"Ethical hacking: The need for cyber security," By S. Patil, A. Jangra, M. Bhale, A. Raina and P. Kulkarni 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering
S. Patil, A. Jangra, M. Bhale, A. Raina and P. Kulkarni, "Ethical hacking: The need for cyber security," 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI), Chennai, 2017, pp. 1602-1606.
doi: 10.1109/ICPCSI.2017.8391982
"
Abstract:
Hacking is basically expertise in any field. Hackers are classified as per working and as per knowledge. The ethical hackers come under white hat hackers. Ethical hackers use hacking techniques in order to provide security. They are legally authorized hackers. Various tools are used in order to carry out hacking. The most common hacking technique used is phishing. Since, there is a rapid growth in the number of attack, there is a need for people to learn ethical hacking concepts to secure themselves.
SECTION 1.
Introduction
Ethical hacking also known as penetration testing or white hat hacking, involves the same tools, tricks, and techniques that hackers use, but with one major difference that Ethical hacking is legal. Ethical hacking is performed with the target's authorization. The intent of ethical hacking is to find out vulnerabilities from a hacker's viewpoint so systems can be better secured. It's part of an overall information risk management program that gives the permission for ongoing security enhancements.
Security is the condition of being protected in opposition to danger or loss. In the case of networks, it is also called the information security. Computer security is required because most organizations can be damaged by antagonistic software or intruders. There may be several forms of damage which are interrelated which are produced by the intruders.
Types of Hackers:
As per working
White Hat Hackers
Black Hat Hackers
Grey Hat Hackers
Hactivists
State Sponsored Hackers
Suicide Hackers
As per knowledge
Script Kiddies
Admins
Coders
Need for Ethical Hacking
The technology of internet of things is growing at rapid rate. Things are getting connected to internet and the only way to secure them is keeping secret password for each. The users feel once they have set a strong password, they are completely secured whereas they are aware of the darker part of this internet. People with intentions to hurt, steal or harm in any of the way called as the Hackers (crackers) constitute the darker part of this web. They intrude into the system using certain techniques. So, here comes the role of Ethical Hacker, the good ones. To stay secure from getting hacked most basic strategy would be to learn to think like a hacker. How the hacker carry out hacking, what tools and techniques are used by them. An ethical hacker does the same. He/She knows how a hacker can intrude into his/her system, so all the existing vulnerabilities in his/her system are scanned and removed. A user study by Garfinkel and Miller[1], states that many users may still be vulnerable inspite of having strong passwords. The future is life bounded in internet hence, security is the most important factor to be taken care of. This is why people should learn ethical hacking.
SECTION 2.
Ethical Hacking
Who is an Ethical Hacker?
An ethical hacker is a white hat hacker who does hacking for some good cause(like securing any organization). Ethical hackers basically are the good people. They have legal authorization to intrude into other's system. The ethical hackers scan the ports, websites and find the vulnerabilities through which a cracker can attack.
The attacks could be easily done once the vulnerabilities for any system is known. To be secured in this world of internet, you must know how a hacker(cracker) can intrude into your system
Learning the concepts of hacking and applying them for securing any system, organization or for any good cause is what defines ETHICAL HACKING.
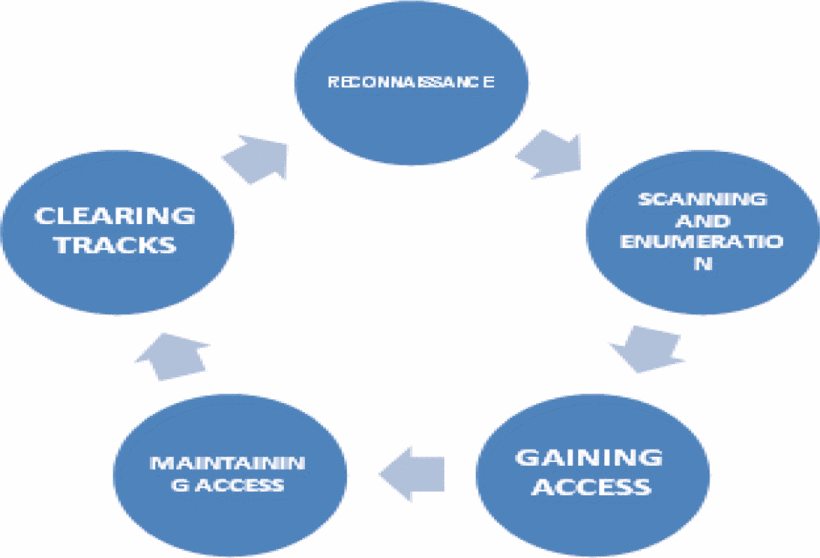
The Fig. 1 explains the steps for carrying out ethical hacking which consists of 5 blocks –
Reconnaissance
Scanning and Enumeration
Gaining Access
Maintaining Access
Clearing Tracks
Figure 1
Fig. 1.
Steps of ethical hacking
View All
2.1 Reconnaissance[2]
Reconnaissance is a set of processes and techniques used to secretly discover and collect information about a target system.
During reconnaissance, an ethical hacker attempts to collect as much information about a target system as possible, following the seven steps listed below –
Gather preliminary information
Identifying active machines
Determine open ports and access points
OS fingerprinting
Reveal all the services on ports
Network mapping
2.2 Scanning and Enumeration
The second step of ethical hacking and penetration testing involves two terms that is scanning and enumeration.
Scanning is a common technique used by a pen tester to discover the open doors. Scanning is used to find out the vulnerabilities in the services running on a port. During this process you have to find out the alive host, operating systems involved, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, servers/services, perimeter devices, routing and general network topology (physical layout of network), that are part of the target organization.
Enumeration is the initial attack on target network. Enumeration is the process to gather the information about a target machine by actively connecting to it.
2.3. Gaining Access
Once the reconnaissance is done and all the vulnerabilities are scanned, the hacker then tries to gain the access with the help of certain tools and techniques.
It basically focuses on the password retrieval. For this hacker can either use bypassing techniques(like using konboot) or password cracking techniques (like pwdump7).
2.4 Maintaining Access
Once an attacker has gained the access of the targeted system, he/she can exploit both the system and its resources and furthermore use the system as a launch pad to scan and harm other systems, or he/she can keep a low profile and continue exploiting the system without the actual user noticing all these acts. Both these actions can destroy the organization leading to a catastrophe. Rootkits gain access at the operating system level while a Trojan horse gains access at the application level. Attackers can use Trojan horses to transfer user names, passwords, and even credit card information stored on the system.
Organizations can use intrusion detection systems or deploy honeypots to detect intruders. The latter though is not recommended unless the organization has the required security professionals to leverage the concept of protection.
2.5 Clearing Tracks
An attacker needs to destroy evidence of his presence and activities for several reasons like evading detection and further punishment for the intrusion. Erasing evidence often known as ‘clearing tracks’ is a requirement for any attacker who wants to remain obscure and evade trace back. This step usually starts by erasing the contaminated logins or any other possible error messages that may have been generated on the victims system from the attack process. For instance, a buffer overflow attack usually leaves a message in the system logs which needs to be cleared. Next, attention is turned to affecting changes so that future logins are not logged.
The first thing a system administrator does to monitor the unusual activity happening in the system is by checking all the system log files, it is important for intruders to use a utility to modify the system logs so that they cannot be traced by the administrator. It is important for attackers to make the system look like it did before they gained access and established backdoors for their use. Any files that were modified need to be changed back to their original attributes so that there is no doubt in administrators mind that the system has been intruded.
An attacker can use the system as a cover to launch fresh attacks against other systems or use it as a means of getting to another system on the network without being detected. Thus, this phase of attack can turn into a new cycle of attack by using the five steps all over again.
SECTION 3.
Tools
Table 1: Tools used for reconnaissance
Table 1:
Table 2: Tools used for scanning
Table 2:
Table 3: Tools used for gaining access
Table 3:
Table 4: Tools used for maintaining access
Table 4:
Table 5: Tools for clearing tracks
Table 5:
SECTION 4.
Common Hacking Technique
Phishing[3]
Phishing is a form of social engineering in which an attacker tries to fraudulently acquire sensitive information from a victim by impersonating a reliable third party.
It is worth noting that the phishers are getting smarter. Observing the trends in other online crimes, it is inevitable that future phishing attacks will incorporate greater elements of context to become more effective and thus more hazardous for society.
Figure 2
Fig. 2
Process of phishing attack[4]
View All
The above fig. 2 shows the process of phishing attack. The attack is basically done using a fake page which is similar to the trusty webpage. The attacker send the fake page link via email. This includes the fake mailing process. Once the user clicks on the fake page link and login using his/her credentials, which directly reaches the attacker and the user is phished.
Figure
View All
Phishing attacks take benefit of both technical and social vulnerabilities, there is a large number of different attacks; an excellent overview of the most commonly occurring attacks and counter measures can be found in [5].
SECTION 5.
Conclusion
Ethical hacking must be practiced. It requires basic knowledge of networks and cyber security. This paper collaborates most of the basic terminologies related to ethical hacking. It gives a brief information about who an ethical hacker is, and why there's a need for world to learn it. It also describes how hacking is carried out and what are the different tools and technologies used.
Thus, this paper gives a basic understanding in context of ethical hacking.
REFERENCES
[1].
Simson Garfinkel and Robert Miller. Johnny 2: A user
test of key continuity management with s/mime and outlook
express. Symposium on Usable Privacy and Security (SOUPS
2005), July 6-8, 2005, Pittsburgh, PA.
[2].
website:h
ttps://www.tutorialspoint.com/ethical_hacking/ethical_ha
cking_reconnaissance.htm
l
[3].
Tom Jagatic, Nathaniel Johnson, Markus Jakobsson, and Filippo
Menczer. Social Phishing. Magazine Communications of the
ACM
[4].
Website:http://www.digit.in/technology-guides/fasttrack-to-cyber-
crime/the-12-types-of-cyber-crime.html
[5].
Aaron Emigh. Online identity theft: Phishing technology,
chokepoints and countermeasures. ITTC Report on Online Identity
Theft Technology and Counter measures; http://www.anti-
phishing.org/Phishing-dhs-report.pdf, October 2005. "
S. Patil, A. Jangra, M. Bhale, A. Raina and P. Kulkarni, "Ethical hacking: The need for cyber security," 2017 IEEE International Conference on Power, Control, Signals and Instrumentation Engineering (ICPCSI), Chennai, 2017, pp. 1602-1606.
doi: 10.1109/ICPCSI.2017.8391982