All About Chlamydia - Part 3
How to Know You Have Contacted Chlamydia
For men

• itching and burning sensation around the penis opening
• Testicular pain and swelling
• Abnormal excretion (thick, yellow-white, milky or watery) of the penis
• Damaged or reduced semen
• Pain from reactive arthritis in the joints, eyes and urethra
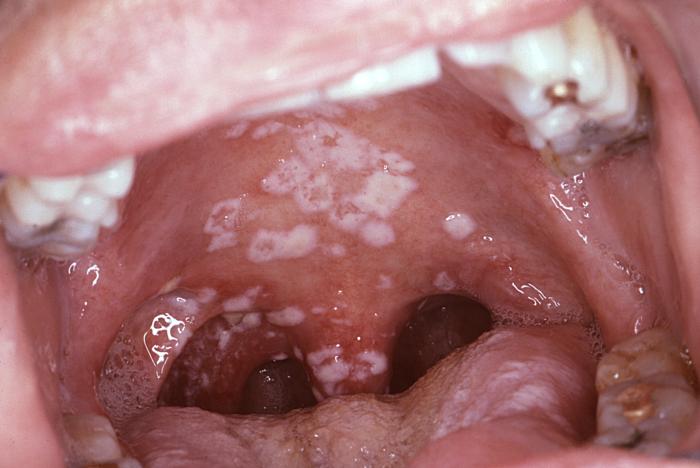
• Sore throat, causing discomfort while swallowing
• Inflammation, tenderness and pain in and around the testicles.
For women
• Abnormal vaginal discharge that may smell
• Pain during urination caused from a cervical infection (cervicitis)
• Burning sensation while urinating and frequent urinating.
• Bleeding between menstrual cycles
• Unusually heavy periods
• Lower back pain
• Nausea
• Abdominal pain with fever
• Pain and bleeding during sex
• Pelvic Inflammation (PID)
• A painful feeling around the hips
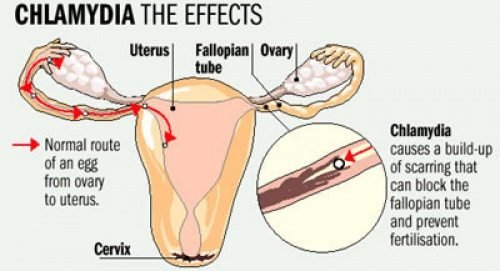
• Infertility resulting from damage to the hairs lining of the fallopian tubes, which help guide, the egg from the ovaries to the womb. This damage leads to scarring, causing the tubes to become blocked and unable to fertilize an egg.
• Itching and burning feeling around the vagina
For both men and women
• Pain while urinating
• Rectal pain
• Discharge or bleeding from the anus
• Diarrhea in severe cases
• Swelling in or around your anus
• Cough and high fever
• Lymph nodes swollen in the neck
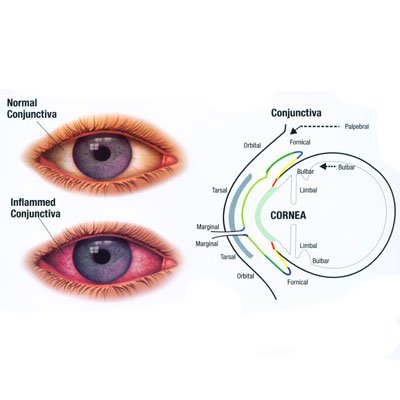
• Vision problems that can lead to blindness
• Redness, itching, eyelid discharge and inflammation of the eyes
For pregnant women
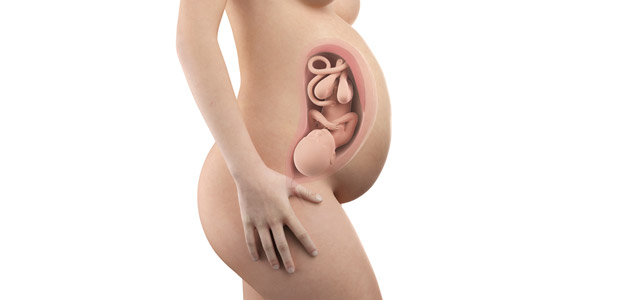
• Growth of the fetus outside the uterus and in the fallopian tubes (ectopic pregnancy).
• Early contractions, leading to premature birth
• Reduced fetus growth, resulting in very low birth weight
• Miscarriages
• Death of infant at birth
• Uterine infections
For Infants
• Infection of the eyes: Babies develop conjunctivitis, discharge of pus from the eye, redness and swelling of the eyelid, in severe cases of blindness.
• Pneumonia / respiratory infection, characterized by rapid breathing, stuffy nose and cough
• Respiratory failure if pneumonia is not treated.
Tests to determine if Chlamydia has been contacted
The test can be done through the following methods:
• A urine sample is sent to a competent laboratory for analysis to help diagnose if the patient has chlamydia
• The area that could be infected is cleaned with a cotton swab and tested to detect the presence of the bacteria.
• A blood sample is collected and tested for antibodies against chlamydia. Chlamydia is not a blood-borne disease or infection, so this test cannot be used for diagnosis. However, it is used to tell whether or not the individual has had the bacteria in the past.
Can chlamydia be treated?
The answer is yes!
Once treated can there be a reinfection of the chlamydia bacteria?
Some diseases cause some kind of immunity against future reinfections.
This is not the case with chlamydia. If you have sex with an infected person, you can be re-infected with the Chlamydia bacteria, even if you have just finished the treatment.
It is recommended that both partners be treated at the same time and resist sexual intercourse until treatment is complete to prevent relapse or reinfection.