Using Distributed Cloud Computing to Solve Block Chain Scalability Problem
ArcBlock block cornerstone recently released its second milestone product in its 2019 roadmap: ABT Chain Node, which perfectly combines all the features of cloud computing and decentralized block chains. In an interview with CryptoSlate, ArcBlock CEO Fang Zhihong and Matthew McKinney, Director of Marketing and Commerce, introduced the latest developments.
Like Polkadot and Cosmos, ArcBlock is building a platform to connect block chains from the protocol layer.
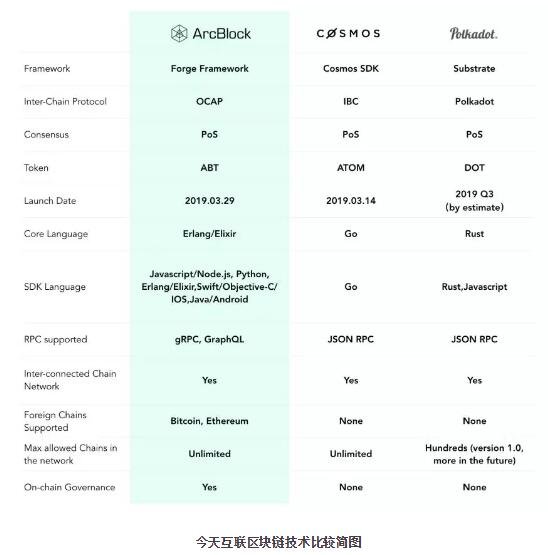
The Seattle-based company describes its services as "Block Chain 3.0", allowing applications to interact with block chain networks such as Bitcoin, Etherfield and Hyperledger from a single code base. The network aims to create a decentralized application ecosystem that is "interconnected, interoperable, independent and not controlled by central nodes".
ArcBlock Pass ABT currently ranks 160th in market value, trading at $0.252 at the time of writing. ABT passes are used to pay for access to the ArcBlock system.
Start with nodes
According to McKinney, the goal of ABT link nodes is to become "the simplest block link node software in the world".
For most currently encrypted currencies, running nodes have become hardware and software-savvy enthusiasts who use dedicated servers to concentrate their efforts on mining games. Encrypted currency mining is specially designed to be resource-intensive, and the calculation of PoW mining generation has little value beyond protecting the security of public chain networks.
McKinney emphasizes that unlike PoW, ArcBlock's mining model is based on value generation on the Web.
According to ArcBlock's technical documentation, "In addition to protecting network security, ArcBlock's resource miners are also responsible for performing useful calculations through the PoS consensus mechanism.
For more information about participating in ArcBlock mining, see this link
When cloud computing encounters block chains
ArcBlock uses cloud computing servers instead of mines to provide users with the resources they need to build DApp, which is identical to today's software development model. The company claims that ABT link nodes are the first software to run AWS spot instances in a decentralized way.
These nodes do not require "centralized hubs or relays", making the company declare that the ABT chain network is a "completely decentralized" structure. In order to achieve this goal, ABT passport protocol uses the PoS consensus.
It is said that the separated nodes through this cloud computing model have the ability of fault tolerance, automatic upgrade and easy migration. In addition, they can run locally, connect directly between users, or connect to the public chain network to provide online services.
ABT chain nodes downloaded more than 10,000 times in the first day of release, indicating that the product has attracted much attention from the market.
ABT chain nodes have recently provided several low-cost reference architectures for productive block chain networks, such as Digital Ocean servers and AWS spot instances. Using the droplet plan of $15 a month in Digital Ocean, users can execute 100 transactions per second (TPS) on the network, thus solving the bottleneck in the PoW mechanism. By comparison, the TPS of ETF is only 15.
And cloud computing companies seem to be paying attention to this latest model. So far, ArcBlock has established partnerships with cloud computing vendors including Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure, Digital Ocean, China, and AURO Cloud in Canada.
ArcBlock recently joined the newly established Block Chain Council of the Huazhou Association of Technology Industries as a founding director. The board includes heavyweight players in the Northwest Pacific Block Chain industry, such as T-Mobile and Microsoft.
ABT chain nodes now look promising. If software developers can run on multiple block chain protocols and get the computing resources they need, the speed of block chain application development will be amazing.