Explaining The Legality of Cryptocurrency
The global updates on legality in Crypto-Blockchain space. And Indian Government’s take on Cryptocurrency.
The traditional investors are saying ‘But Bitcoin is illegal’ to the Blockchain based startup founders. The government officials are scratching their head over the regulations. The techno-phobic commoners are thinking that it must be illegal because terrorists are using it. And the newbies are saying that it’s crashing.
People are making up mind against the technology without understanding the use cases.

[Photo by Andre Francois on Unsplash]
At first, I thought, the reason is lack of easy-to-understand educational material on the subject. But people use complex tech every day with no knowledge of it.
For example, people generally do not understand how the nuclear reactors are producing electricity and if it is good or bad for them? Even though the Nuclear energy is not the long-term solution for electricity generation. It is not desirable, safe, or CO2 free, but no one is skeptic about it.
The above-stated analogy doesn’t fit right into the Blockchain-crypto scenario but that’s the answer to the question below.
What is the reason for resistance against Cryptocurrency?
The major challenges before those who are trying to form regulations for digital currency are —
- How to control the money?
- How to collect taxes?
- How to tackle anonymity?
For the national governments, it is hard to wrap it in traditional regulations, but it will be a boon for all if they leverage the technology. For those who are shouting “BAN”, have no reason at all.
What do we have on the upside?
The Crypto-fanatics can list hundreds of reasons here but I have listed a few visible ones —
- Fast and easy cross-border transactions with low fee irrespective of the amount.
- No need of Bank like infrastructure on several locations which incurs extra cost.
- Secure. (The banking industry has got it’s fair share of hack and fraud cases)
- Smart-contracts reducing the manual work that goes into accounting and settlement.
- Decentralized power.
Despite the upsides, there are challenging roadblocks in its mass adoption.
Every technology goes through three phases before it touches the masses
In the first phase, the creators adopt it. In the second phase the market adopts it (current phase for Blockchain and Cryptocurrency). Second phase is the transfer of trust from creator to the market. In the final phase the masses adopt it — the transfer of trust from market to the users.
On each of those stages there is some resistance and at times the adoption needs to be supplemented by adaption. (this concludes the answer)
Along with the people — the market, governments, and policymakers will need to adapt according to the new needs of this technology. As published in a report by International Monetary Fund. (more about it later in this blog)
Bitcoin Legality by Country/Regions
Bitcoin is not restricted in 106 of 251 countries/regions. — Coin Dance
I’ve collected the information on the legality status of Cryptocurrencies from two different sources which are curated by the community.
These maps can be trusted. They are curated by the tech-enthusiasts and early adopters residing in those countries.
Credits: Coin.Dance
Community-driven Bitcoin statistics and services.
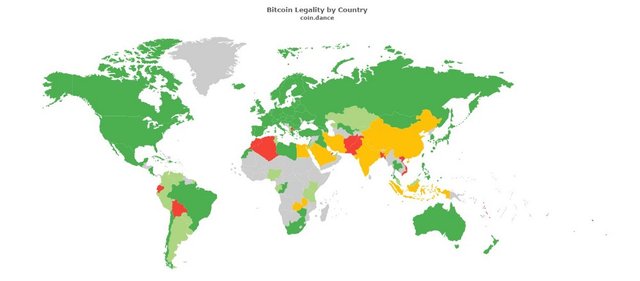
Crypto Regulation World Map: Green=Legal/Regulated, Yellow=Restricted/Not-regulated, Red=Illegal
Credits: BitLegal
BitLegal tracks the evolving regulatory landscape of Blockchain technology around the world.
Last Updated: 8 May 2018
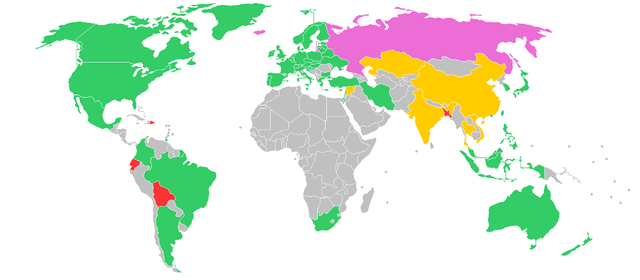
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. [ Author: Habarithor]
💚 permissive: It’s legal to use bitcoin.
🌸 contentious: Some restrictions on legal usage of bitcoin.
🍋 contentious: Interpretation of old laws, but bitcoin isn’t prohibited directly
🔴 hostile: Full or partial prohibition.
Grey zones: Unclear
What is so Contentious or Hostile about it?
Apart from money control, taxation, and anonymity — The government authorities in those countries have other reasons to restrict the banks and people to deal with digital currency.
The other reasons are:
- Old Laws
The old definition of money, commodity, or asset/property as declared in the constitution of many countries can’t fathom the Digital Currency. They fail to identify Cryptocurrency as money or asset and thus they cannot classify it.
The lawmakers could have never predicted this and there is only one thing we can say — The testaments do not serve any purpose now.
The inability of laws to accept digital currency is a roadblock for the regulatory authorities. The nations with right infrastructure and willingness modified their policies quickly. Others are finding it tough to give it a room.
- Public Safety
Many countries along with the Indian Govt. are concerned about the security of public money. In case of a hack or downtime or failure of service, who will be responsible.
Their question is, ‘Who should we run behind in case of a fraud or complaint?’. The IT acts are old, they didn’t comprehend that they’ll ever need to tackle crimes in decentralized applications.
- Anonymity
Governments want to keep a record of who owns what. They need to audit the wealth of the public for numerous purposes. In Cryptocurrency it is hard to keep an account of that. Moreover, the governments do not have a trusted official body to deal with the technology.
- Control over money
The Central Reserve Banks and Federal Banks want to exercise control over money. They will lose control over inflation/deflation in the market, supply of currency, and liquidity in the market. The current financial system is dependent upon credit and debt, these traditional notions are not crystal clear in Cryptocurrency.
So, what are the implications of this?
The issues and the threat it poses cannot be ignored.
Yet to support the easy transactions, banking for remote people without additional infrastructure, and cashless transactions for the complete population the central banks will need to adapt their policies in the digital age.
The global financial crisis resulted in the creation of the autonomous currency and the shortcomings of the traditional model fueled its growth. In the long run, this multi-billion dollar experiment with money and traditional banking will converge to bring in the best of their properties.
Asking that, Is Blockchain necessary? or Can we do fine without it? Is like asking a caveman if they were for or against fire. The same is true for Artificial Intelligence. (but let’s keep AI for another day)
Let’s take a look at some press releases, regulations, and reports from authorities in the financial world to see things from their perspective.
International Monetary Fund — The Long and Short of Digital Revolution
An article published on IMF.org in June 2018.
“Smart policies can alleviate the short-term pain of technological disruption and pave the way for long-term gain.”
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., consisting of “189 countries working to foster global monetary cooperation… — Wikipedia

Src: http://www.imf.org [The image belongs to IMF. Used for educational purpose only. It will be taken down if reported]
The above image is a part of this report authored by Martin Mühleisen (The director of the IMF’s Strategy, Policy, and Review Department.)
“ This digital transformation results from what economists who study scientific progress and technical change call a general-purpose technology”, writes the author.
A general purpose technology is the one which has potential to create influence across all sectors and industries and which continually improves itself. In history, the general-purpose technology which transformed the world were the steam engines, printing press, and electricity.
The first efficient steam engine was made in 1774. It was 1812 until the first commercial steam locomotive was put on the rail. The economy saw effective growth by the year 1830.
Same is true with electricity, the production and distribution of the electricity took years to dissolve in our everyday life. Today we do not imagine a home without electricity, and for the Internet, this shift is in the last phase.
An important component of a disruptive technology is that it must first be widely adopted before society adapts to it.
The nature of general-purpose technologies is very disruptive. An instance of this phenomenon is, Queen Elizabeth I denied to patent the knitting machines invented by William Lee in fear that this will take away the jobs of commoners. But the principle of operation of that machine is still in use after centuries.
The conclusion of the article is — such technologies must be harnessed for the benefits in the long term. One key distinction between the digital revolution and the steam & electricity revolution is the pace in which it expanded. World Wide Web came in 1989 and within 30 years the revolution is here.
The digital revolution should be accepted and improved rather than ignored and repressed.
“ With good policies and a willingness to cooperate across borders, we can and should harness these exciting technologies to improve well-being without diminishing the energy and enthusiasm of the digital age.” concluded the author.
The press releases by Reserve Bank of India
The governments are not untouched by the upsurge in this sector.
The RBI was very well aware of repercussions of not handling the Cryptocurrencies in their early days.
That early press release by a government body regarding Bitcoin in 2013 is surprising. In 2013 the price fluctuated between $22 per Bitcoin to $1000.
Link to that press release.
Following is one of the recent press release —
Attention of members of public is drawn to the Press Release issued by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on December 24, 2013, cautioning users, holders and traders of Virtual Currencies (VCs) including Bitcoins regarding the potential economic, financial, operational, legal, customer protection and security related risks associated in dealing with such VCs.
Although they could have made India a breeding ground for Crypto-exchanges by regulating them and forming taxation rules in the early days.
That would’ve given a boost to the country’s economy, making it a desirable place for Blockchain-Crypto startups.
Here is another press release to reiterate the concerns —
Vide press release dated February 1, 2017, RBI has also clarified that it has not given any license/authorization to any entity/company to operate such schemes or deal with Bitcoin or any VC.
In the wake of significant spurt in the valuation of many VCs and rapid growth in Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), RBI reiterates the concerns conveyed in the earlier press releases.
Despite all these press releases, it is clear that the government do see significant potential in the underlying technology.
The government officials are positive about the Blockchain technology. Some recent projects funded by the Govt. of India also conveys the same — IIT Kanpur to design Rs 334-mn blockchain architecture for e-governance.
At present, the RBI restricted the Banks to deal with the Cryptocurrency exchanges for the safety of public money. That is why India lies in the yellow zone in the above Map.
The major issue for RBI and Finance ministry of India is to handle fraud, customer care, and money laundering associated with it. The current laws in the IT Cell and consumer protection act cannot be justified for Cryptocurrencies.
The Finance minister of India has repeatedly said that they’ve formed a committee to come up with regulations for Cryptocurrency in India.
The three major crypto-exchanges ZebPay, Koinex, and BuyUcoin from India are looking very positive about the upcoming policies. They have found some ways around the current regulations and they are operating normally.
For the non-tech savvy
The Cryptocurrency exchanges and the Blockchain based product companies are not all the same.
In some cases, the Blockchain based application has not much to do with the Cryptocurrency, which means the legality of Cryptocurrency does not affect all the Blockchain based solutions alike.
The underlying technology is legal but some applications (like Cryptocurrency) on top of it are contentious and hostile in the books of central banks and governments. But the scenario is likely to change as we progress and tackle the foreseen issues.
To conclude,
The Revolution Will Not Be Centralized
The credits for this sub-title goes to Reddit.
Which means, a written word in the government’s book cannot keep a ban on Cryptocurrency.
If people want to use them, they will. The Cryptocurrency do not seek the approval of central authorities. Yet the mass adoption is not possible without the intervention of regulatory bodies.
There are both challenges and opportunities for us in the digital age. The central banks are seeing competition for the first time. The competition is good for any market. This will force them to improve the age-old financial system and to make fiat more lucrative, they may try to offer Cryptocurrency like features in them. The banks never had competitors, now they do.
The Cryptocurrencies do face deflation risk, volatility, taxation issue, lack of regulation, public awareness etc. but not the solid use cases.
This blog was originally published on HapRamp's Medium Blog by @rajatdangi.
Recommended read: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2018/06/central-bank-monetary-policy-and-cryptocurrencies/he.htm
Go here https://steemit.com/@a-a-a to get your post resteemed to over 72,000 followers.