EDR vs MDR vs XDR: What is the Difference?


Today’s digital landscape is highly dangerous, especially during times of increased remote work. To ensure the security of corporate networks, many organizations are implementing various endpoint solutions. This article explains three types of endpoint security solutions: endpoint detection and response (EDR), managed detection and response (MDR), and extended detection and response (XDR).
What Is EDR?
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) is a combination of solutions that you can use to identify and mitigate threats or vulnerabilities on endpoint devices. EDR security solutions are designed to increase visibility into your distributed devices and apply proactive protections to identify, block, and eliminate threats.
There are three main components to EDR solutions:
- Data collection—uses agents on devices or firewalls on the connection between endpoint and network to gather data on traffic, authentication, and process executions.
- Detection engine—analyzes collected data to identify potential threats and anomalous activity. Can also detect signature based threats.
- Data analysis engine—correlates data from across endpoints to detect the movement of threats across a system.
Most EDR include features for:
- Threat intelligence—solutions can ingest information about existing threats and indicators of compromise (IoC) that is then used to help identify activity and accurately flag it as malicious or not.
- Alerts and forensics—solutions can alert IT teams in real time about potential threats and provide context for the event to help with investigation.
- Trace back—solutions include the ability to track movement or events across your system and identify the endpoint that activity originated on.
- Automated response—solutions include scripts that enable you to perform common response events, including blocking processes, blocking traffic, or isolating activity.
What Is MDR?
Managed detection and response (MDR) is a service where a vendor provides detection and response services for a customer in exchange for a contract or subscription payment. It typically involves a combination of technology solutions and a team of remote security analysts can provide assistance to your in-house team or manage detection and response independently for you.
MDR solutions typically include the following capabilities and tools:
- EDR—can be cloud-based or installed locally with remote access. These solutions enable MDR teams to collect data and initiate responses remotely on your behalf. .
- Perimeter telemetry—includes firewalls, web application firewalls (WAFs), intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS), and network infrastructure tools, such as proxies. These tools enable teams to collect data and consistently monitor the security and performance of network perimeters.
- Incident management and response—MDR teams can take over incident management and response with remote controls or can provide guidance for in-house teams. Often, MDR teams can employ higher level experts than organizations who can then leverage that expertise without the employee cost.
- Threat intelligence—MDR solutions typically ingest external intelligence to ensure that the broadest range of threats are detected and prevented. Vendors may also create intelligence specific to the customer that in-house teams can apply to security management.
The main benefit of MDR is that it provides security capacity to an organization that may not otherwise have access to. By outsourcing detection and response, organizations can reserve their in-house teams for higher level or internal threats. This can significantly reduce an organization’s costs and enable them to prioritize specialist tasks.
What Is XDR?
Extended detection and response (XDR) is the next generation of EDR solutions that goes beyond individual layers of protection. Instead, it includes multiple layers, and extends beyond endpoint devices to include your systems as a whole.
Traditional solutions often provide large numbers of alerts that may be incomplete or without context due to a focus on endpoints. For example, according to SANS, EDR solutions are often only able to detect around 26% of threats and 54% of these threats may be ignored or overlooked due to the high volume of alerts that are sent.
Additionally, with EDR it can take up to 197 days to identify a breach and 69 days to contain it. This is because of the specialized expertise and complex investigations that must occur to identify and eliminate threats accurately.
Where EDR focuses on technological gaps in perimeter security with additional tools, XDR provides a combination solution to simplify workflows. This enables teams to focus on investigating, responding, and developing preventative strategies rather than managing the over 40 tools that many organizations employ.
When implemented, XDR enables security teams to:
- Identify advanced and hidden threats more quickly
- Track threats and activity across systems
- Reduce technological management tasks and increase productivity
- Perform and complete more efficient investigations
- Derive more value from solution investments
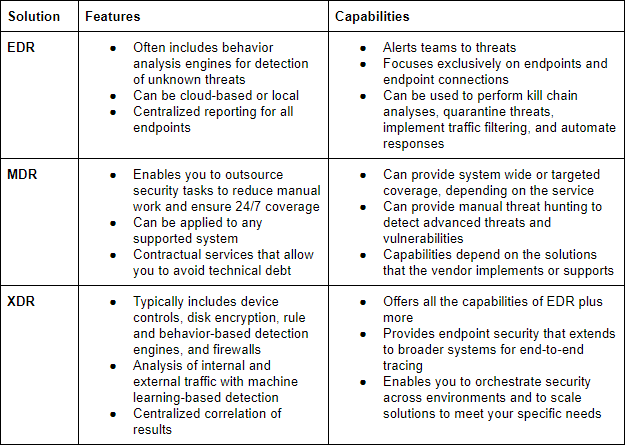
EDR vs MDR vs XDR
Although all three solutions are dedicated to protecting your perimeter, and by extension your systems, from threats they serve slightly different roles and offer different capabilities. The type of solution you should choose depends largely on what solutions you already have in place, how happy with those solutions you are, and what security team resources you have in-house.
To give a better understanding of which solution may best benefit you, consider the following comparison:
Conclusion
Each endpoint security solution offers unique capabilities and features you can leverage to improve endpoint coverage in your organization. EDR offers the most basic security features, and MDR and XDR solutions extend capabilities beyond typical EDR. Depending on your needs, you can add MDR for 24/7 coverage and outsources incident response, and XDR for advanced features like disk encryption and AI-based analysis.