SLC | S21W2 | Costs for Entrepreneurs - Cost Elements
Assalam o Alaikum how are you I am fine I hope you all are fine too people are enjoying the full joys of life First of all I thank the steemit team for this excellent teacher for the second week. I would like to thank this special teacher whose name is:@yolvijrm
canva editing

Q.1 - What is the relationship between costs and financial accounting?
This paper focuses on one of the most important areas in financial accounting, that is, Cost.
In financial accounting costs are defined as the amount which a business incurs while rendering a product or service it offers. They make up a large part of cost, party in the pricing strategy and are crucial in arriving on other strategic decisions. Knowledge of the Costa and Financial Accounting enables organizations to optimize resources, control expenditure and fulfill its financial goals and objectives.
What are The Costs?
Costs are includes the expenses which are used any product or services where it could materials, labor, overheads and many more. These can be nominal costs such as rent for premises, and personnel costs which do not alter with production volume; or they can be cost of materials or direct expenses which change as the output rate changes. Other expenses which include administrative and marketing expenses contribute towards the general functionality of the business. The effective control of costs means that resources are utilized to the fullest, and that profitable improvement can be made. Organizations make use of direct and indirect cost classifications to determine exact production costs when choosing prices. This approach secures competition that must be welcomed so that quality and financial balance which are key to sustainable growth are not compromised.

Costs that companies take into consideration while presenting their financial statements for a particular financial year are of different types.
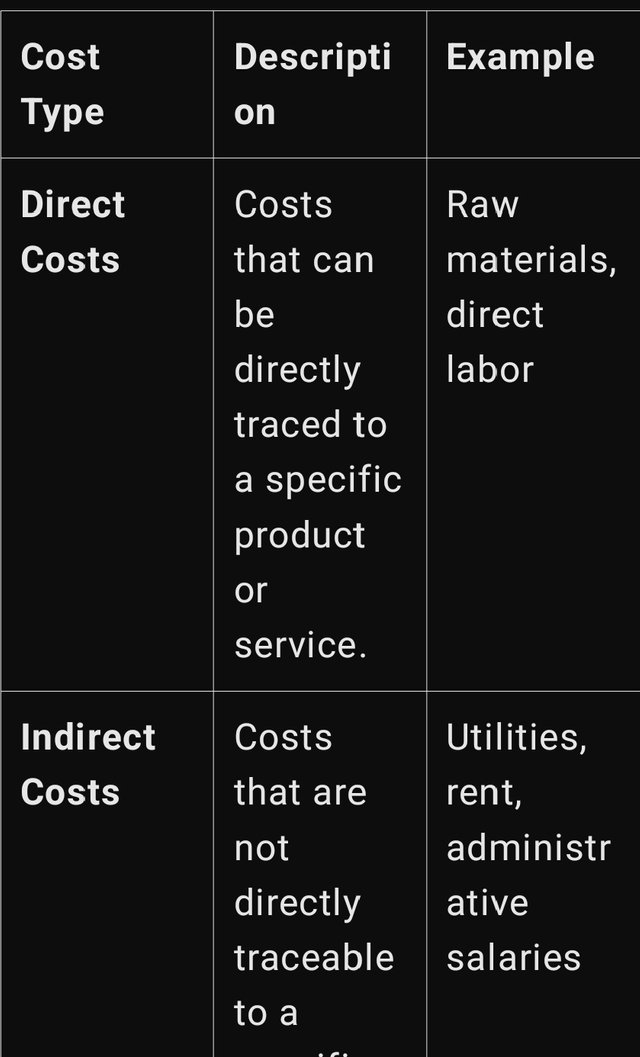
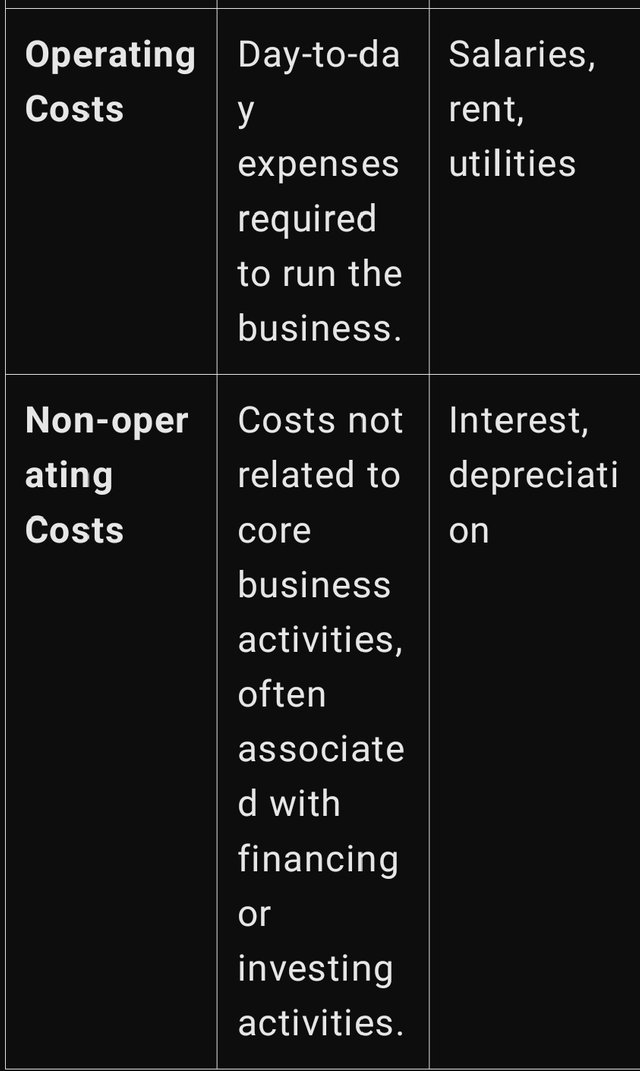
There is classification of costs in financial accounting that distinguishes cost according to its nature and its behaviour. Here’s a breakdown of the main categories:
Costs are an important element of financial accounting which deals with the provision of reports on an organization’s financial position to its stakeholders.
1. Cost Recording and Reporting
In financial accounting, costs are reported in more details and classified in such a way that prepared financial statements are presented fairly. Assets practices includes monitoring of direct costs, such as raw material and labour and also indirect costs for production. Such records to necessary financial statements like the income statement that displays expenses and revenues and the balance sheet displaying the liability and asset findings. On the part of cost control, the precise measurement and documentation of costs is essential to attesting to the reliability and reliability of the reported financial data.
2. Decision-Making
In details, the financial accounting data compiled for the management help this entity to make decisions since the management appreciates costs. For example, variable and fixed cost determination can be of great help in finding breakeven point, setting the correct price for products or services, controlling the production rates. Some of the other ways that business people applied accounting cost data includes: companies can also be able to compare past cost data with current and past dates so that they can be able to predict in future what it is likely to happen and make some necessary changes that would enhance profitability.
3. Budgeting and Cost Control
It also assists in creation of budget by presenting historical cost information and making recommendations on where cost can be cut. Cost behavior knowledge helps a business to distribute resources effectively, control cash flow and avoid unnecessary expenditures. Accomplishment of cost control is vital for enhancing organizational competitiveness as well as achieving sustainable strategies.
Conclusion
It is crucial to financial management to find how both costs and financial accounting are connected. Financial accounting entails identifying, recording, accumulating, analyzing and presenting data regarding cost so as to enhance understanding of a business’s financial health. This is a perfect reason to name effective cost management as an essential business concept and a strategic tool for businesses in any field of industry.

Q.2 - Establish the difference between fixed costs and variable costs, providing examples of each.
Converting fixed cost and Variable cost
In relation to cost classification, it is very crucial in all business to be abreast with the difference between fixed and variable costs. Both are important when it comes to determining and comparing total expenditure, cost setting and profit optimization; but fluctuating concerning production or sales volume, they exhibit quite a different behavior.
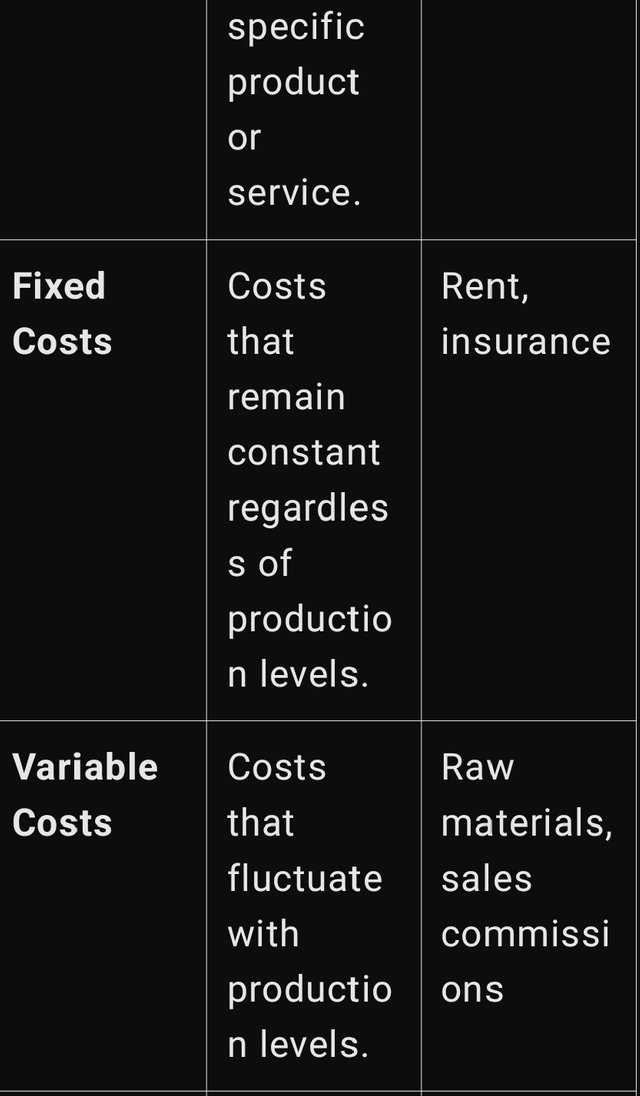
Fixed Costs
These are known as the variable or the manufacturing costs which occur only when a certain minimum level of production or sales has been reached within a company. This increases the reliability of forecasting and identifying the fixed costs since their changes for the undisturbed period will not be significant. However, they do not reduce even during lower production level, which can prove disadvantageous during certain time frames. Examples of fixed costs include:
Rent: This means that firms often provide a fixed number of dollars on a monthly or yearly basis for rents for office or factory space are not tied to the number of goods produced.
Salaries of permanent staff: Administrative personnel and other workers, employed under a full-time contract, are paid a salary that does not change depending on their performance.
Depreciation: These may include equipment, machinery, which over a period of time will be depleted at a constant rate which is a fixed cost.
Insurance premiums: This is normally because most business insurance policies include level premium provisions that must be paid continually, even during the periods that business is slow.

Since fixed costs do not depend on the level of production, these costs form the basic cost for most companies and affects the business’s profitability(ptr. All these are essential costs that firms must factor into their break-even point because they are incurred before the organization can record a profit.
Variable Costs
Semi variable cost on the other hand vary in direct proportion with the scale or volume of production or level of business activity. This flexibility makes it possible for firms to regulate these costs in relation to the production scale, cutting down costs at the same time as the output reduces and only adding costs while the production scale goes up. Examples of variable costs include:
Raw materials: Expenses on materials used in manufacturing activities depend on the volumes being manufactured.
Direct labor: These include the wages based on time or production specials which include those given per hour or common per-diem contractors.
Packaging: Pac kaging materials are needed only as far as products are made which are proportional to or dependent upon the volume of production.
Sales commissions: Expenses that result in payment to the sales staff commonly cover provisions that are linked to the quantity of sold products.
It is important for business because separates fixed and variable costs. These costs can help businesses identify break-even and understand the effects volatility in production on the-profit line. Cost control is defined by achieving a proper cost structure of fixed costs to keep them certain while variables are appropriately driven to the market conditions to make businesses most profitable.

Q.3 - In a real or fictional case, identify the cost elements in manufacturing a product or providing a service.
Cost Elements in Manufacturing a Product: Real and Fictional Case
It is crucial to identify and differentiate cost elements to form a solid perception toward manufacturing costs as well as for resource control and setting a strategic cost in any manufacturing. These costs can be grouped to various factors that contains various aspects with both explicit and implicit costs.
1. Direct Materials: These are the basis of production, the materials that are used to develop a product. For instance, if we are to relate a real life application, it would be in the production of smartphone by a given company. Direct materials could be electronics parts, displays, batteries and housing materials. These materials, for each unit of production, have an explicitly associable quantity with the produce.
2. Direct Labor: This is in addition to payments for salaries for the employees who directly participate in the value addition process. Smartphone example of direct labour would be the workers on the assembly line or technical staff installing components. This cost differs with the quantity of the production that a company intends to produce.
3. Manufacturing Overheads: Other production supporting costs are covered under overheads. This includes; Cost of power and water, periodic maintenance of machines and appliances, and writing off of factory based plant and equipment. For example, the cost incurred in providing electricity to machinery used in the assembly line in producing the products or in actually preparing each unit is accumulated even though they may not be directly proportional to the units being manufactured.
4. Administrative and Selling Expenses: These are costs incurred in managing and marketing the product but do not directly relate to manufacturing costs for the product For instance; cost of paying the administrative personnel, cost of airing and placing the advert and the cost of transporting the product among others. In college for example, these costs fund operations but they do not entail either manufacturing or making of smartphones.
5. Research and Development (R&D): Another kind of expense, especially typical for the hi-tech industries, is the expenses on the development of new or enhancement of existed functions. In the smartphone case, Research and Development costs are imperative since the players in this industry are ever inventing ways of doing things to meet market demands.
These cost elements help one to have a view of all costs associated with the production of a given product. The above analysis aids the companies in controlling costs, fixing appropriate prices, and therefore makes them profitable.

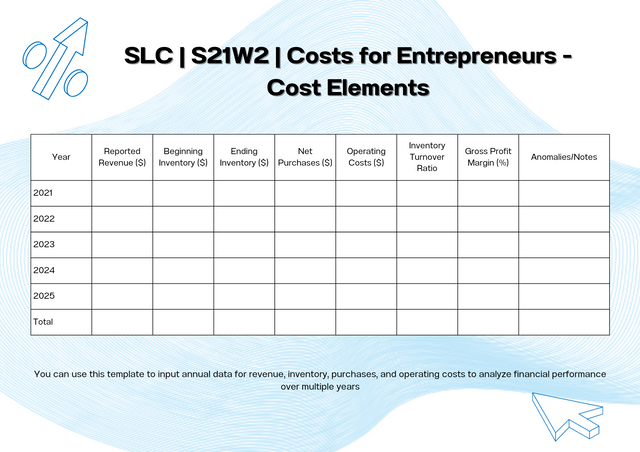
Q.4 - The company Steemians manufactures a single product. During a given period, the following costs were incurred:
Certainly! Here’s a breakdown of the cost analysis for the Steemians company's product, presented in a structured way with a table for clarity:
Retail Price and Costs for Steemians Company Product
Steemians is a manufacturing company that specialises in the production of a single product. Within a specific timeframe, they faced several kinds of cost, which are essential for assigning the overall production costs, evaluating profitability, and setting the price. The following is a breakdown of various cost aspects related with the production process of the products they offer.
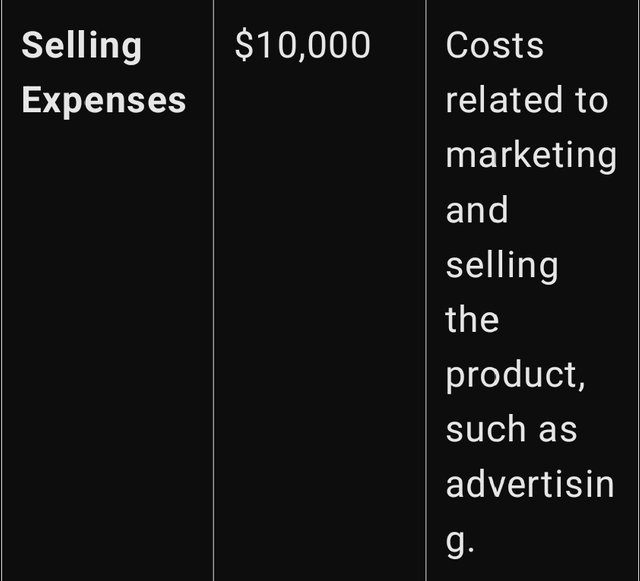
Table of Incurred Costs
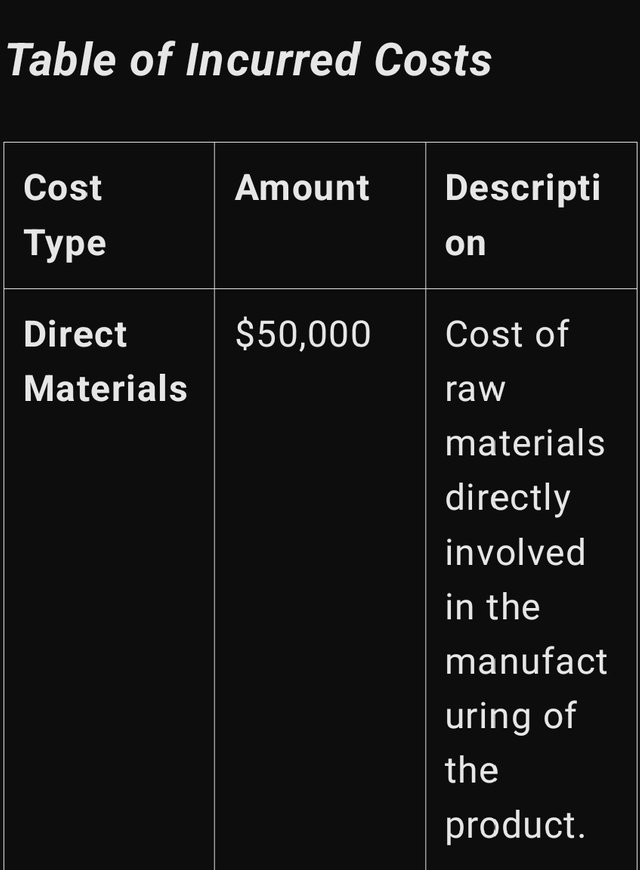




1. Direct Materials: Direct material means the material without which the final product cannot be produced and which then forms parti of the product. To Steemians, these are base and encompass a chunk of the cost plan. For instance, if they deal in electronics, then Semiconductors, boards, circuits etc are considered as IC’s.
2. Direct Labor: Direct labour costs are the wages paid to those employees that directly involved in making of the product. It is an embodied cost that varies depending on the units of production being made at a particular period. This cost, through mostly a result of salaries for production line workers, such as those who directly assemble the product or operate a machine, can be significantly high.
3. Manufacturing Overhead: Overhead therefore encompasses all those expenses which are would towards the manufacturing process but cannot be specifically associated with cost of the final product. Others include electrical energy, water and equipment such as vehicles, generators, elevators, office furniture among others. Some of the overhead costs are fixed for example the rent of factory coat while others are variable such as that of electricity.
4. Administrative Expenses: These are the costs that go to meeting the overall management and other support functions within the business. Some do not vary with production, they are salaries of executives and office expenses.
5. Selling Expenses: Selling expenses are the overhead costs of promoting and making the product available for consumption. This includes expenses on advertisement and promotions, commissions for salespersons and other promotional expenses. Selling expenses include expenses made to reach the consumers and ultimately make the sale.
Total Production Cost Break-up
It shows the general accumulated expenditure to meet the cost of making the product during the given period of time at $125,000. For pricing decisions, the company has to take into account these costs and the targeted level of profit required by the enterprise to be sustainable. Furthermore, with this breakdown the prospects for possible cost cutting become evident. For example, it can be to increase profitability through better control of overhead expenses, or more efficient utilization of direct labour.
Summing up, this relatively detailed cost structure gives the members of the Steemian community information about the company’s production costs. With these components, the company can make a proper decision and analyze the factors which led to higher price and determine the measures which should be taken to control costs and increase profit in the future production cycles.
i would like to invite @patjewell @josepha @beautiful12 to take part in this contest

Greetings @shabbir86
1.- You have identified how costs represent an important source of information for financial accounting. This is where a large part of the transactions that produce the result of the fiscal year, and therefore the profit or loss, originate.
2.- You have pointed out very well the difference between fixed and variable costs, giving examples of each of them. We would have liked you to exemplify it in a real or fictitious company.
3.- You have identified the cost elements in the manufacture of telephones, segregating correctly each one of the cost elements and explaining in detail each one of them.
4.- Although you have classified each of the costs incurred by the Steemians company, we would have liked to have distributed and totaled them by segments, but you still did a good job.
Thanks for joining the contest
@yolvijrm Thank you so much for your rivew
X Permotion
https://twitter.com/shabbir_saghar/status/1854172241484820896?t=NsfOp9cgJgZyckPr7Bu9lA&s=19