SLC | S21W2 | Costs for entrepreneurs - Cost elements
Hello everyone! I hope you will be good. Today I am here to participate in Steemit Learning Challenge of @yolvijrm about the Costs for entrepreneurs - Cost elements. It is really an interesting and knowledgeable contest. There is a lot to explore. If you want to join then:

What is the relationship between costs and financial accounting?
The relationship between costs and financial accounting is integral. They both play important roles to track, analyze and report the financial situation of the business. Here is a detailed information that how these are connected to each other:
Cost Recording and Allocation
Financial accounting captures all business costs. It includes the costs for the materials and labour. This organises financial records by managing the different costs. This ensures accurate data which is very useful for the authentic report.
Expense Reporting
Financial account translates the costs to the expenses on the statement of income. It adds details about the spendings of a business in a given period. This includes the cost of the goods sold, operational expenses and other outflows of money. Financial account represents the profit of the business by accurately representing costs as expenses.
Inventory Valuation
Costs are important in financial accounting to calculate the inventory values. Different cost methods are used to determine the costs for the inventory. First in first our and last in first out are the most used methods. This affects the net income in the balance sheet and cost of the goods which are sold.
Budgeting and Forecasting
Financial account helps the businesses to set budgets and financial forecasts based on the cost data. Cost information of the past provides information about the future spending. It helps the businesses to allocate the resources effectively.
Financial Analysis and Decision-Making
Financial accounting aggregates cost information that is essential for ratio analysis, break-even analysis, and profitability assessment. This analysis helps in decision-making, such as whether to reduce costs, increase prices, or invest in cost-saving initiatives.
Taxation and Compliance
Financial accounting records the costs correctly for the tax purposes. It mentions the deductable expenses clearly to comply with the tax regulations. Accurate allocation of the cost helps to reduce the taxable income.
Transparency and Stakeholder Communication
Financial accounting re order are very useful. The investors and stakeholders rely on these records. They help to understand the cost structure of the company. Transparent cost reports help to buy or trust. They ensure transparency. The stakeholders can take decisions based on the financial records.
On the whole costs are the foundation of the financial accounting. Costs impact the financial reports and the decisions. So by accurately recording the costs financial account helps us to manage profit and spendings. It provides strategic planning.
Establish the difference between fixed costs and variable costs, providing examples of each.
Fixed costs and variable costs are the important categories of the business expenses. These costs behave differently when the production level or the activity of the business is changed.
Here is the difference between the fixed costs and variable costs:
Fixed Costs
These are the fixed expenses. They do not change with production levels. These costs are applied irrespective of the business production. These costs are predictable. Fixed costs include rent, salaries and insurance.
Examples of Fixed Costs
Here are the examples of the fixed costs:
Rent or Lease Payments
The business needs physical space for its existence. The monthly rent of the physical space remains same. It does not depend on the production.
Salaries of Permanent Staff
Generally the salaries of the workers in the business also remain same. This cost does not depend on the sales or output of the business.
Insurance
Premium membership of the property and insurance for the health also remains constant.
Depreciation
Th reduction in the value of the fixed assets such as equipment and buildings is recorded consistently over the time.
Variable Costs
These are the costs which fluctuate with the production. Variable costs include raw materials and utilities. As the production increases the variable costs increases. Similarly when the production decreases variable costs decreases. These costs directly depend upon the activity of the business.
Examples of Variable Costs
Here are the examples of the variable costs:
Raw Materials
Costs for the materials vary based on the number of the goods produced. For a bakery flour and sugar are the raw materials.
Packaging
Packaging cost is also a variable cost. It increase with the number of the items produced and sold. Because in a product based business it is necessary to pack each product.
Sales Commissions
Most of the companies offer sales commission to the salespeople. They earn commission on the basis of the volume of the sales. In this way these costs vary directly with revenue.
Utilities
Electricity costs can rise with the increased use of the machine. So in this his way the utility expenses are tied with the production levels.
A T-Shirt Printing Business
Let us take a look at the fixed and variable costs of a T shirt printing business.
Fixed Costs
The monthly rent for the workspace is a fixed cost. Moreover the salaries of the office staff are also the fixed costs and the business needs to pay the salaries each month. Equipment costs are also the fixed costs because they do not vary on the basis of the shirts printed. So the fixed costs do not depend on the number of the shirts printed in the factory.
Variable Costs
All those costs of the shirt printing business will be variable costs which will carry according to the production of the products. The cost of the fabric to prepare shirts is a variable cost. The ink which is used for the printing purposes is also a variable cost. There is the need of packaging for each shirt so it varies with the production level and it becomes variable cost. The more shirts are printed the higher costs will be applied.
Fixed costs provide stability and predictability of the business. But on the other hand if we see that the sales are low then these costs become a burden on the business. Variable costs are directly linked with the output. These are the flexible costs and they increase with the production. There is the need to manage both the costs to optimise the business effectively.
In a real or fictional case, identify the cost elements in manufacturing a product or providing a service.
Here is a fictional example of the business to identify the cost elements in manufacturing a product or providing a service. I am going to give the example of a custom furniture manufacturing business. It produces wooden tables crafted by hand. All the costs which are involved in the manufacturing each table are given below:
Direct Costs
These are all the costs which are directly linked to produce each table.
Manufacturing Materials
For the production of the tables raw materials are required. These are directly used to make the tables. Raw materials include wood, nails, glue and varnish for the production of a table.
| Raw Materials | Cost |
|---|---|
| Wood | $50 |
| Nails | $5 |
| Glue | $3 |
| Varnish | $8 |
| Total | $66 |
Labour
For the manufacturing of the table there is the need of the labour because without labour tables cannot be made. Carpenters and woodworkers work collectively to build the tables. The wages are paid to the carpenters and woodworkers for the production of each table.
| Labor Type | Role Description | Cost per Table |
|---|---|---|
| Carpenter | Cuts, shapes, and assembles the wood | $100 |
| Woodworker | Works on finishing, sanding, and detailing | $75 |
| Total | $175 |
Indirect Costs (Overhead)
These are necessary costs for the production but these are not directly linked with each table. Indirect costs include the following:
Factory Rent
The cost to pay the rent of the factory or a workshop where the tables will be manufactured. This is a fixed cost and this cost is distributed to all the units produced.
Utilities
In the workshop electricity, water and gas are required. These are essentials to operate the machines and tools. These costs can vary slightly but these are generally classified as overhead costs.
Depreciation on Equipment
Depreciation cost is also the part of the indirect costs because the equipment serves for the multiple products. It includes the gradual cost of wear and tear on the equipment such as saws, sanders and drills.
Quality Control and Supervision
The product quality should always be good for the satisfaction of the customers and for the growth of the business. So the cost of hiring quality control staff is not directly involved in the creation of the table.
| Indirect Cost | Description | Cost per Table |
|---|---|---|
| Factory Rent | Fixed cost of renting the factory or workshop | $200 |
| Utilities | Costs for electricity, water, and gas | $50 |
| Depreciation on Equipment | Wear and tear on equipment (e.g., saws, sanders, drills) | $30 |
| Quality Control and Supervision | Cost of hiring quality control staff | $40 |
| Total | $320 |
Administrative and Selling Expenses
The expenses of administration and selling purposes are not the part of the manufacturing process. But these costs support the overall business. These costs include the following:
Marketing and Advertising
Marketing and advertising is an important factor to sell the product. For this purpose we need to pay for the digital ads, brochures and website.
Sales Commissions
The company pays commission to the sales staff for selling the tables. They are paid on the basis of each table sold.
Office Supplies
The costs for the office supplies are also included. The business needs to pay for the paper, pens and computer software which are used by the administrative staff.
General Administrative Salaries
There are persons who manages the finances, order and customer inquiries. The business will also pay the accountants and customer service provider for the smooth operations of the business.
| Administrative & Selling Expense | Description | Cost per Table |
|---|---|---|
| Marketing and Advertising | Digital ads, brochures, website, etc. | $60 |
| Sales Commissions | Commission paid to sales staff per table sold | $25 |
| Office Supplies | Paper, pens, software, etc. | $10 |
| General Administrative Salaries | Salaries for accountants, customer service, etc. | $50 |
| Total | $145 |
In this furniture manufacturing example the direct costs are directly linked with the production. All the indirect costs support the production but they are not traced to a single table. Moreover administration and selling expenses are not part of the manufacturing costs. But they are also necessary for the operations of the business.
Here’s the final table with the Grand Total that combines all the costs from manufacturing materials, labour, indirect costs, and administrative expenses:
| Cost Category | Total Cost per Category |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing Materials | $66 |
| Labor Cost | $175 |
| Indirect Costs (Overhead) | $320 |
| Administrative & Selling Expenses | $145 |
| Grand Total | $706 |
This Grand Total represents the total cost per category considering all the categories. I have taken all the costs fictionally so they can be higher or lower than the real life costs. I have just taken them as an example for the better understanding of the explanation.
Separate direct costs from indirect costs and non-manufacturing costs, and also calculate the total direct and indirect manufacturing costs.
In order to separate and calculate the direct, indirect and non-manufacturing costs I will categorize each cost.
Breakdown of Different Costs
| Concept | Cost | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Direct raw material | 130 | Direct Cost |
| Direct labor | 100 | Direct Cost |
| Manufacturing Supplies | 210 | Indirect Cost |
| Depreciation of plant and machinery | 25 | Indirect Cost |
| Plant Manager | 65 | Indirect Cost |
| Taxes and plant insurance | 70 | Indirect Cost |
| Building maintenance | 50 | Indirect Cost |
| Public services | 35 | Indirect Cost |
| Delivery costs | 70 | Non-Manufacturing Cost |
| Sales Commissions | 65 | Non-Manufacturing Cost |
| Sales and administrative expenses | 80 | Non-Manufacturing Cost |
| Maintenance of distribution equipment | 65 | Non-Manufacturing Cost |
| Advertising | 20 | Non-Manufacturing Cost |
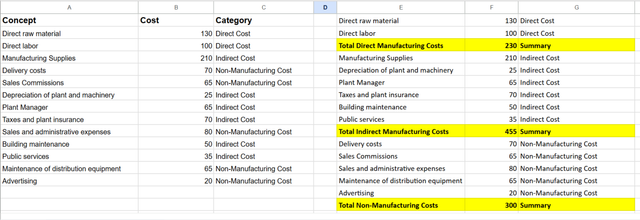
Here in the above table I have label each cost to its cost category.
Here I have created separate tables for each category and at the end there is the sum of the cost.
Direct Cost
| Concept | Cost | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Direct raw material | 130 | Direct Cost |
| Direct labor | 100 | Direct Cost |
| Total Direct Costs | 230 |
Indirect Cost
| Concept | Cost | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Supplies | 210 | Indirect Cost |
| Depreciation of plant and machinery | 25 | Indirect Cost |
| Plant Manager | 65 | Indirect Cost |
| Taxes and plant insurance | 70 | Indirect Cost |
| Building maintenance | 50 | Indirect Cost |
| Public services | 35 | Indirect Cost |
| Total Indirect Costs | 455 |
Non-Manufacturing Cost
| Concept | Cost | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery costs | 70 | Non-Manufacturing |
| Sales Commissions | 65 | Non-Manufacturing |
| Sales and administrative expenses | 80 | Non-Manufacturing |
| Maintenance of distribution equipment | 65 | Non-Manufacturing |
| Advertising | 20 | Non-Manufacturing |
| Total Non-Manufacturing Costs | 300 |
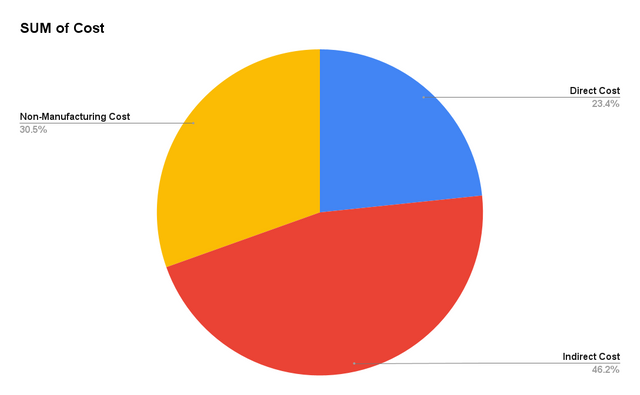
Grand Total Costs = 230 (Direct) + 455 (Indirect) + 300 (Non-Manufacturing) = 985

Here is the work of the Google Sheets I have created charts based on the data feed in the Google Sheets. You can check my work in the Google Sheets. I have created a pivot table to represent the different costs and to sum up all the costs according their category.
Google Sheet This link is only accessible for the professors as I have added their emails in this to view.
I invite my friends @sergeyk, @chant and @ripon0630 to join this learning challenge to learn and enhance their knowledge further.
X Promotion: https://x.com/stylishtiger3/status/1854173221861441747
Greetings @mohammadfaisa
1.- You have adequately established the importance of costs for financial accounting, being an important source of information for reporting, and therefore in decision making.
2.- You have pointed out very well the difference between fixed and variable costs, giving examples of each of them, and bringing them to reality in a T-shirt printing business.
3.- You have identified the cost elements in the manufacture of tables, segregating correctly each of the cost elements and explaining in detail each of them.
4.- You have classified each of the costs incurred by the company Steemians, identifying each group to which they belong, presenting the behavior of these through graphs.
Thanks for joining the contest