For Crypto Rookies – What is cryptocurrency exchange?

1. Definition and classification of cryptocurrency exchanges
Few examples of centralized exchanges:
- Binance
- Bittrex
- Huobi
- OKEx
- Bithumb
Centralized exchanges hold a large amount of user funds. By design they are vulnerable to hackers as there is a single point of failure. As mentioned in our former blog, South Korean cryptocurrency exchange Coinrail and Bithumb were hacked in this year June with the loss of $37.2 million and $30 million separately. In response to the problems of centralized trading, more and more decentralized exchanges have begun to appear, which is also considered to be the future form of cryptocurrency exchange.
At present, decentralized exchanges mainly have the following problems:
- The scalability of blockchain has not been resolved, the transaction speed is relatively slow, and the network is often congested.
- Every transaction requires a high fee and is inefficient for important trading frequency.
- Trading transactions could be manipulated by miners or validators on low blockchain network like (Bitcoin Gold)
Few examples of decentralized exchanges:
- Bitsquare
- BlackHalo
- Coinffeine
- IDEX
- Cryptobridge
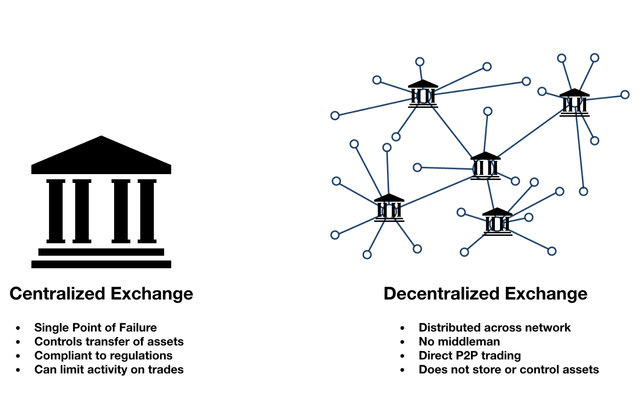
2. The Profit model of cryptocurrency exchanges
Bloomberg measured the fee income of the main exchange on March 2018 in accordance with the exchange's 24h trading amount. The fee rate is based on the announcement in the official website of each exchange. The calculation of the fee rate is generally between 0.1% and 0.3% of the transaction amount.
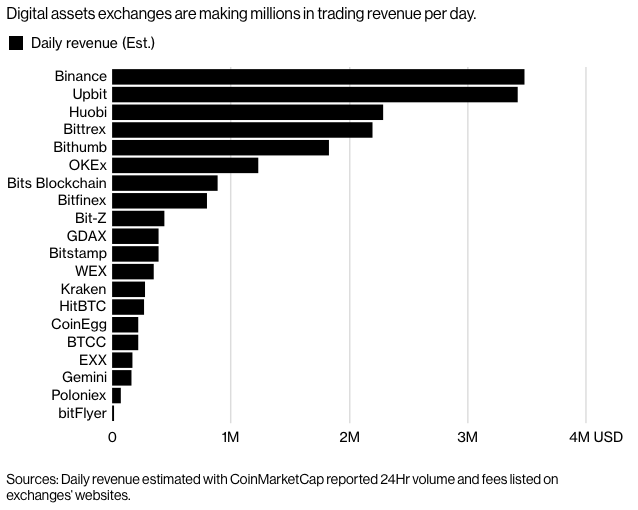
Two case study of centralized cryptocurrency exchanges
- BitMEX exchange, large daily trading volume
BitMEX is the first exchange to launch a perpetual, leveraged swap contract, it has a 40 percent market share over the BTC-USD trading pair, the most liquid Bitcoin trading pair in the global market.
Globally, there are currently 200 digital currency exchanges that can generate transactions. Among them, only the BitMEX has the single-day transaction volume of more than $3.76 billion.
- FCoin exchange, the new black horse
In May 2018, a new China-based crypto exchange, FCoin debuted. FCoin is not a traditional company. It took a key step in the evolution of the digital asset trading platform to the community. However, FCoin has generated a lot of debate with regard to its FT issuance mechanism. Part of the Chinese media has criticized the model, referred to as “trans-fee mining” by the platform. “Trans-Fee Mining” is the mechanism through which trading fees paid in BTC or ETH are fully reimbursed in value with cryptocurrency’s native token (FT Token).
One of the critics has been Binance CEO Changpeng Zhao, who wondered:
“YOU PAY TRANSACTION FEES TO THE PLATFORM WITH BTC AND ETH. THEN THE PLATFORM PAYS ‘100%’ BACK TO YOU WITH ITS TOKEN. ISN’T IT JUST BUYING PLATFORM TOKEN WITH BTC AND ETH? HOW IS THIS DIFFERENT FROM AN ICO?”
The key to maintaining the FCoin model is that new capital can flow continuously, or is to provide a constant flow of traffic to the exchange. Without traffic, the exchange is gone. Therefore, the Fcoin model is over drafting the future of the digital currency exchange. Let’s see if trans-fee mining model will last in the future.
Coins mentioned in post: