three years of liberation war, the Chinese Communist Party in 1949 overthrew the Kuomintang government.
The People’s Republic of China (1949-)
October 1, 1949, Beijing 300,000 people gathered in Tiananmen Square held the founding ceremony. Chairman of the Central People’s Government Chairman Mao Zedong solemnly declared: the People’s Republic of China was formally established.
At the beginning of the founding of the PRC, the Chinese government successfully completed land reform in area that accounted for more than 90% of the country’s total agricultural population. Three hundred million farmers have shared about 47 million hectares of land. The first five-year plan, implemented between 1953 and 1957, made great achievements: the average annual growth rate of national income was more than 8.9%; the establishment of a number of basic industries which were necessary for the industrialization of the country and had not previously been included, including aircraft and automobile manufacturing, Heavy and precision machinery manufacturing, power generation equipment manufacturing, metallurgical and mining equipment manufacturing and advanced alloy steel and non-ferrous metal smelting.
From 1957 to 1966, China carried out large-scale socialist construction. In 1966 compared with 1956, the national industrial fixed assets increased by 3 times the original price. National income increased by 58 per cent on a comparable basis. The output of major industrial products have several times or even ten times the growth. From May 1966 to October 1976, during the “Cultural Revolution”, the country and its people suffered the most serious setbacks and losses since the founding of the People’s Republic of China.
October 1976, Jiang Qing counterrevolutionary group was shattered, “Cultural Revolution” ended, China entered a new historical period. The former General Secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC), Deng Xiaoping, resumed the policy of “reform and opening-up” since 1979 and put the emphasis on modernization. Through the reform of economic system, political system, gradually established a road with Chinese characteristics. Since the reform and opening up, China has undergone profound changes. Whith rapid economic development, people’s living standards improved significantly.
Chinese history chronology
Xia Dynasty: 2070 BC – 1600 BC
Shang Dynasty: 1600 BC – 1046 BC
Western Zhou Dynasty: 1046 BC – 771 BC
Spring and Autumn: 770 BC – 476 BC
The Warring States Period: BC 475 BC – 221 BC
Qin Dynasty: 221 BC – 207 BC
Western Han Dynasty: 206 BC – 24 AD
Eastern Han Dynasty: AD 25 years
Three countries (Wei, Shu, Wu): AD 220 – 265 years
Western Jin Dynasty: AD 265 – 316 years
Eastern Jin Dynasty: AD 317-420 years
The Southern and Northern Dynasties AD 420 – 589 years
The Sui Dynasty: AD 581 -618 years
Tang Dynasty: 618 AD – 907 years
Five generations: AD 907 years – 960 years
Northern Song Dynasty: 960 AD – 1127 years
Southern Song Dynasty: AD 1127-1279 years
Yuan Dynasty: Year 1271 – 1368 years
Ming Dynasty: 1368 AD – 1644 years
Qing Dynasty: AD 1644 – 1911 years
Republic of China: AD 1912 -1949 years
The People’s Republic of China: 1949 –