Understanding the Internal Combustion Engine: A Revolutionary Technology
The internal combustion engine (IC engine) has been a cornerstone of modern engineering, revolutionizing transportation, industry, and the way we live. From powering cars to aircraft, this engine has significantly shaped the world since its inception.
What is an Internal Combustion Engine?
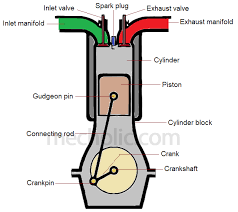
An internal combustion engine is a type of heat engine where fuel combustion occurs within the engine itself. Unlike external combustion engines (e.g., steam engines), IC engines burn fuel in a confined space, generating high-pressure gases that directly produce mechanical work.
How Does It Work?
The basic working principle of an IC engine involves the following steps, often referred to as the four-stroke cycle:
Intake: A mixture of air and fuel is drawn into the cylinder.
Compression: The piston compresses the mixture, increasing its pressure and temperature.
Power (Combustion): A spark ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion that pushes the piston downward, producing power.
Exhaust: Burnt gases are expelled from the cylinder to prepare for the next cycle.
This sequence repeats rapidly, creating a continuous source of power.
Types of IC Engines
IC engines are classified based on:
Fuel Type:
Gasoline engines (petrol engines)
Diesel engines
Gas engines (natural gas, LPG)
Ignition Method:
Spark-ignition engines (used in gasoline engines)
Compression-ignition engines (used in diesel engines)
Configuration:
Single-cylinder vs. multi-cylinder
Inline, V-type, or flat engines
Application:
Automotive engines
Aircraft engines
Marine engines
Advantages of IC Engines
High Efficiency: Especially when compared to older steam engines.
Compact Design: Small, lightweight, and easily portable.
Versatility: Can be adapted for various uses, from cars to generators.
Fast Startup: No need to wait for external heating, unlike steam engines.
Challenges and Environmental Impact
Despite their utility, IC engines have significant drawbacks:
Pollution: Emissions like CO₂, NOx, and particulates contribute to air pollution and climate change.
Resource Dependency: Relies heavily on fossil fuels, a finite resource.
Noise and Vibrations: These can be a source of environmental and operational discomfort.
To address these issues, modern engines are equipped with catalytic converters, and industries are transitioning toward electric and hybrid technologies.
The Future of IC Engines
While electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining popularity, IC engines are far from obsolete. Advanced research focuses on improving efficiency, reducing emissions, and incorporating alternative fuels like hydrogen and biofuels. These innovations ensure IC engines remain relevant in various applications.
Conclusion
The internal combustion engine is a marvel of engineering that has powered humanity’s progress for over a century. As we transition into a more sustainable future, the IC engine’s legacy will persist through its influence on modern engineering and transportation technologies.
What are your thoughts on the future of IC engines? Share your insights in the comments!