Cryptocurrency Blog. Whats is it? Who developed it? How it works. Most knonw Cryptocurrency and more.
What is cryptocurrency and how cryptocurrencies emerged as a side product of digital cash
Few people know, but cryptocurrencies emerged as a side product of another invention. Satoshi Nakamoto, the unknown inventor of Bitcoin, the first and still most important cryptocurrency, never intended to invent a currency.
In his announcement of Bitcoin in late 2008, Satoshi said he developed “A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. “
His goal was to invent something; many people failed to create before digital cash.
Announcing the first release of Bitcoin, a new electronic cash system that uses a peer-to-peer network to prevent double-spending. It’s completely decentralized with no server or central authority. – Satoshi Nakamoto, 09 January 2009, announcing Bitcoin on SourceForge.
The single most important part of Satoshi ‘s invention was that he found a way to build a decentralized digital cash system. In the nineties, there have been many attempts to create digital money, but they all failed.
… after more than a decade of failed Trusted Third Party based systems (Digicash, etc), they see it as a lost cause. I hope they can make the distinction, that this is the first time I know of that we’re trying a non-trust based system. – Satoshi Nakamoto in an E-Mail to Dustin Trammell.
After seeing all the centralized attempts fail, Satoshi tried to build a digital cash system without a central entity. Like a Peer-to-Peer network for file sharing.
This decision became the birth of cryptocurrency. They are the missing piece Satoshi found to realize digital cash. The reason why is a bit technical and complex, but if you get it, you‘ll know more about cryptocurrencies than most people do. So, let‘s try to make it as easy as possible:
To realize digital cash you need a payment network with accounts, balances, and transaction. That‘s easy to understand. One major problem every payment network has to solve is to prevent the so-called double spending: to prevent that one entity spends the same amount twice. Usually, this is done by a central server who keeps record about the balances.
In a decentralized network, you don‘t have this server. So you need every single entity of the network to do this job. Every peer in the network needs to have a list with all transactions to check if future transactions are valid or an attempt to double spend.
But how can these entities keep a consensus about this records?
If the peers of the network disagree about only one single, minor balance, everything is broken. They need an absolute consensus. Usually, you take, again, a central authority to declare the correct state of balances. But how can you achieve consensus without a central authority?
Nobody did know until Satoshi emerged out of nowhere. In fact, nobody believed it was even possible.
Satoshi proved it was. His major innovation was to achieve consensus without a central authority. Cryptocurrencies are a part of this solution – the part that made the solution thrilling, fascinating and helped it to roll over the world.
What are cryptocurrencies really?
If you take away all the noise around cryptocurrencies and reduce it to a simple definition, you find it to be just limited entries in a database no one can change without fulfilling specific conditions. This may seem ordinary, but, believe it or not: this is exactly how you can define a currency.
Take the money on your bank account: What is it more than entries in a database that can only be changed under specific conditions? You can even take physical coins and notes: What are they else than limited entries in a public physical database that can only be changed if you match the condition than you physically own the coins and notes? Money is all about a verified entry in some kind of database of accounts, balances, and transactions.
How miners create coins and confirm transactions.
Let‘s have a look at the mechanism ruling the databases of cryptocurrencies. A cryptocurrency like Bitcoin consists of a network of peers. Every peer has a record of the complete history of all transactions and thus of the balance of every account.
A transaction is a file that says, “Bob gives X Bitcoin to Alice“ and is signed by Bob‘s private key. It‘s basic public key cryptography, nothing special at all. After signed, a transaction is broadcasted in the network, sent from one peer to every other peer. This is basic p2p-technology. Nothing special at all, again.
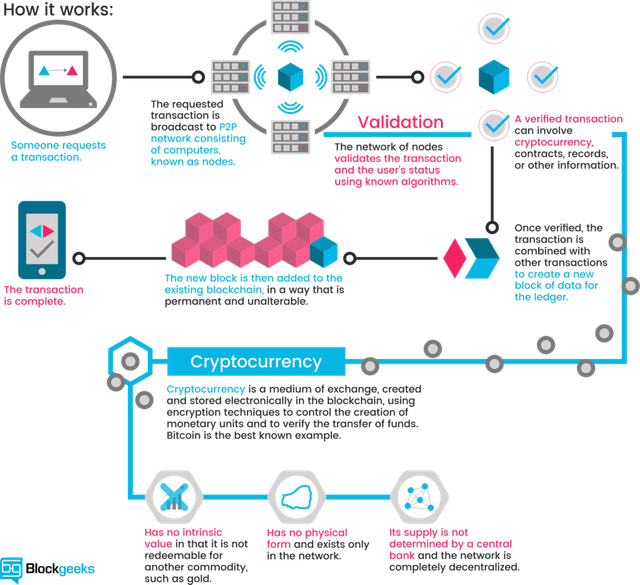
The transaction is known almost immediately by the whole network. But only after a specific amount of time it gets confirmed.
Confirmation is a critical concept in cryptocurrencies. You could say that cryptocurrencies are all about confirmation.
As long as a transaction is unconfirmed, it is pending and can be forged. When a transaction is confirmed, it is set in stone. It is no longer forgeable, it can‘t be reversed, it is part of an immutable record of historical transactions: of the so-called blockchain.
Only miners can confirm transactions. This is their job in a cryptocurrency-network. They take transactions, stamp them as legit and spread them in the network. After a transaction is confirmed by a miner, every node has to add it to its database. It has become part of the blockchain.
For this job, the miners get rewarded with a token of the cryptocurrency, for example with Bitcoins. Since the miner‘s activity is the single most important part of cryptocurrency-system we should stay for a moment and take a deeper look on it.
“In the next few years, we are going to see national governments take large steps towards instituting a cashless society where people transact using centralized digital currencies. Simultaneously, the decentralized cryptocurrencies – that some even view as harder money – will see increased use from all sectors.” – Caleb Chen London Trust Media
What are miners doing?
Principally everybody can be a miner. Since a decentralized network has no authority to delegate this task, a cryptocurrency needs some kind of mechanism to prevent one ruling party from abusing it. Imagine someone creates thousands of peers and spreads forged transactions. The system would break immediately.
So, Satoshi set the rule that the miners need to invest some work of their computers to qualify for this task. In fact, they have to find a hash – a product of a cryptographic function – that connects the new block with its predecessor. This is called the Proof-of-Work. In Bitcoin, it is based on the SHA 256 Hash algorithm.

You don‘t need to understand details about SHA 256. It‘s only important you know that it can be the basis of a cryptologic puzzle the miners compete to solve. After finding a solution, a miner can build a block and add it to the blockchain. As an incentive, he has the right to add a so-called coinbase transaction that gives him a specific number of Bitcoins. This is the only way to create valid Bitcoins.
Bitcoins can only be created if miners solve a cryptographic puzzle. Since the difficulty of this puzzle increases the amount of computer power the whole miners invest, there is only a specific amount of cryptocurrency token that can be created in a given amount of time. This is part of the consensus no peer in the network can break.
Revolutionary properties
If you really think about it, Bitcoin, as a decentralized network of peers which keep a consensus about accounts and balances, is more a currency than the numbers you see in your bank account. What are these numbers more than entries in a database – a database which can be changed by people you don‘t see and by rules you don‘t know?
“It is that narrative of human development under which we now have other fights to fight, and I would say in the realm of Bitcoin it is mainly the separation of money and state.” – Erik Voorhees, cryptocurrency entrepreneur.
Basically, cryptocurrencies are entries about token in decentralized consensus-databases. They are called CRYPTOcurrencies because the consensus-keeping process is secured by strong cryptography. Cryptocurrencies are built on cryptography. They are not secured by people or by trust, but by math. It is more probable that an asteroid falls on your house than that a bitcoin address is compromised.
Describing the properties of cryptocurrencies we need to separate between transactional and monetary properties. While most cryptocurrencies share a common set of properties, they are not carved in stone.
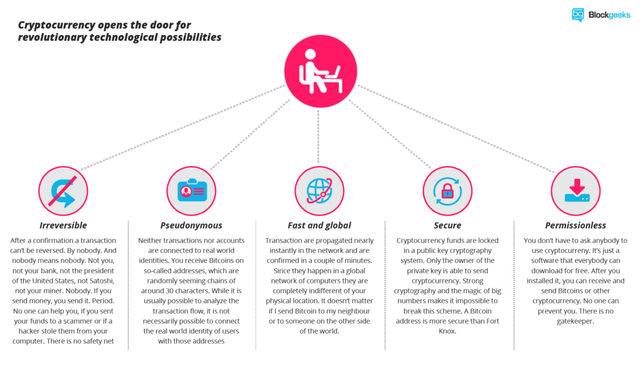
Transactional properties:
- Irreversible: After confirmation, a transaction can‘t be reversed. By nobody. And nobody means nobody. Not you, not your bank, not the president of the United States, not Satoshi, not your miner. Nobody. If you send money, you send it. Period. No one can help you, if you sent your funds to a scammer or if a hacker stole them from your computer. There is no safety net.
- Pseudonymous: Neither transactions nor accounts are connected to real-world identities. You receive Bitcoins on so-called addresses, which are randomly seeming chains of around 30 characters. While it is usually possible to analyze the transaction flow, it is not necessarily possible to connect the real world identity of users with those addresses.
- Fast and global: Transaction are propagated nearly instantly in the network and are confirmed in a couple of minutes. Since they happen in a global network of computers they are completely indifferent of your physical location. It doesn ‘t matter if I send Bitcoin to my neighbor or to someone on the other side of the world.
- Secure: Cryptocurrency funds are locked in a public key cryptography system. Only the owner of the private key can send cryptocurrency. Strong cryptography and the magic of big numbers makes it impossible to break this scheme. A Bitcoin address is more secure than Fort Knox.
- Permissionless: You don ‘t have to ask anybody to use cryptocurrency. It’s just a software that everybody can download for free. After you installed it, you can receive and send Bitcoins or other cryptocurrencies. No one can prevent you. There is no gatekeeper.
Monetary properties:
- Controlled supply: Most cryptocurrencies limit the supply of the tokens. In Bitcoin, the supply decreases in time and will reach its final number somewhere in around 2140. All cryptocurrencies control the supply of the token by a schedule written in the code. This means the monetary supply of a cryptocurrency in every given moment in the future can roughly be calculated today. There is no surprise.
- No debt but bearer: The Fiat-money on your bank account is created by debt, and the numbers, you see on your ledger represent nothing but debts. It‘s a system of IOU. Cryptocurrencies don‘t represent debts. They just represent themselves. They are money as hard as coins of gold.
To understand the revolutionary impact of cryptocurrencies you need to consider both properties. Bitcoin as a permissionless, irreversible and pseudonymous means of payment is an attack on the control of banks and governments over the monetary transactions of their citizens. You can‘t hinder someone to use Bitcoin, you can‘t prohibit someone to accept a payment, you can‘t undo a transaction.
As money with a limited, controlled supply that is not changeable by a government, a bank or any other central institution, cryptocurrencies attack the scope of the monetary policy. They take away the control central banks take on inflation or deflation by manipulating the monetary supply.
“While it’s still fairly new and unstable relative to the gold standard, cryptocurrency is definitely gaining traction and will most certainly have more normalized uses in the next few years. Right now, in particular, it’s increasing in popularity with the post-election market uncertainty. The key will be in making it easy for large-scale adoption (as with anything involving crypto) including developing safeguards and protections for buyers/investors. I expect that within two years, we’ll be in a place where people can shove their money under the virtual mattress through cryptocurrency, and they’ll know that wherever they go, that money will be there.” – Sarah Granger, Author, and Speaker .
Most known Cryptocurrency
- Bitcoin
Having the first-mover advantage, Bitcoin is the world’s first peer-to-peer decentralized digital currency, which is now not only the most recognized and known cryptocurrency, but also the only digital currency that is most widely accepted and used in numerous real-world transactions.
With a market cap of approximately $80 billion and a supply of more than 16.5 million Bitcoins, one Bitcoin (until recently) had a value of more than $4,800, making it the costliest virtual currency on the market. Recently, it broke an all-time record high and hit a historic mark when its value peaked at a whopping $5,856.10 on October 13, 2017.
With Bitcoin ATMs and widespread knowledge and adoption, it is now easier than ever to mine and obtain Bitcoins and make actual transactions.
Coinbase operates one of the most popular wallets and is a simple way to buy Bitcoins, while Xapo is known for its ease of use in Bitcoin transactions and as a bitcoin cold-storage vault.
The main advantages of Bitcoins over other cryptocurrencies, according to Bitcoin developer and Medium writer Jimmy Song, are its network effect and proven security. According to him, other advantages of Bitcoins that make them unique are:
- Bitcoin is more accessible with more merchants, more exchanges, and software/hardware support systems available.
- It has the largest developer ecosystem with more software and more implementations.
- First mover advantage: Large user base, loyalists, and entrepreneurs creating companies (open source projects, startups) around it.
- It is far more liquid than other digital currencies · Security has been proven far more than its much younger counterparts with usage by almost every metric exceeding that of altcoins.
- It has a large lead as a store of value.
Bitcoin should, however, not be confused with Bitcoin Cash. Bitcoin Cash is a breakaway part from Bitcoin, which is now a separate cryptocurrency itself. Bitcoin Cash has a market cap of nearly $5.5 billion, and one BCH can be bought for $nearly $330 as of this writing.
- Ethereum
Proposed in late 2013, Ethereum is a decentralized platform for applications that run exactly as programmed without any chance of fraud, censorship, or third-party interference. It provides a decentralized virtual machine, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which can execute scripts using an international network of public nodes.
Ethereum is a platform built for smart contracts, but it has been controversial and resulted in diverging blockchains.
The market cap of Ethereum is more than $29 billion with a price of approximately $300 (from a mere $8 at the start of 2017). In the historic quarter for cryptocurrencies, Ethereum’s rise has been almost negligible in terms of what is expected from digital currencies, it has gone up just 8%.
The Ethereum Wallet is a gateway to decentralized applications on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows you to hold and secure ether and other crypto-assets built on Ethereum, as well as write, deploy and use smart contracts.
Despite Ethereum being overshadowed by Bitcoin in various arenas, recent news and developments in the Ethereum realm have started igniting deep interest in this cryptocurrency.
Recently, Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin spoke about Ethereum’s capacity to have transactional power to equal Visa in the next two years. Buterin believes the cryptocurrency and its blockchain can replace credit card networks and gaming servers.
Also in major news this year, thirty big banks, tech giants, and other organizations (including J.P. Morgan Chase, Microsoft, and Intel) are uniting to build business-ready versions of the software behind Ethereum. The Ethereum alliance arrives as a challenger to several other extant blockchain ventures.
In April 2017, a Microsoft demo day in New York featured Ethereum blockchain strongly. There, three high-profile companies – Bank of America, tech firm Mojix, and digital travel firm Webjet – demoed products built using Ethereum to streamline various aspects of their industries and usher in new levels of transparency.
- Altcoins
Altcoins or "Alternative coins" are the alternative cryptocurrencies launched after the success of Bitcoin. Altcoins promote themselves as better substitutes to Bitcoin. The success of Bitcoin as the first peer-to-peer digital currency paved the way for many to follow.
Although the list is constantly changing, the top 10 Altcoins (contenders of Bitcoin) are:
- Ethereum
- Ripple
- Litecoin
- Dash: Digital+ cash
- NEM
- Ethereum Classic
- Monero
- Zcash
- Decred: Decentralized credit
- PIVX: Private Instant Verified Transactions
Sources:
- https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-cryptocurrency/
- http://www.businessinsider.com/list-top-cryptocurrencies-analysis-comparison-2017-10/
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://blockgeeks.com/guides/what-is-cryptocurrency/
Congratulations @mialdf! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Congratulations @mialdf! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!