How Do Benzodiazepines Work?
One of the most popular classes of drugs in the United States is benzodiazepines, which include Xanax (alprazolam), Valium (diazepam), Ativan (lorazepam), and Klonopin (clonazepam). These are all drugs you’ve probably heard of, particularly Xanax, which physicians prescribe for all types of anxiety-related conditions.
The most popular benzodiazepine in the United States: Xanax. WebMD
Benzodiazepines are anxiolytic drugs, which means they act to reduce anxiety. As expected, they are often employed in the treatment of anxiety, depression, and panic disorders. However, benzodiazepines are a versatile drug, and also have significant uses as anticonvulsants, sedatives, and muscle relaxants. They can be used to help people recover from alcohol addiction, deal with restless leg syndrome, or cope with chemotherapy-associated nausea.
I think most people understand that benzodiazepines have a tranquilizing, or calming, effect on the nervous system. This is why they can be used to treat seizures, panic attacks, insomnia, and severe anxiety: they reduce activity in the brain, and act to dampen the physiological symptoms of these disorders.
But how do they work in the brain?
Benzodiazepines act on neurons, which are the chief signaling cells in your nervous system. When activated, neurons release signals in the form of neurotransmitters, which bind to their receptors on neighboring neurons.
There are several types of neurotransmitters. For the sake of benzodiazepines, you only need to know about one: GABA. GABA stands for gamma-aminobutyric acid, and is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
There are several types of receptors for GABA, but to keep it simple we will focus on the type A receptor. The type A receptor is a large multi-protein complex, forming a channel that allows chloride ions to move from outside to inside of the cell, and vice versa.
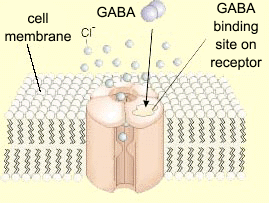
The ionotropic GABA receptor. The Brain from Top to Bottom
When GABA binds to it’s type A receptor on an adjacent neuron, it typically increases flow of negatively charged chloride ions into the cell. This changes the intracellular charge relative to the charge of the extracellular environment, making it more difficult to activate the cell. The scientific term for this state is hyperpolarization.
Why is GABA important, and why would you want to prevent neuronal activity? One thing to understand about the brain is that there are tons of excitatory neuronal inputs. GABA modulates these signals, so that for a given neuron, it’s activity is within a specific range. (Of course, this range is specific for the type of neuron and it’s location within the brain, which I won’t delve into here!)
So, back to benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines act as positive allosteric modulators of the GABA-type A receptor. This means that benzodiazepines bind and induce a small but important conformational change in the GABA-type A receptor. When GABA binds this altered receptor, an increased concentration of chloride ions flows into the neuron, meaning that GABA induces greater hyperpolarization of the cell. Although the binding of GABA itself is not altered, the outcome of GABA binding is increased. Overall, the neurons are more inhibited in the presence of benzodiazepines.
That’s basically how benzodiazepines work. They don't act by directly inhibiting other neurotransmitters; in fact, they don't even directly interact with GABA. It's all through the GABA-receptor.
This is a very simplistic view, so for those neuroscientists pulling their hair out at my lack of detail: my apologies. I’ve been asked this question before, and I wanted to develop a simple go-to answer.
My next question is: why are benzodiazepines such an addictive class of drugs? (I do have some ideas... for next time!)
Hmm, they can be dangerous drugs. Or else why do they sometimes cause suicidal thoughts?
Yes, they can definitely be dangerous- I will cover in my next post!
Congratulations @eweinzap! You received a personal award!
Click here to view your Board
Congratulations @eweinzap! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!