Fact Checking The Fact Checkers, They Are Never Going To Quit Lying To You
Sometimes you just want to shake your head wondering when they are going to quit lying to you. Two reports published in Frontiers, one in November 2021 and another in May of 2023 shows a definitive link to types of lymphomas, the first in a human and the latter in a mouse.
In a fact check done on the mice reported to have received the BNT162b2 mRNA booster it states that:
The Instagram post references a case report published in Frontiers in Oncology in May that examined a study involving 14 mice injected with the Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine. The case report focused on one mouse in the study that died of lymphoma, a cancer of the lymphatic system, two days after receiving its second dose of the vaccine.
But the report does not assert this event "proves" the mouse developed cancer because of the vaccine, as the Instagram post claims.
The article then goes on to say:
There are also several problems with the study that make the claim faulty, Dr. David Gorski, a professor of surgery and oncology at Wayne State University, told USA TODAY.
First, the vaccine doses given to the mice were between 480 and 600 times the size of those typically given to humans when accounting for body weight, Gorski wrote in a blog post that also debunked the claim.
Another problem stems from the way the vaccine was given, Gorski said. Humans receive it as a shot into a muscle. But the report detailed how the vaccine was injected directly into the mice's tail veins in the study, which Gorski said gives the vaccine a direct path to the animals' heart and lungs.
“If it’s injected into the muscle, most of the vaccine stays in a relatively small area. It doesn’t really go very far,” Gorski told USA TODAY. “If you inject it into the bloodstream, it’s in the bloodstream – it’s going everywhere. … Nothing like what is done in real life.”
The study also tracked the body weights of the mice. Roughly a week before it received the vaccine, the mouse that died prematurely began losing weight – a key indicator of illness in mice. And the particular breed of mouse used in the study is known to spontaneously develop cancers, specifically lymphomas, Gorski said.
“That leads me to think the mouse probably had cancer before,” he said.
Researchers have gone on to vaccinate more than 70 mice during the study, and the one described in the case report was the only one to develop cancer, Eens said.
One would think it's bad enough he tells an outright lie on a well established fact that the vaccine does not just stay localized at the injection site but went on to use a sickly mouse in the study without having confirmed the mouse, which in that particular breed is prone to develop cancers, specifically lymphomas, had already developed cancer. That's a pretty crucial point in my opinion to try and just brush it off. If the mice were prone to develop lymphomas why wasn't it tested to make sure it's weight loss wasn't due to having developed lymphoma prior to the injection.
In a lot of studies done with mice they get pretty specific with how they chose the mice they did for a study. The study will usually state a specific number of healthy mice were chosen for the study and the procedures they underwent to make sure the mice were healthy.
If ignorance wasn't bliss enough for them in this particular case why not look at other case reports of where lymphoma development had occurred after a BNT shot, one not just in a mouse but a human, as in this report of a man who developed lymphoma after having received the BNT shot instead of rubbing it off with this statement:
In fact, the report states evidence to make such a determination is "lacking" and that a causal link between the two events "cannot be unequivocally established and may represent coincidence."
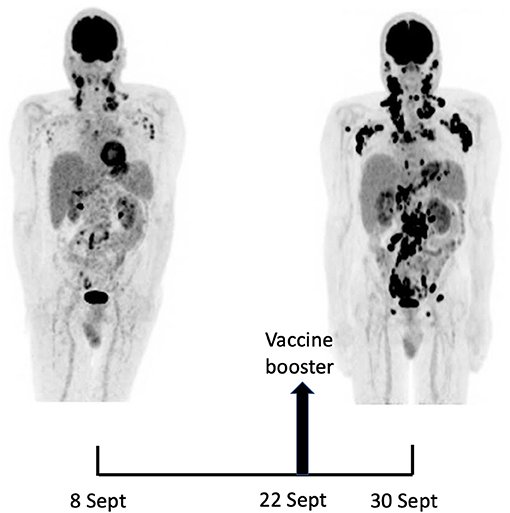
Because not only did the man develop lymphoma but it spread even further upon a second shot and booster. The report could have been readily found among the publications of Frontiers as both reports were published there.
A 66-year-old man with no significant medical history except for hypertension, hypercholesterolemia and type 2 diabetes presented on September 1, 2021 with cervical lymphadenopathies that became recently apparent during a flu-like syndrome. The two doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine had been administered, respectively, 5 and 6 months earlier in the left deltoid. Besides moderate asthenia, he did not report any constitutional symptom. Blood examination indicated a mild inflammatory syndrome, without anemia or white blood cell changes; Lymphocytes immunophenotyping was unremarkable. Protein electrophoresis and immunoglobulin levels were normal and Coombs test was negative.

The man shows up relatively healthy presenting flu like symptoms five to six months after having gotten the BNT vaccine. They determine he has developed lymphoma and in preparation for chemotherapy they decide to vaccination him again only to find out it made the matter worse.
But, but, but instead of outright claiming a correlation they run with a similar tagline as seen with the mouse:
Interestingly, in none of these studies, the possibility that the mRNA vaccines could have played a role in the development of malignant lymph nodes was considered. Indeed, the consensus so far is that the occurrence of hypermetabolic lymphadenopathies should not question the safety of mRNA vaccines, neither in healthy individuals nor in patients with neoplastic conditions
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first observation suggesting that administration of a SARS-CoV-2 vaccine might induce AITL progression. Several arguments support this possibility.
Well to my knowledge this is the first observation of a human test subject over a mouse. It probably doesn't quite matter in the finally equation of it all, both man and beast ended up regretting being subjected to the "new science" of never questioning the science. SMH, just think of all the mice lives that could be saved if they'd just check the publications on the human test subjects.