SLC | S21W6 | Costs For Entrepreneurs - Cost Structure
This is my homework post for Steemit Learning Challenge Season 21 Week 6 assignment of Professor @yolvijrm’s class, Cost Structure.

Note :
- I performed this task on Windows 10 PC, Google Chrome.
Task 1 - What is a cost structure, and what is its importance for entrepreneurship?
1.1. What Is A Cost Structure
Cost Structure in economics is a framework or system used to understand and analyze expenses in a business. It is an important part of the business model as it determines how a company allocates its resources to run operations, create products or services, and generate profits.
Cost Structure describes the different types of costs that a company has to incur to run its operational activities, create, and deliver value to its customers. Cost structure helps businesses understand their expenses and optimize resources to remain competitive and profitable.
In other words, cost Structure helps businesses maximize the potential profits they can achieve.
1.2. The Importance of Cost Structuring For Entrepreneurship
Therefore, Cost Structure is an important component in a business, especially in the following areas:
- Decision Making. Understanding cost structure helps businesses determine product prices, identify operational efficiencies, and design business strategies.
- Financial Management. By knowing the composition of costs, companies can manage budgets more effectively and increase profitability.
- Business Model Strategy. Cost structure plays an important role in supporting the business model strategy, whether it focuses on low-cost (low-cost strategy) or high value (value-driven strategy).
- Profitability Improvements, as it allows entrepreneurs to calculate the profit margin for each product or service and with it the entrepreneur can look for ways to reduce expenses without sacrificing quality.
- Appropriate and Competitive Pricing, as with Cost Structure the entrepreneur can better understand costs and enable him to set prices that are competitive enough in the market while remaining profitable.
- Risk Management. Cost Structure can be useful to help entrepreneurs deal with market fluctuations, as fixed and variable costs help entrepreneurs prepare strategies to deal with changes in demand. It also helps entrepreneurs identify costs that can be reduced especially in difficult times.

Task 2 - Provide examples of businesses that use the cost structure methods explained; explain your answers.
Companies that want to make greater profits and those that are struggling with difficulties can use Cost Structure for these purposes. Examples of companies that apply Cost Structure are:
- Lodging businesses during the Covid-19 pandemic several years ago increase promotions and discounts to keep people staying there because few people are traveling due to social distancing. However, they can reduce amenities (quantity and/or quality). This kind of decision is categorized into low cost strategy.
- Fast-food franchises such as KFC, A&W and McDonald's utilize Cost Structure and focus on fixed and variable costs by standardizing services at all outlets to control these costs. They also work with large suppliers (chicken, meat, flour, spices, cooking oil, etc) to get cheaper prices due to large purchases.
- Inter-city transportation companies that serve routes from cities in Java to cities in eastern Indonesia, for example Jakarta - Bali, provide meals and snacks on the way, which of course all have been paid for by passengers when buying tickets. The company can adjust the snacks provided depending on macro and micro conditions, e.g. when there are global economic difficulties they can provide fewer snacks and smaller portions of food and/or increase ticket prices. Options such as these would be among the considerations with other options. World-renowned airline companies like AirAsia do this to provide cheaper flights.
- Certain companies use Value-Driven Strategy, which is a business approach that focuses on delivering superior value to customers, often through product quality, premium service, exceptional customer experience, or exclusive brand positioning. This strategy is usually applied by businesses that target customers who are willing to pay more for a product or service that has a higher value than just a low price. Examples of such companies are Apple (a manufacturer of premium gadgets), Tesla, and Starbuck (a premium coffee franchise).
- Companies that use quota telecommunication services can, over time, evaluate their monthly average needs, and if it turns out that they have to increase their quota at a price that is more expensive but overall more profitable than always paying for excess minutes of telephone calls, then it makes sense and is the right decision to make.

Task 3 - What are the elements of a cost structure? Provide examples.
Cost Structure has elements that reflect the different types of costs involved in running a business. Here are the main elements in the cost structure and their examples:
- Fixed Costs, i.e. any type of cost that does not change despite changes in production or sales volume. For example: Building or office rent, fixed employee salaries, software subscription fees.
- Variable Costs, i.e. any type of cost that changes with changes in production or sales volume. Examples:
- Raw materials for production, the higher the production volume, the more raw materials are needed, so the costs required are also greater.
- Logistics costs that depend on the number of shipments. The higher the demand, the higher the number of shipments, so the shipping costs also increase. And vice versa.
- Sales commission for salespeople. The more goods sold by the agent (salesperson), the more commission needs to be given.
- Semi-Variable Costs, which are all types of costs that have elements of both variable and fixed costs. Example:
- Salary with a bonus or commission system. For example: an employee will be given a bonus if he is able to achieve a certain sales target. At a certain level, the employee's salary is a fixed cost, but when he exceeds the sales target, his salary becomes a variable cost.
- Electricity costs that have a monthly base cost (fixed component) and additional costs based on the amount of energy used (variable component).
- Quoted telephone charges. The fixed component is the cost of the monthly subscription package, while the variable component is the additional fee that must be paid for the use of telephone minutes outside the quota.
- Direct Costs, which are all costs that can be directly attributed to the production of a particular good or service. For example:
- Raw material costs, e.g. plastic seeds for the plastic appliance industry.
- Salaries of direct labor in the factory, i.e. those directly related to the production process such as machine operators.
- Indirect Costs, which are all costs that cannot be directly attributed to the production of specific goods or services but are still required for operations. For example: marketing and advertising costs, administrative costs such as management staff salaries, production machinery maintenance costs, vehicle servicing costs, drinking water costs.
- Operating Costs, which are any costs associated with the day-to-day operations of the business. Examples: electricity costs, water costs, telephone costs, IT system maintenance costs (computers, internet networks, and so on).
- Economies of Scale, which is the cost advantage obtained when a business increases its scale of production, so that the cost per unit decreases. For example:
- transportation cost per unit decreases when handling large volume shipments.
- Large discounts from raw material suppliers due to bulk purchases.
- Sunk Costs, which are any costs that have been incurred and cannot be recovered. Example:
- Research and development costs incurred but ultimately fail to produce a product.
- Advertising costs that end up with no results.
- Opportunity Costs, which are potential profits lost due to choosing one decision over another. Example:
- Turning down another investment opportunity to focus capital on a current project.
- Choosing to lease a machine instead of buying which could save more in the long run.

Task 4 - Prepare the cost structure of a business dedicated to making cakes. It has a production of 5 cakes per day and expects to obtain a total profit margin of 25%.
For this case, the steps that need to be taken are:
Below is my calculation of the assigned case. I used Spreadsheet application and took some screenshots showing my calculation process.
- The Fixed Cost calculation
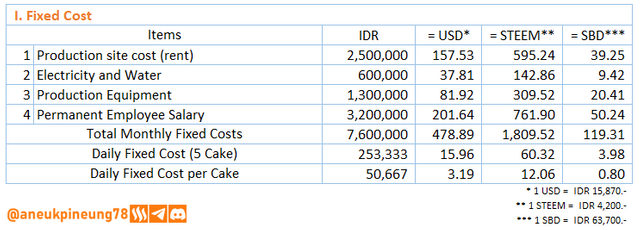
Image is clickable and might show larger resolution. - The Variable Cost calculation
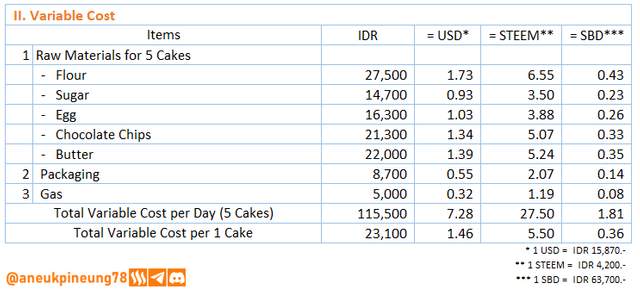
Image is clickable and might show larger resolution. - Total Production Cost calculation
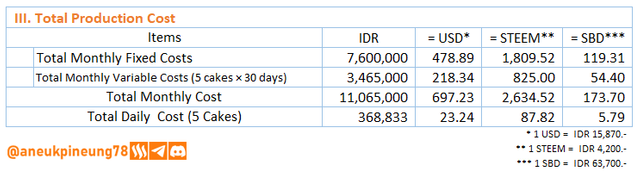
Image is clickable and might show larger resolution. - Selling Price calculation
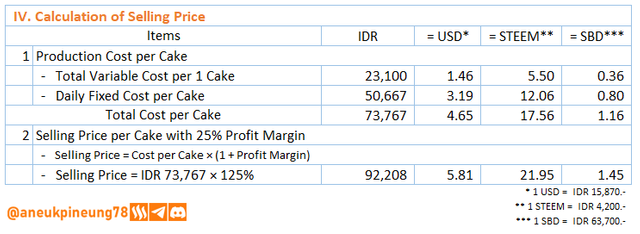
Image is clickable and might show larger resolution.
If all goes well and all cakes are sold, the monthly financial summary will look as follows.
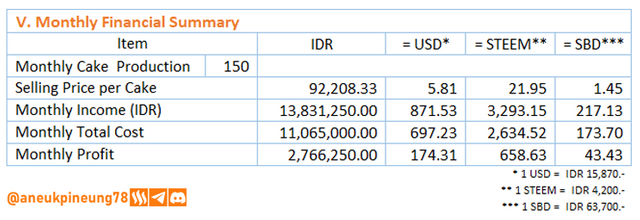

Thanks
Thanks, Professor @ yolvijrm for the lesson. I invite @rayfa, @seribubulan, @saintkelvin17.
Pictures Sources
- The editorial picture was created by me.
- Unless otherwise stated, all another pictures were screenshoots and were edited with Adobe Photoshop 2021.




Greetings @aneukpineung78
1.- You have presented the concept and importance of the cost structure, making it known that these allow the company to visualize the costs, to facilitate the strategies to apply.
2.- You have shown acceptable examples of businesses that fit structural methods, each following the stated objectives.
3.- You have presented the elements of the cost structure, each of them represents an important percentage of investment by the company.
4.- You have developed the exercise proposed for this task in an acceptable manner.
Thanks for joining the contest
https://x.com/aneukpineung78/status/1865431314511568966
Wah artikel yang sangat menarik ini tentang Enterpreuner dalam kewira usahaan. cocok bagi yang punya Perseroan Terbatas maupun Perseroan Perorangan.
Iya bang seribubulan,, apakah ada ikut menulis?