Concept of total eclipse of the moon and total eclipse of the sun
A partial eclipse occurs when part of the moon enters the Earth's main shadow (points A and C in the figure), and when all of the moons are in (point B in the picture).
A lunar eclipse is a phenomenon in which part or all of the moon is hidden by the shadow of the Earth, leaving some or all of the bright spots on the moon seen from the Earth dark. It only happens during the month when the earth is between the moon and the sun. During the central eclipse of the moon, the moon stays in the dark for up to an hour and 40 minutes. However, since the lunar orbital plane (Baekdo plane) leans about 5 ° to the Earth's orbital plane (ecliptic plane), no lunar eclipse occurs during the full Moon, as there is little opportunity for the sun-terrestrial - Moon to be aligned. When a total lunar eclipse occurs, the moon is also seen as a faint red light from the Earth, receiving a reflection from the Earth.
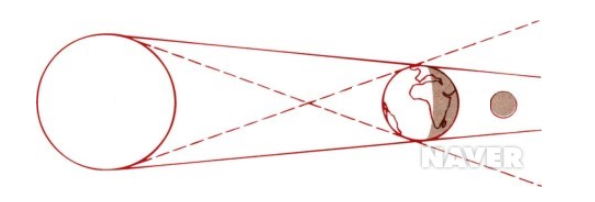
When the solar-month-world is placed in a straight line in space, it creates an area on Earth where the sun can not be seen because of its shadow. From the ground up, it looks as if the moon is slowly blocking out the sun, which is called a total eclipse. Normally, because the Moon is not orbiting the Earth, every five months or so, the sun-month-path of the Earth would actually be on a straight line, so the total eclipse of the sun would occur.
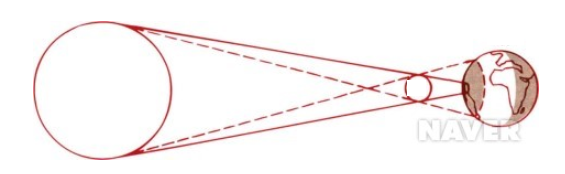
A total eclipse of the globe occurs about once every two years, when the exact angles of the Sun, Moon, and Earth increase by 180 °, usually lasting about 30 to 6 minutes. Solar astronomers study solar corona, as the sun's extreme atmospheric corona is apparent when total solar eclipses occur, do not miss an important observational opportunity that appears about once every two years.
I was confused. Thank you for the explanation.
It's confusing, isn't it?