SLC | S21W2 | Costs For Entrepreneurs - Cost Elements
It is another warm welcome to everyone on this blog. Without any waste of time, let's launch into the matter of the day.
What Is The Relationship Between Costs And Financial Accounting? |
|---|
 Source Source |
|---|
Financial accounting and costs are closely related as they duo play extremely important roles in business decision-making.
Financial Accounting:
Financial accounting concentrates on preparing financial statements such as Balance Sheets and Income Statements to provide stakeholders with information regarding a company's financial performance and position.
Cost Accounting:
This involves analyzing and reporting costs connected with the production of goods or services. It assists managers make knowledge-based decisions about pricing, budgeting, as well as resource allocation.
A. Cost classification
Financial accounting utilizes cost classifications such as direct materials, labor, and overhead to report expenditures on financial statements.
B. Asset valuation
Financial accounting values assets like inventory and property with the use of cost-based methods.
C. Budgeting
Financial accounting influences budgeting decisions using the means of analyzing historical costs and forecasting future expenditures.
D. Expense recognition
Financial accounting recognizes expenditures, like the cost of goods sold, on the Income Statement.
E. Cost allocation
Financial accounting appropriates costs to different departments or products making use of methods like absorption costing.
F. Performance evaluation
Financial accounting utilizes cost data to assess business performance, like calculating return on investment (ROI).
Establish The Difference Between Fixed Costs And Variable Costs, Providing Examples Of Each. |
|---|
In cost accounting, Fixed Costs and Variable Costs are two fundamental concepts.
Fixed Costs
- Remain constant irrespective of changes in the volume of production or sales
- Not directly influenced by fluctuations in business activities
- Principally long-term commitments
The examples of fixed costs include the following:
- Rent or lease payments
- Insurance premiums
- Property taxes
- Annual software licenses
- Salaries and benefits (administrative staff)
- Depreciation and amortization
- Mortgage payments
- Executive salaries
Variable Costs
- Fluctuate alongside changes in production volume or sales
- Directly connected to business activity
- Principally short-term commitments
The examples of variable costs include the following:
- Raw materials or direct materials
- *Utilities (e.g., electricity, water, gas)
- Shipping and transportation costs
- Sales commissions and discounts
- Labor costs (production staff)
- Marketing and advertising expenditures
- Inventory costs
- Fuel and maintenance expenditures
The major differences between fixed costs and variable costs can be categorized as follows:
A. Timeframe
While fixed costs are principally long-term, variable costs are short-term.
B. Variability
While fixed costs remain constant, variable costs change.
C. Impact on profitability
Fixed costs influence profitability irrespective of sales, while variable costs influence profitability based on the volume of sales.
D. Relationship to production
Fixed costs aren't directly associated with production, while variable costs are.*
Understanding fixed and variable costs helps businesses to make knowledge-based pricing decisions, optimize resource appropriation and manage cost efficiently. It also helps improve profitability and develop precise budgeting and forecasting.
In A Real Or Fictional Case, Identify The Cost Elements In Manufacturing A Product Or Providing A Service. |
|---|
Let's consider a fictional case of a t-shirt manufacturing company.
Company: Hisgeneral T-Shirt Manufacturings
Product: Customized T-Shirts
Fixed Costs:
- Factory rent: $4,000/month
- Equipment depreciation (printing, cutting, sewing): $1,500/month
- Salaries (administrative staff): $7,000/month
- Insurance (liability, property): $1,000/month
- Marketing expenses (branding, advertising): $2,500/month
Total Fixed Costs = $16,000
Variable Costs:
- Raw materials (t-shirt fabric, thread, ink): $4/shirt
- Labor costs (production staff): $3/shirt
- Utilities (electricity, water): $0.60/shirt
- Packaging materials (bags, labels): $0.20/shirt
- Shipping costs: $2/shirt
Total Variable Costs = $9.8
Semi-Variable Costs:
- Maintenance expenses (equipment repair): $450/month + $0.10/shirt
- Quality control expenses: $950/month + $0.50/shirt
Total Semi-Variable Cost = $1,400.6
Direct Costs:
- Raw materials
- Labor costs
- Packaging materials
Indirect Costs:
- Factory rent
- Equipment depreciation
- Salaries (administrative staff)
- Marketing expenses
Other Costs:
- Opportunity costs (e.g., forgone revenue from idle capacity)
- Sunk costs (initial investment in equipment)
Total Cost per Unit:
Total Fixed Costs / Total Units Produced + Variable Costs per Unit
= ($16,000/month / 4,500 units) + $9.80/shirt
= $3.55 + $9.80
= $13.35/shirt
Comprehending these cost elements will help Hisgeneral T-Shirt Manufacturings set competitive prices, enhance production levels, effectively manage cost, enhance profitability, and make knowledge-based decisions about investments and expansions.
The above example illuminates and explicitizes the importance of identifying and classifying cost elements in manufacturing and service provision.
The Company Steemians Manufactures A Single Product. During A Given Period, The Following Costs Were Incurred: |
|---|
You Are Asked To Separate Direct Costs From Indirect Costs And Non-manufacturing Costs, And Also Calculate The Total Direct And Indirect Manufacturing Costs.
You Can Present The Example Using Google Sheets.
The costs can be grouped into direct, indirect, and non-manufacturing costs as follows:
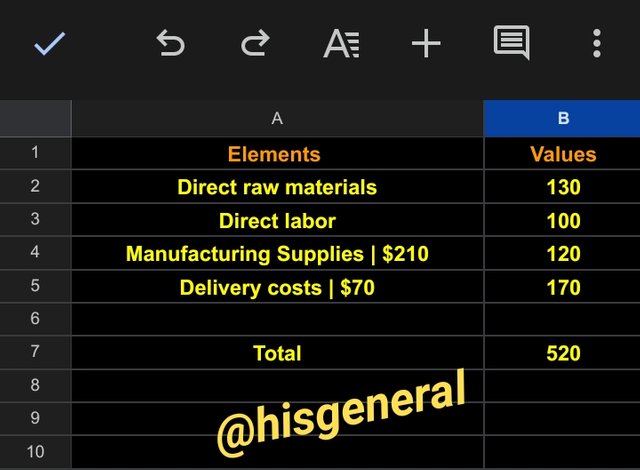
Direct Costs
- Direct labor – 100
- Manufacturing Supplies – 210
- Delivery costs – 70
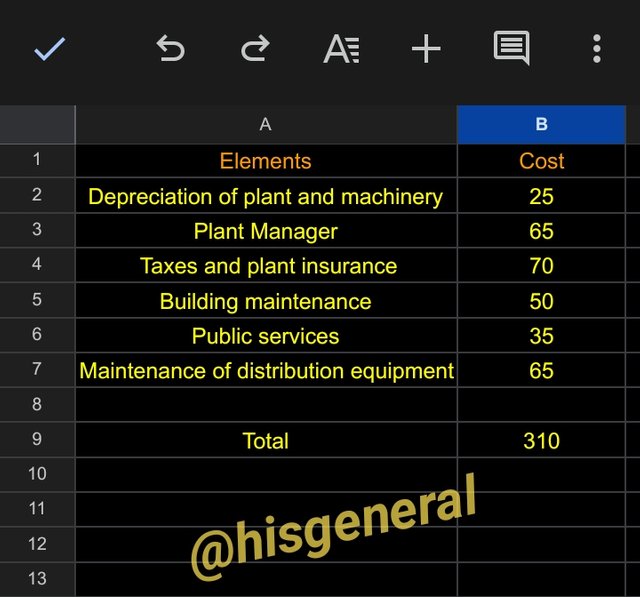
Indirect Costs
- Depreciation of plant and machinery – 25
- Plant Manager – 65
- Taxes and plant insurance – 70
- Building maintenance – 50
- Public services – 35
- Maintenance of distribution equipment – 65
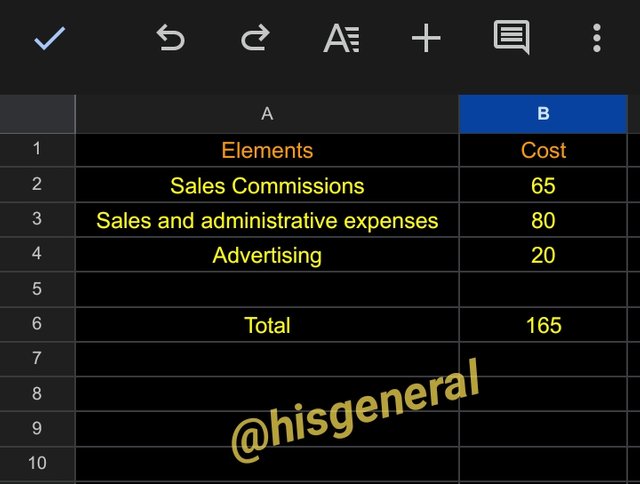
Non-Manufacturing Costs
- Sales Commissions – 65
- Sales and administrative expenses – 80
- Advertising – 20
Total Direct Costs = 380
Total Indirect Costs = 310
Total Non-Manufacturing Costs = 165
Thanks for your time reading through my publication, I want to invite @dar22, @ogechukwu-martha, and @bossj23
X promotion link
Greetings @hisgeneral
1.- You have explained in broad strokes the relationship between costs and financial accounting, idetifying how costs become an important source of information for finance, and their respective reports.
2.- You have pointed out the difference between fixed and variable costs, giving examples of each of them. We would have liked you to give examples for a specific type of business.
3.- In this opportunity you have established the fixed and variable costs for a T-shirt manufacturing company, however it was required the identification of the cost elements, which according to what was explained in the class, are raw material, labor and indirect costs.
4.- You have classified each of the costs incurred by the company Steemians, however there are some adjustments in the classifications, because shipping costs are not direct costs, they are part of the cost of sales.
Thanks for joining the contest
Thanks for reviewing, sire