Today's Theme HISTORY OF AGRICULTURE
There are numerous choices for those wishing to examine a horticulture based degree because of the idea of the expansiveness of the subject. With the investigation of current ideas, for example, GM, natural change, manageability and additionally the business and logical sides, potential understudies are ruined for decision for work and degree alternatives. Much of the time, a college degree ought to be sufficient to discover great business and understudies in the US taking a college degree have a particular favorable position over different nations because of the measure of the business here. There remains a lack of horticulture graduates as well, so it ought not be hard to discover profitable business. For those going into agribusiness as a profession, once you have picked this as a noteworthy it is astute to pick such related subjects as science, sustenance, science and any natural alternatives your school or college may offer. With a college degree, you can oversee cultivates and farms, fisheries and timberlands, work with soil protection or numerous other "outside" choices.
For investigate degrees, for instance those identified with the earth, hereditary qualities and particular rearing, farming building and innovation, a propelled degree is a reasonable prerequisite - commonly a MS in the event that you need to center around lab work as opposed to handle work.
source
Take in more about the numerous professions in horticulture.
Horticulture is characterized as the development and misuse of creatures, plants (counting growths) and different types of natural life for human utilize including nourishment, fiber, prescriptions, fuel and whatever else. It is, and has been since there was an agrarian market, one of the biggest businesses of individuals; in the USA today, farming speaks to 20% of the US economy . Before sorted out agribusiness, it is trusted that the nourishment supply could accommodate only 4 million individuals all around .
Indeed, even as innovation changes, farming adjusts and would never end up out of date - even in a period when it may possibly be endlessly not quite the same as what it may have been at the beginning of horticulture. All things considered, we are continually going to need to build the quantity of yields we develop for sustenance and for apparel, colors and oils, seed advancement and designing to adapt to the developing needs of the total populace, regardless of whether the photo isn't as depressing as the most preservationist concerns may recommend . Today, farming is as much a science as a workmanship. With a need to adapt to the developing needs of the planet's populace, and to discover approaches to continue delivering nourishment and different harvests as we venture into peripheral scenes, and adjust to an evolving atmosphere, changes in agribusiness hones, sustenance innovation and bio innovation will keep on being a major piece of human progress.
The History of Agriculture
Ancient times
For a large portion of our reality, people were seeker gatherers. This implies individuals carried on with a traveling way of life, moving with the seasons to take after the nourishment supply. As the icy masses withdrew and vegetation examples and development zones changed accordingly, it implied that the need to move so frequently turned out to be somewhat less fundamental - however without a doubt the way of life carried on for a huge number of years as individuals tried to boost their asset obtaining (4, p574-5). Seeker gatherer social orders would have known which crops were best to abuse with each season.
The "seeker gatherer" moniker can be a misnomer as it is trusted today that roaming groups didn't all of a sudden simply choose one day to quit moving and to set up changeless settlements - however the purposes behind the progress have been investigated in extraordinary arrangement is as yet not settled (4, p561-3). It is likely that some level of semi-roaming way of life created where individuals basically set up camps for quite a while at once, cordoning off regions of wild products that had the most copious assets (5, p146). It is additionally likely that they had groups of domesticated animals that they took with them wherever they moved, keeping them secure to misuse for drain, meat, hide and different assets. The need to ensure stores of nourishment for the following season may likewise have had an influence.
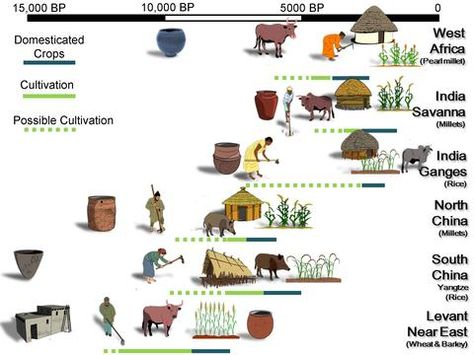
Archeologists and scientistss have followed the birthplaces of cultivating to around 10,000 years prior, to some place in the Indus Valley, and potentially as a different improvement in China along the Yangtze River (6). It is realized that people initially trained yields and later animals in sufficiently awesome numbers to perceive the indications of ponder misuse (5, p141-3).
Early Civilization
Early human advancement can be viewed as a blast time in horticultural science and innovation. Around 5500 BC (7, p26-28), the Sumerian human advancement of the Middle East and other early pre Greco-Roman developments comprehended the requirement for a particular horticultural workforce for their social orders to flourish. It is in this period that we saw the creation of water system in addition to other things, and this particular workforce, and spotlight on agrarian innovation permitted the advancement of the main urban areas. Thus, these drove the principal composed laws and prompted the advancement of complex social orders. Starting here of view, horticulture drives civilisation: including religious practices, social mentalities and legitimate codes.
Old Egypt had a standout amongst the most complex social orders of the antiquated world before the ascent of the Greek development, and it was for the most part because of their agrarian framework (7, p27-8). The River Nile depended intensely on the seasons and every year, the stream would surge its banks and part of the encompassing field (called The Inundation). Their development and without a doubt their religious structure (8), was worked around the nurturing idea of the River Nile and the kingdom's substantial dependence on the waterway and delta framework . A large portion of Egypt was and still is desert with a couple of key desert gardens, which implies that the farming focused on a little piece of the nation.
The Greeks and Romans took quite a bit of their rural innovation from different civic establishments with which they had contact - most outstandingly those of the old Near East, for example, Mesopotamia, through Sumeria. From Egypt, those social orders took coordinate impact once the nation was vanquished by Alexander the Great and later by the Roman Republic. It was here at the introduction of present day human advancement that we saw genuine extensive scale creature and plant agribusiness . Innovation might not have propelled an extraordinary arrangement, but rather the procedures made agribusiness sufficiently proficient to support the domain's vast urban communities, making it a fundamental industry.
Ahead of schedule to Modern Civilization
The Middle East kept on observing much development in the farming businesses, something that students of history allude to as The Arab Agricultural Revolution . This was on account of the decent variety of the nearby geographies, the harvests developed in the Middle East and Indus Valley that European social orders desired, and later went about as an exchange connect between Far East and Europe .
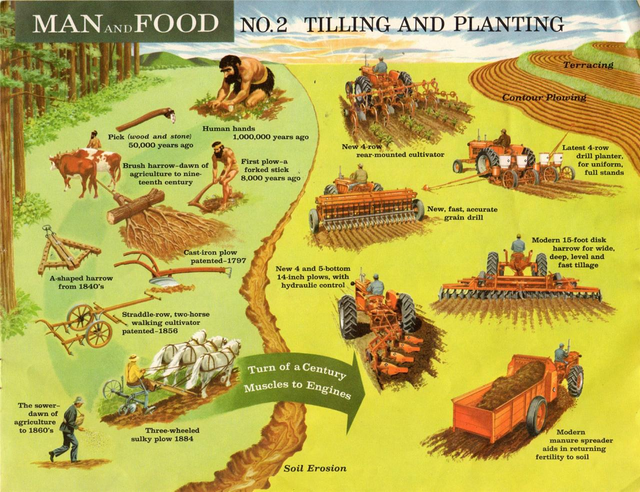
In Europe, minimal changed before the ascent of the kingdoms around the eleventh century when the Church wound up real landholders and brokers, pioneers, instructors and held both fleeting and profound forces. The frameworks prompted through feudalism, regardless of whether common rulers or church possessions, tried to enhance yields with the developing populace, and normally we saw noteworthy innovative advances in this period as well . It was a time of gigantic specific cross-reproducing, especially in creature domesticated animals, and frameworks of association. In a few zones of Europe, we can see the leftovers of the horticultural framework today as medieval edge and wrinkle strip cultivating. It is because of the cloisters of Europe that we see propels into what we call "negligible scenes" - zones where crops don't develop in awesome numbers the we see farming designing on an uncommon scale. Floodplains were depleted, wild forests changed over to fields and bracken cleared for field, zones with low fruitfulness were changed over or modified to make appropriate utilization of them ; for instance, grain develops well on salty soil, making it perfect to develop on floodplains. Current rural practices saw its last present day advancement in the sixteenth century when agriculturists thought of harvest turn - the possibility that one could expand yields by exchanging land use around consistently all together not to debilitate the dirt. One year the field would have crops planted, the next year it would be utilized for domesticated animals and the third it would be kept decrepit . In spite of the fact that prior social orders had utilized it to a specific degree, just in the sixteenth century was the strategy culminated.
The Americas
Mass farming practices were not especially show in North America until the entry of the European pioneers. It's absolutely not genuine that the Native Americans had no farming; to be sure, there is prove for some constrained agrarian practices yet it was not general over the clans. Some were totally traveling and some were generally static - these were not land either, a few clans in the east had totally trained products. When we take a gander at the south-western states, especially Arizona and New Mexico, we see farming on a mechanical scale - particularly the development of maize trims that were presented from current Mexico, whatever is left of Mesoamerica and past. It is likely that farming went toward the North America moderately late, maybe in the vicinity of 2500 and 2000 BC and we see it broadly with so much human advancements as the Hohokam, the Anasazi and antiquated Pueblos , conceivably creating in Mesoamerica around 6000 BC with the training of maize.
In Mesoamerica and South America, with the Inca, the Maya, Olmecs and the Aztecs, generally early improvement of farming allowed the working of gigantic urban communities that awed the European colonizers; it was immediately distinguished that these civic establishments had a great horticulture construct economy that remained in light of a standard with Europe, testing what was then comprehended about the advancement of development. In Mesoamerica it was corn and in South America it was the modest potato - today the staple harvest of a great many people in the western world, alongside coca and the training of creature species, for example, llama and alpaca.
Present day Farming
Present day cultivating started around the eighteenth century in what is for the most part alluded to as "The British Agricultural Revolution" when a few advances and changes were made to cultivating in a short space of time that saw gigantic increments in yield and a more proficient process. The three field trim revolution framework was supplanted with a four field framework and clearing nook acts directed land administration, particular cross-reproducing started on a modern scale to build edit measure and additionally yields making a few cultivars simultaneously. Creature cultivation likewise enhanced, prompting a more noteworthy surplus than had been allowable under the old framework. It is said that these progressions allowed the modern upset and much more noteworthy centralization of urban improvement, powering the domain. In what capacity? More harvests for less laborers, better strategies for keeping and supplanting supplements in the dirt implied that more individuals could work in industry. At the point when the Corn Laws in England were canceled, it started the worldwide nourishment economy; about a similar time, Charles Darwin's Theory of Evolution put horticulture on the cutting edge way of a science as we comprehended the advancement of harvests.
The following changes would not be until the War Years when the military forces created (and required with proportioning) serious cultivating; it has been a divine being send, and since 1970, worldwide grain generation has quadrupled . New plastics and additionally the improvement of nitrates permitted significantly more prominent yields again and it has through this framework, now set up for just about a century, enabled more noteworthy access to nourishment substantially more inexpensively. However for a few, the earth has paid a value that some rural researchers have attempted to address.
The Ecological Age
"Maintainability" is the trendy expression today as we hope to adjust a few clashing needs - to secure the earth and to prompt practices that ensures it while accommodating the developing needs without bounds populace development. Today, our sustenance supply sustains 7 billion individuals and there is sufficiently still surplus for all the more going ahead . We know however that a portion of these practices have adversy affected the land. Excessively numerous trees are being chopped down to clear a path for horticultural land (domesticated animals and harvests), and soils are getting to be depleted rapidly while pulverizing biological communities.
There have been inquiries concerning the utilization of a few herbicides and pesticides and the most recent couple of decades have seen numerous destructive substances restricted in North America and the EU. We are as yet concurring on worldwide gauges and endeavoring to reclassify the parameters of what is horticulturally and environmentally solid, taking into account our product needs while not harming it for who and what is to come. Farming innovation may conceivably be nearly another insurgency as biotech moves to the bleeding edge of rural science.
Sources
- http://www.maine.gov/doe/agriculture/
- http://www.futurist.com/articles-archive/future-of-agriculture/
- http://pages.ucsd.edu/~dkjordan/arch/neolithic/Neo1-AgRev.html
- http://classes.uleth.ca/200701/anth1000b/foraging%20to%20farming.pdf
- http://dash.harvard.edu/bitstream/handle/1/12211496/S0959774300001815a%202.pdf?sequence=2
- http://lib.gig.ac.cn/local/nature/449,459.PDF
- http://pleasanton.k12.ca.us/avhsweb/murphyc/web/apworld/summer/farm.pdf
- http://fathom.lib.uchicago.edu/1/777777190168/
- http://www.jstor.org/stable/263080?seq=1#page_scan_tab_contents
- http://www.jstor.org/discover/10.2307/2116954?sid=21105910120473& uid=3738032&uid=2&uid=4


We @farms are pleased with this post and find it informative and educative....
Resteem
(to be a part of this community; ensure to always use #farms and #steemchurch for agricultural related post)
SteemChurch Farm ( @FARMS)
Great write up. Indeed it was so amazing reading through it . great to hear from you.
Thanks for sharing.