SLC21/WK3: Introduction to Basic Electrical Motors, Switchgear, and Motor Starters
Write two differences between current and voltage.
Write two differences between AC electricity and DC electricity.
Write the difference between an AC motor and a DC motor.
Write two main differences between DOL, Star-Delta and forward reverse starter.
Differences between current and voltage:
Definition:
- Current: Electric charge moving across a conductor is what it is. In amperes (A).
- Voltage (V): Current flows when two points in a circuit have different electrical potentials. Volts are used to measure things.
Nature:
- Current: It is the one that discusses how electrons actually go through a conductor.
- Voltage: Current flows as a result of the pressure or force pushing the electrons.
The two main distinctions between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) electricity are as follows:
Flow Direction:
AC (Alternating Current): Electric charge flows in a direction that alternates on a regular basis.
DC (Direct Current): Electric charge flows in a single direction alone.Source:
AC: Usually produced by power plants, this energy source is utilised for industrial and residential electricity.Batteries, solar cells, and DC power supply are the usual sources of DC, which is frequently utilised in electronic equipment.
Here’s the primary difference between an AC motor and a DC motor:
Power Source:
AC Motor (AC): runs on alternating current, with the current's flow direction fluctuating on a regular basis.
DC (Direct current): motor is the one that runs on just a single direction of current.Design and Components:
AC Motor: Synchronous and induction motors are common types and are typically easier to construct because they do not require a commutator or brushes.
DC motor: is a little more complicated and requires more maintenance because it has brushes and a commutator to regulate the direction of current flow.
Their uses are impacted by these distinctions; DC motors are frequently utilised in low-power or variable-speed applications, such as electronics and automotive systems, whereas AC motors are typically utilised in high-power applications, such as industrial machinery.
These are 2 differences among DOL (Direct-On-Line), Star-Delta, and Forward-Reverse starters below:
- Starting Method and Current Control:
The DOL Starter generates a strong starting current, up to 6-8 times the full-load current, by connecting the motor directly to the full line voltage.
The Star-Delta Starter lowers the starting current to roughly one-third of that in DOL by starting the motor in a star configuration to lower the initial current and then switching to a delta configuration for regular operation.
Forward-Reverse Starter: Modifies the phase sequence to regulate the motor's rotational orientation, enabling it to run either forward or backward without affecting the starting current.
Application and Purpose:
DOL Starter: Easy to use and reasonably priced, this starter is ideal for small motors where high starting torque is required or starting current is not an issue.
Star-Delta Starter: Suitable for industrial applications, this type of starter is used for larger motors where a lower starting current is necessary to prevent significant inrush current.
Forward-Reverse Starter: Mostly utilised in machines that need to operate both forward and backward or in conveyors where motor direction control is required.
B. Write the names and pictures of the electrical switchgear used in your home.
Our home is equipped with electrical switchgear, specifically distribution boxes or panels that regulate power from various sources. The elements in the picture are broken down as follows:
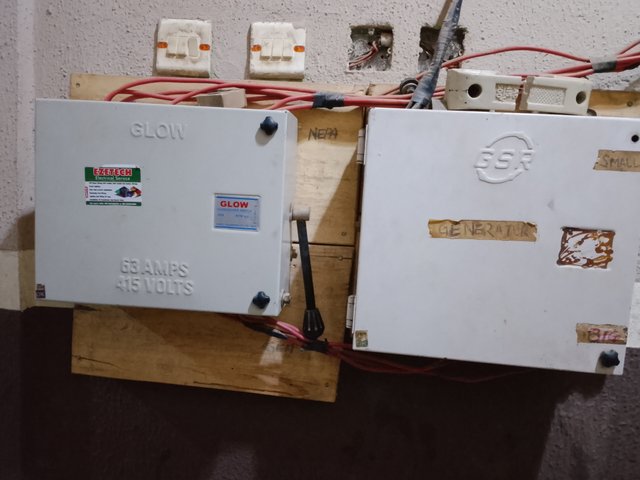

(Left side) Glow Box - This box is marked "GLOW" and has a 415 volt and 63 amp rating. Probably from the utility (NEPA as mentioned above), it serves as a distribution box for incoming main power.
The "GENERATOR" switch appears to be the label on the Generator Box (right side). It regulates the generator-based power source. This switchgear enables switching to generator power in the event that the main power is unavailable.
These boxes are a component of a system that enables power source switching (e.g., utility power and generator).
C. The specifications of the motor is :

According to the motor nameplate in the picture, this motor's specifications are as follows:
KW (Power): 37.0 kW
HP (Horsepower): 1 HP ≈ 0.746 kW, which is equivalent to 37.0 kW, but not explicitly stated.
Speed (RPM): 2960 RPM
Ampere (Current): 62.8 A
Voltage: 415 V
Frequency (Hz): 50 Hz
Power Factor (PF): A PF of 0.8 to 0.9 at full load is typical for motors of this type, however it is not stated explicitly.
Further Details:
Efficiency: 92.5% S1 (continuous duty) is the duty.
TEFC (Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled) is the enclosure. Class of Insulation:F
Ambient Temperature: 50 °C - IP Rating: IP 55 (protected against dust and low-pressure water jets)
The current of my home's 220 volts, 5 HP motor is calculated in the below image

The power circuit of the star delta starter and the devices used is explained below
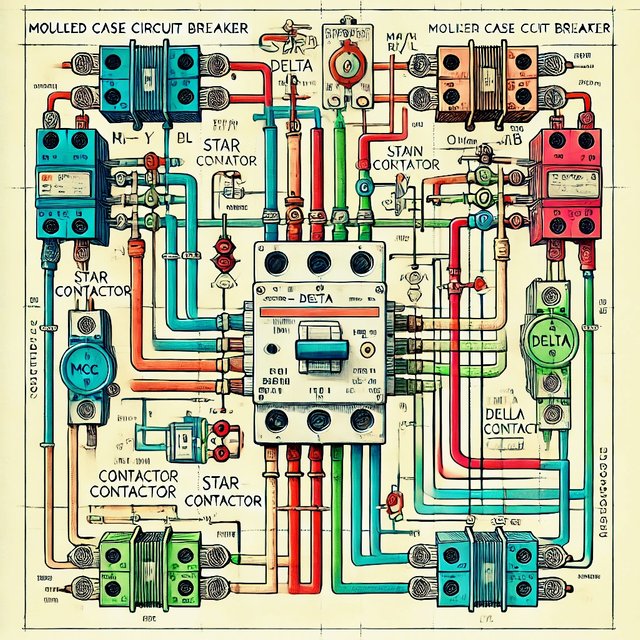
The image was created using Tinkercad and edited with my phone, to bring out the colour that describe and differentiate each component and path
A three-phase motor's starting current is usually decreased by using a star-delta starter.
- Components Required:
Moulded case circuit breakers, or MCCBs, are used to guard against short circuits and overloads.
Overload Relay (O/L): Cuts power when necessary to prevent the motor from overheating from overcurrent.
Main Contactor (MC-1): This is the main switch that connects the motor to the three-phase power source. During the starting phase
4.Star Contactor (MC-2) joins the motor windings in a star pattern.
- Delta Contactor (MC-3): After the motor reaches speed, it connects the motor windings in a delta arrangement.
- To Draw the Power Circuit for Star Delta Starter, see steps below:
Three-Phase Supply Line: - Sketch the three input lines for the three-phase power supply, denoted by the symbols R, Y, and B.
Circuit Breaker (MCCB): - Attach the MCCB immediately following the input lines that are three phases long. Every phase is connected to the MCCB.
Overload Relay: Attach the MCCB's output to the overload relay. This will guarantee that in the event of an overload, the relay can trip the complete circuit.
Main Contactor (MC-1): Attach the overload relay's output to the MC-1 main contactor. In both the star and delta phases, the motor is powered by this contactor.
The next thing is to break the circuit into two routes, one would lead to MC-2 (Star Contactor) and the other to one MC-3 (Delta Contactor). This can be done after MC-1.
To set up the windings in a star pattern, connect the star contactor MC-2. To accomplish this, join one end of each winding to create a common point.
You must connect the delta contactor MC-3 in order to configure the windings in a delta configuration. The windings (R to Y, Y to B, and B to R) are looped end to end to achieve this.
Motor Connection: Attach the motor windings to the outputs of MC-2 and MC-3 At any one time, only one of these contactors will be active:To lower the starting current, the MC-2 (Star Contactor) is turned on during the startup phase.
When the motor settles into a steady speed for full power operation, the MC-3 (Delta Contactor) is turned on..
Control Circuit : A timer is usually incorporated into the control circuit of the star-delta starter to reduce the inrush current and switch from the star configuration (MC-2) to the delta configuration (MC-3) after a specified period of time.
This circuit enables the motor to start in a star configuration. For maximum power, it then shifts to a delta configuration.
- Summary of Connections:
MCCB -> Main Contactor (MC-1) -> Overload Relay (O/L) -> Divided into: - MC-2 (Star Contactor) -> Motor Windings with Star Configuration - MC-3 (Delta Contactor) -> Motor Windings configured for delta
- In conclusion, everyone working in industrial maintenance, electrical engineering, or similar sectors has to comprehend basic electrical motors, switchgear, and motor starters. Numerous devices and applications are powered by motors, and switchgear makes sure that electrical power is distributed and controlled safely. Motor starters, such as DOL and star-delta starters, offer motor protection and control while they are starting and running. These elements work together to provide electrical systems that are dependable, safe, and effective in both commercial and industrial environments. Maintaining system performance, avoiding electrical risks, and guaranteeing smooth operation in a variety of applications all depend on having knowledge in this field.
Hi teacher @mahadisalim
I invite @sors @olaspecial @olawalium
https://x.com/opeyemioguns3/status/1857158164103188621?t=Xdwv9a9EYQi3oPWricgmsA&s=19
This is a very useful topic, especially for those who are new to electrical engineering. Best wishes for the contest dear.