SLC | S21W6 | Costs for entrepreneurs - Cost structure
Hello Everyone
I'm AhsanSharif From Pakistan
Greetings you all, hope you all are well and enjoying a happy moment of life with steem. I'm also good Alhamdulillah. |
|---|

Design On Canva
Cost Structure
Cost structure refers to the costs that we incur to run our business, including the creation of various types of products or services, etc. It is a model that provides us with a good framework for understanding our business and for it. Through it, we can create a better financial plan that allows us to make profitable decisions. There are some of its components that we will see below.
Fixed Cost:
Fixed costs refer to the expenses that we have to pay in all situations because these are the expenses that we have to pay in both cases when our business is good or bad. These expenses include the rent of our facilities, the salary of employees or the depreciation of goods. Therefore, all these things have to be paid, so a businessman has to maintain a basis for this, whether, during low sales or high sales, he has to manage his expenses effectively.
Variable Cost:
In our business, it fluctuates depending on the production or activity. These are the costs that increase or decrease in direct proportion to the volume of goods or services produced. These costs include raw materials, packaging, shipping, sales commissions, etc. If a business person understands this in a good way and understands how it directly affects the profit, then it will be better for him. He improves the variable cost in his business reduces all his total costs and gets a good profit.
semi Variable Cost:
This is often known as a mixed cost, which includes both fixed and variable components. For example, a utility bill has fixed charges, so we have to pay them, so based on the level of consumption, we can also include our variable cost charges. As in another example, we see that the salary of our employees, some employees also have to pay some bonuses on performance, which they get along with their basic salary. Therefore, it becomes a little difficult for us to manage these semi-variable cost expenses because they combine elements of both.
Economies of Scale:
This refers to our cost advantages because when our production increases, the cost per unit of our products decreases because the more goods we buy together, the more we get in terms of profit. Because we can spread the goods over a larger number of goods, it also helps us to be more competitive in the market. Therefore, efficiently scaling the business gives us a good profit by reducing the cost per unit without increasing our total costs proportionally.
Importance
- This is because it allows us to do a good analysis. If we want to calculate our profit margin, we need to understand our cost structure because it helps us to determine our pricing strategy and achieve a good profit by covering our costs.
- If we have a clear cost structure, we can predict all our future expenses and it helps us to manage our resources in a good way. Through this, we can also avoid cash flow problems because it gives us a financial forecast.
- To set the prices of our products, we need to understand our cost structure because prices that do not meet our cost can cause us losses, and demand for high-priced products also decreases.
- This helps us a lot in understanding the break-even point because our sales are at a point where they cover our total cost because to have a higher profit we have to increase our sales as well, so it helps us understand that.
- Businessmen can identify areas where their expenses are high but sales are low, so they can reduce all unnecessary expenses and achieve a better profit, after analyzing the cost structure.

Free
Here are the examples that fit these components of Cost Structure:
Fixed Cost Example:
Restaurant Business:
Let's take the example of a restaurant. A restaurant has many fixed charges that do not depend on the number of customers. Just like we have to pay monthly rent for the space where the restaurant is located, we cannot change this based on how busy our restaurant has been.
We have to pay salaries to our waiters, managers, and kitchen staff, which are fixed whether the number of customers increases or decreases. Similarly, utility bills have to be paid, which include lighting, etc. Or there are kitchen appliances whose use may fluctuate, as the cost of heating and refrigeration is constant. In such a situation, the restaurant has to manage all expenses carefully and ensure that all their expenses do not depend on the fluctuations of their customers but rather they are covering all their costs.
Variable Cost Example:
E-commerce Business:
E-commerce businesses, such as Amazon or their websites, sell their products online, and the prices of their products fluctuate according to their sales volume. As with any product that is being sold online, businesses bear the cost of purchasing the product. Therefore, it is a direct variable cost that increases with sales.
The costs for packaging and shipping are paid by the business whenever something is sold online. Those costs are based on the quantity of the order we place. If our business is using a sales agent, they can also earn some commission on the sale of our product. People with e-commerce businesses control their variable costs so that they can earn a good profit.
Semi Variable Cost Example:
Retail Store:
A retail clothing store can experience this because the clothing store in the store requires electricity. Electricity costs are generally fixed. This fluctuation in electricity can also affect its cost because sometimes there are busy shopping seasons. During this time, lights, air conditioners, and display lights are running more, which results in higher costs.
Similarly, the salary of an employee can fluctuate. Usually, we give them a fixed salary, but depending on the work, we have to increase it. When they sell more, they get a bonus or if they work overtime, these variable expenses are added to their salary. In such a situation, we need to keep a close watch, especially when we are selling more because at that time our expenses increase.
Economies of Scale Example:
Manufacturing Business:
Here we talk about a large company that makes its smartphones and takes advantage of economies of scale. They increase their production and with this increase, they reduce their cost per unit. As they order their products in large quantities, such as display batteries or chips, when they order them, the suppliers offer them a special discount, which makes the price per unit seem very low.
At a higher level, it allows the company to invest in specialized machinery so that they can improve their production. This way, the total labor costs are reduced because we have more work and we have to pay less labor because our product is produced in less time. Thus, these companies produce units in large quantities, so they have to pay the same fixed charges, but their products are being produce in large quantities, due to which they reduce the cost per unit, and on this too they earn good profits.

Free
The elements of the cost structure may vary depending on the type of business, so the entrepreneur incurs it according to his category. Expenses vary depending on the type of business and its industry, and accordingly, they may also vary. Generally, there are two major elements, which we know as fixed costs and variable costs. Along with these two well-known elements, some additional elements play an important role, which we know as semi-variable costs direct and indirect costs.
Fixed Cost: These are the expenses that we have to pay in any case because they remain constant over time. They do not depend on the income of our business, whether our sales are good or bad, we have to pay them. For example, if we talk about any one store, they have to pay the rent of that store. It does not depend on how many sales you have made or how many customers have come through your door. Or any software company, regardless of how many employees it has, their salaries remain constant. They have to be paid in all circumstances, and they do not depend on their products.
Variable Cost: These are the costs that are higher or lower depending on our production. These costs are based on how much our company is producing and how much it is selling. For example, any company that sells its products online has to bear shipping and delivery costs because they depend on their volume. Similarly, for any bakery that makes its product, the price of flour, sugar, and various ingredients may increase.
Direct Cost: These are the costs that we estimate when producing our product or service. For example, if a furniture manufacturing company wants to make a table, it needs wood and nails to make it, so this will be its direct cost. Similarly, let's take another example: if we are buying an item and that item is used only to produce a single product, the cost of operating and maintaining that item is called direct cost.
Indirect Cost: These are costs that are used by our business as a whole. These costs are not directly linked to the production of our services. For example, the water and electricity used in a factory are indirect costs because they are not just for a single product but for the entire operation. Similarly, any items of paper, printer, or furniture in an office are also indirect costs because they are used as a whole and not for any specific purpose.
Opportunity Cost: Opportunity cost is not tied to our direct cost structure. It represents what a company loses when it chooses one option over another. Whenever we are making a business decision, these elements have an influence. For example, in a startup, in addition to marketing, they go towards product development, so the opportunity cost is the potential customers that we get through advertising.
Economies of Scale: Economies of scale refer to cost advantages because they are the experience of businesses that increase production, while the cost per unit decreases as the company grows. For example, a clothing manufacturer buys fabric in large quantities, which results in lower unit costs for smaller buyers.
Semi-Variable Cost: They include two types of components: fixed and variable, which we also know as mixed cost. For example, our company's utility bills are fixed charges for electricity during manufacturing, but as our production increases, our electricity consumption increases, and our costs increase.
Here, first of all, we need to create our cost structure, which will produce five cakes per day in our business, and our goal is that we should get a 25 percent total profit margin. We need to break them down into fixed costs, variable costs, and desired profit margins. After that, we will be able to calculate our selling price.

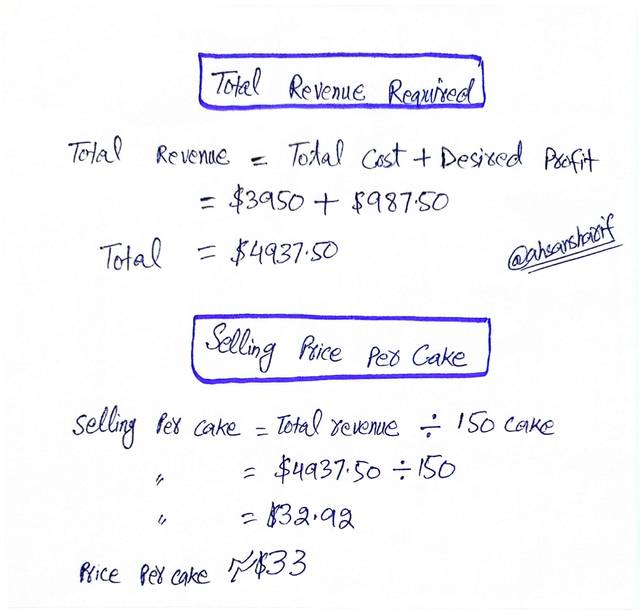
Our selling price for one cake will be approximately $33, which will give us a decent profit.
Thank you so much for staying here. I would like to invite @sahar78, @hudamalik20, @josepha, and @bossj23 to join this challenge.

Upvoted! Thank you for supporting witness @jswit.
Greetings @ahsansharif
1.- You have shared your understanding of cost structures as a method to effectively organize business costs to improve decision making and the importance of pricing.
2.- Have you exemplified the methods of cost structures and the importance of cost structures as explained in the class and provided additional scenarios with semi-variable and economy of scale costs.
3.- You have highlighted the elements of a cost structure, considering that all this will depend mostly on the type of business.
4.- You have developed in an acceptable way the solution to the proposed exercise, explaining each step according to what was explained in class.
Thanks for joining the contest
Thank you so much for the verification and the valuable feedback.
Thank you so much for explaining in details. I understand in another perspective
My pleasure, I wish you success.
Explanations of various business expenses are very clear and with relevant examples. The cake business example is excellent for learning cost analysis. Good luck for this contest.
Thank you so much dear for your valuable feedback. I appreciated
🥰🥰🥰