INTRODUCTION TO GEODESY
Hey everyone!
Different day, same shift. See what I did there? It's been another blessed but hectic day. It is what it is I guess. I hope your day has been awesome. No time to play around though, so here I am with another scientific blog. Bad habbits die hard.
This time I'm taking the chance to make an introductory post about Geodesy, which is the scientific field that serves the purpose of observing and precisely measuring our planet's shape and size. It is the science of accurately defining the coordinates of points on the Earth's surface and broader space, as well as gathering and processing spatial information for mapping purposes. Observations and measurements regarding the Earth's gravitational field are also included.
As I mentioned, this is an introductory post so I will share some general information regarding the history and the objective of Geodesy. I will also share information and dirty little tricks that surveying engineers use to precisely calculate coordinates, so stay focused! Pretty boring, huh?

Image Source: pixabay.com
History
Geodesy is a greek word (Γεωδαισία) which stems from the words 'Εarth' (Γη) and 'divide' (δαίω). The term Geodesy was first mentioned in ancient Greece by Aristotle, who described this scientific field as the art of measurements for precise distribution of the Earth's surface. During the ancient times, Geodesy and theoretical Geometry were considered totally irrelevant scientific fields due to the fact that Geodesy was combining measurements, calculations and practical application of the extracted results on the field. Yes, the greeks were discussing the correlation between different scientific fields 2400 years ago.
It is actually back then when the first geodetic projects were successfully completed. Inevitably, the very first theories about the Earth's shape and size were established, leading to scientific debates which fueled further research in pursuit of the truth. All of a sudden, people started getting increasingly interested in holding discussions about the Universe and the orbital motions of celestial bodies observed in the night sky. This induced the need for the development of methods that would enable observers to track such motions and develop ways of defining and therefore being able to predict their course.

Image Source: pixabay.com
Eratosthenes (276BC - 194BC) is considered as the Father of Geodesy as a scientific field with nowadays' much more complicated meaning. He was the first one to ever calculate the size of the Earth by processing geodetic and astronomical observations and utilizing basic geometry knowledge. Wanna know what he actually did? Okay then... Eratosthenes was a smart guy. What makes him smarter than the average person was his ability to observe and notice. He noticed that the shadows casted by a pole in Alexandria and a well in Syene during the same time of the day had a slight difference in angle.
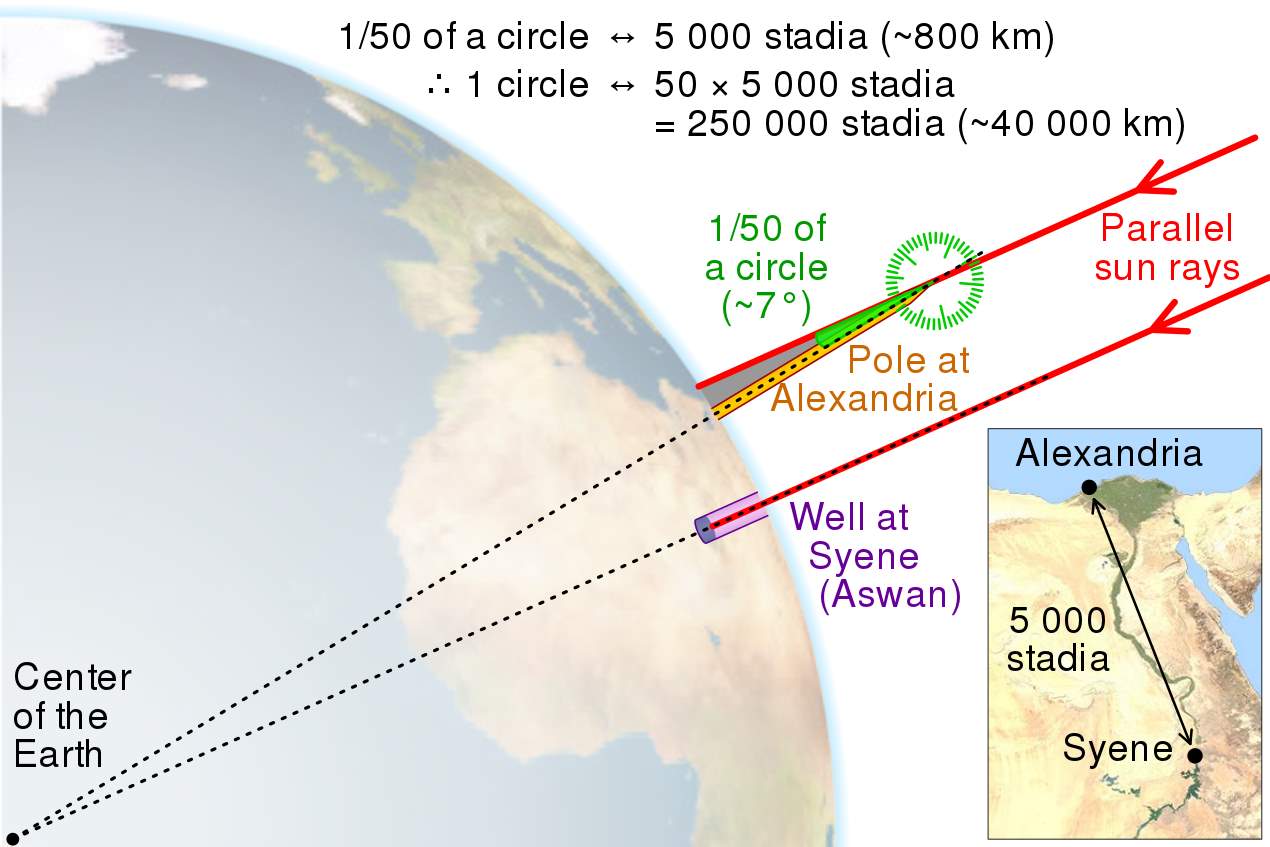
Eratosthenes Calculation of Earth's Circumference. / Image Source: ourplnt.com
He measured the exact distance between those two points and taking for granted that the Earth is not flat (different shadow angles) he assumed that those two points are located on the same arc of a circle with a radius that is equivalent to the Earth's radius. It was then obvious that the difference in angle of the shadows casted by those two different objects situated on different points of the Earth's surface was the same as the central angle of the arc, and therefore by measuring the exact distance between the pole in Alexandria and the well in Syene he could calculate the Earth's circumference. By utilizing basic maths and geometry he then managed to calculate the Earth's radius as well. And he did so with astonishing precision. Are you with me?
During the last couple of centuries and especially by the end of the 17th century the field of Geodesy was enriched with information from various scientific fields, as a result of development and growth regarding science in general. Geodesy as a field of research started shaping its objective according to the people's needs and rights.
Image Source: pixabay.com
Objective
This specific scientific field's purpose of answering all sorts of questions regarding entities' situation, location and motion is fulfilled with the precise calculation of coordinates in specific reference systems. Those questions do have an increasingly significant interest these days, as modern reference and satellite systems along with technical information provided by geographic information systems make it feasible to reach even more precise conclusions and give accurate answers. Information nowadays can be stored, processed, evaluated and distributed much more efficiently and therefore can provide grounds for quality public constructions, concluded with safety and precision. The development of advanced geodetic methods serves the purpose of designing and constructing quality infrastructure regarding transportation, energy and communications.
It's pretty obvious by now that Geodesy combines three basically different but yet relevant fields:
- Geometry : Observations, measurements and calculations are utilized in order to define coordinates which will help produce topographic and hydrographic mappings. Those mappings make it a lot easier to precisely and effectively study a problem and therefore plan and design a solution. Motion and distortion observations of the Earth's crust give out essential information regarding safety in public constructions. Furthermore, geometry plays an important role in establishing international satellite systems accurately which serve navigation purposes.Global satellite systems allow engineers to observe the Earth's motion in detail. This fact makes it easier for engineers to study the Earth's gravitational field, which leads us to our next field.
Geometry./ Image Source: pixabay.com
Gravitational Field : Defining the outer gravitational field of the Earth and the way it affects human measurements and reference systems, makes it possible to determine the Geoid and map its shape. The Geoid is a surface of equivalent gravitational force, which resembles the shape of the oceans being overextended beneath the Earth's surface. The better we know gravity, the easier it gets to define the Geoid's shape, which in return results in more rigorous altitude estimations. Moreover, advanced knowledge of the nature of gravity plays an important role in surveying engineering due to the fact that most classic topographic instruments are directly related with the vertical direction and all angle measurements are affected by any sort of miss.

Gravitational Field./ Image Source: pixabay.comReference Systems : Just like the Earth's spin's parameters, establishing narrow and strict reference systems is extremely significant regarding the accomplishment of desired precision. All measurements and coordinates must necessarily refer to the same system, that's why there is a need for the definition and creation of appropriate reference systems that are relevant to both the Earth's surface and outer space. Reference systems are often established in relation to the direction of the North pole. The system's starting point is frequently placed on the 1st Meridian, however this is highly relevant to geography.
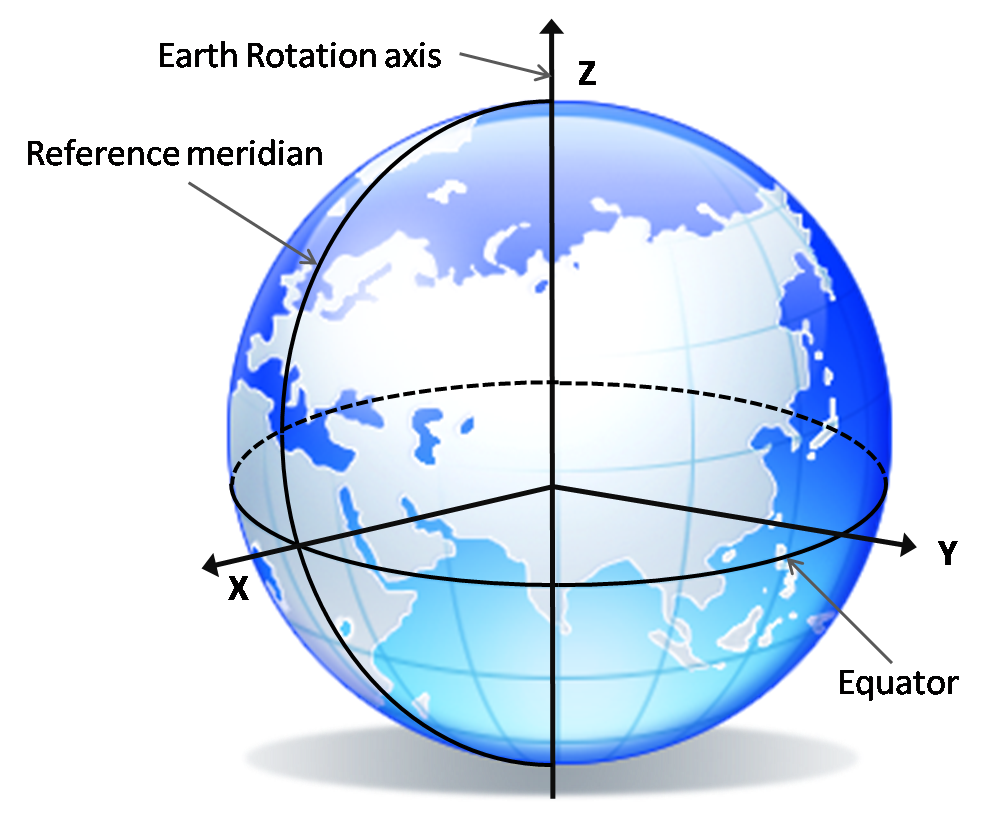
Geodetic Reference System./ Image Source: gnss.be
All three components mentioned above cannot be totally distinguished nowadays, a fact that is easily proven with the utilization of modern satellite systems. In those systems, the calculation of coordinates demands knowledge of the artificial satellites' orbits, gravitational field parameters as well as various parameters describing the Earth's spin. Geodesy as a scientific field can be divided into different technical categories for educational purposes, by emphasizing on different geometric methods of calculation of coordinates. Technological development implemented growth in various scientific fields which are related to Geodesy, and thus contributed to the design and creation of digital instruments which assisted engineers in reaching better conclusions and practically using any corollaries reached. Are you tired yet?
Geodesy is one of the oldest geosciences, like geophysics, geology and geodynamics, however it comes with a higher difficulty level in terms of comprehension for the average person. That is due to the order of magnitude of the quantities measured and parameters involved in geodetic problems, regardless of a person's level of knowledge of maths and physics. Imagination is required! Distances can be too huge for the human mind. Let's just mention that the Earth's radius is approximately 6371 km, the Moon has a radius of roughly 1738 km and the Sun's radius is 695 000 km. The distance from the Equator to the North pole on the Earth's surface is around 10 000 km, while the Earth's mass is about 6e24 kg (6 x 10^24 kg). The moon has a mass of 7.4e22 kg (7.4 x 10^22 kg) and the Sun's mass is around 2e30kg (2 x 10^30 kg). The distance from our lovely green planet to the moon is 384 000 km, while we would need to travel approximately 150 000 000 km to reach the Sun. Just saying.
GPS satellites orbit at an altitude of 20 000 km, however the satellite signals need less than 0.07 seconds to reach our devices on Earth. In an attempt to test your patience, I will proceed to mention how the Earth's angular velocity is approximately 7.292e-05 rad/s (7.292 x 10^-5 rad/s), the product of the gravitational constant and the Earth's mass is roughly 398600e09 m^3/s^2 (398600 x 10^9 m^3/s^2) and the ellipsoid plummet is about 1/300. We should always keep in mind that high precision in all calculations is demanded, especially in cases of extreme accuracy where measurements consist of large numbers of decimal digits. There are occasions in which errors within the first 14 - 16 decimal points are unacceptable.

GNSS GPS Equipment./ Image Source: pixabay.com
Engineering Hacks in Geodesy
Surveying Engineers use control points as constant points which are points of known geodetic coordinates. That basically means that those points location is given, and thus with the utilization of accurate measurements and scientific analysis of the quantities measured it is possible to define the coordinates of other points on the Earth's surface. Distances and angles from control points to target points are measured, the measurements are then processed and corrected and that way engineers create third dimensional models. This is basically the way maps are built. Just like a structure demands strong foundations, third dimensional models induce a need for solid datums. The geodetic datum is just a mathematical term used to describe a geometric entity, however it's equally important with the structure's foundations and therefore needs to be compatible with the precision demanded.
Datums can be great tools but demand great attention and caution. If a datum fails to meet the desired expectations regarding precision then the consequences might be severe. There might be loss of life in horrific accidents in the construction of tunnels or dams or other sorts of public constructions. The unfortunate disadvantage of datums is that just like Geodesy, it is a concept that's quite difficult to wrap one's head around. That's of course because the datum is not a visible entity. Imagination is required. As a result, the datum's precision is perceived as a secondary concern and therefore governments and corporations aren't interested in investing in the creation of perfect datums at all. Ironically enough, the cost of not investing in datums is definitely bigger in the long term, as multiple problems in different constructions will occur simultaneously. All advanced countries of the western world administer their own meticulous and rigid national geodetic reference system.
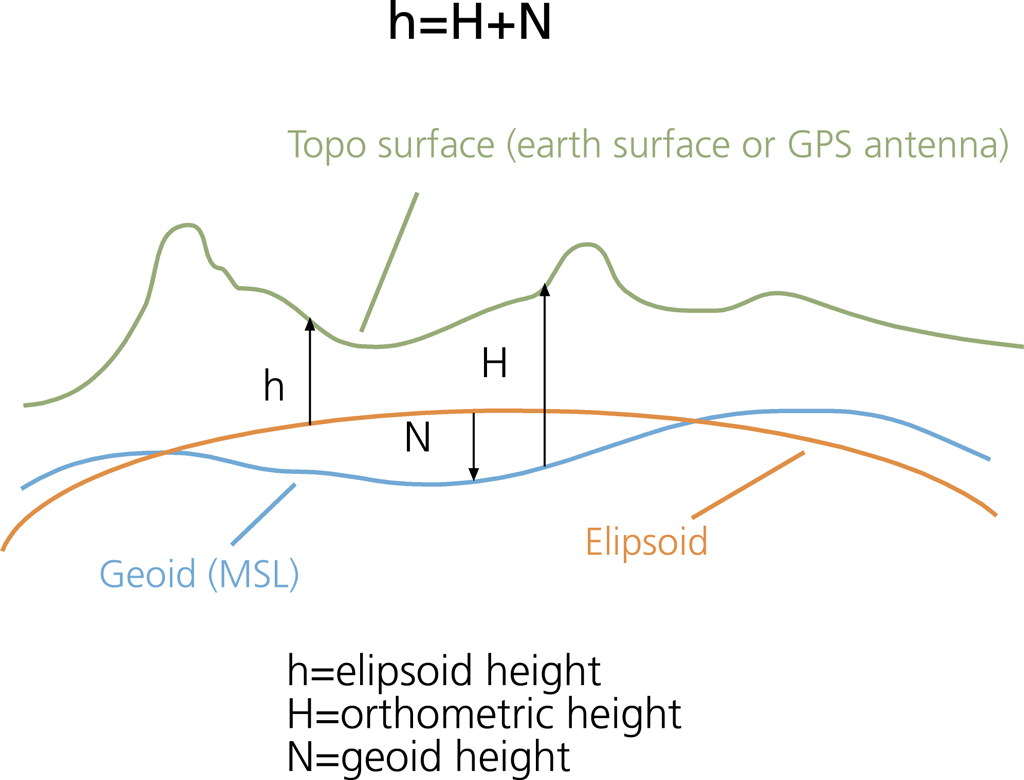
Ellipsoid, Orthometric & Geoid Height./ Image Source: esri.com
The coordinates of control points are given as mentioned above, after being calculated by analyzing processing and correcting measurements (classic/digital instruments - satellites) through the creation and solution of geodetic networks. Geometric Geodesy is evolving rapidly and as a result all classic geodetic and topographic methodologies are changing dramatically and becoming obsolete successively since the late 2000s. For instance nowadays it's possible to track the location of targets even in cases where no visibility is granted or bad weather conditions are making things worse. Furthermore, observations and measurements can be made during the night as well, even between points at distances of hundreds of kilometers. Technology is evolving dramatically and this is affecting Geodesy as well, with advanced equipment, instruments and computers which can provide solutions even to the hardest problems.
Hope you made it till this point! I will probably create a trilogy regarding this Introduction to Geodesy in order to make it less boring than it might sound and more fun for the steemnerds. Follow me at your own risk, these posts will start getting too nerdy. I warned you! :)

IMAGE SOURCES:
REFERENCES:
University Textbooks & Lectures:
Eισαγωγή στη Γεωδαισία / Ιntroduction to Geodesy - TELIONI ELISSAVET (National Technical University of Athens, School of Rural and Surveying Engineering course lectures)
Γεωμετρική Γεωδαισία, Εκδόσεις ΖΗΤΗ / Geometric Geodesy, ZHTH publications. - FWTIOU ARISTIDIS (National Technical University of Athens, School of Rural and Surveying Engineering university textbook)
Δορυφορική Γεωδαισία/ Satellite Geodesy - ΜILAS PARASKEVAS (National Technical University of Athens, School of Rural and Surveying Engineering course lectures.)
Aνώτερη Γεωδαισία / Τοp Geodesics - BITHAS ANASTASIOS (National Technical University of Athens, School of Rural & Surveying Engineering course lectures)
Internet Links:


Thank you for your attention!
Hope you enjoyed this post and did learn a thing or two.
Follow me and stay tuned for more engineering blogs.
Highest Regards
@lordneroo
Being A SteemStem Member
If you keep reminding me the university days , I will unfollow you .
Good job , though. :)
I warned everyone :P
Thanks for your kind words!
This is a really awesome and in-depth article on a topic I didn't even know existed :) Thanks for the read!
Thanks for reading and leaving a kind response! I will be making more posts regarding this issue! ;)
a good post, I've read it in detail. my knowledge of geodesy is kuranf, because I am in mechanical engineering. This post gives me my new knowledge.
congratulations.
regard from Mech Eng Unimal Aceh Indonesia
Hey there, thanks for taking the time to read and leave a kind response. ;)
Mechanical Engineering is such an interesting field! Hope you share your knowledge with us here on Steemit!
Kind Regards
Quiet informative my friend. Learnt a lot from your post👍
Thanks for dropping by ;)
Geodecy must be sad that its siblings geology and geophysics get all the attention!
Lol! Just saw your comment! Epic!