Pharmaceutical Chemistry - Asymmetric Molecules
An asymmetric molecule is defined as an assembly of optically active molecules formed by chemists, usually by bonding four different atoms or groups of atoms to a carbon atom. This carbon atom to which four different groups are attached is also called an asymmetric carbon atom.
.jpg)
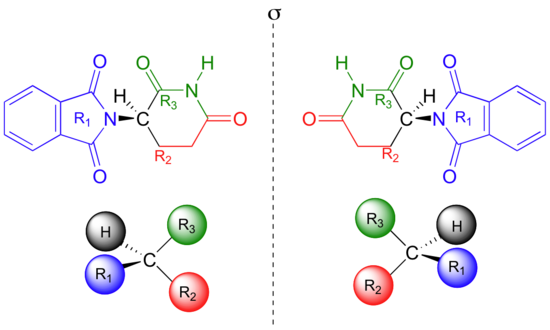
It is possible to explain this situation on the (S) -butan-2-ol molecule. However, there are such molecules that this definition is missing for those molecules. Those molecules are allenes, spiro compounds and anthropic isomers. So how definition should be done? In fact, it is possible to use asymmetric molecules for all of them and it is possible to make a definition which reveals the concept of enantiomer at the same time. "Molecules that overlap with the mirror image" can be defined as asymmetric molecules. Also, the pair of molecules that do not overlap each other with the mirror image is the enantiomer pair of each other that is the stereoisomer.
It is possible to encounter natural asymmetric molecules in the structure of living beings. For example, the quinine molecule in the henna plant, amino acids, vitamins and enzymes found in the human body are important examples for natural asymmetric molecules.
Many metabolic reactions that occur in living organisms occur via enzymes known as biological catalysts. The presence of enzymes with asymmetric structure also reveals the reaction that occurs in our bodies and the selectivity in synthesized molecules. In other words, it is the synthesis of asymmetric molecules through enzymes in our body. These selective functions maintain metabolic activity in the body.
Since only one of the enantiomers of a substance is entangled in asymmetric syntheses, asymmetric oligomers are quite large in both the synthetic chemistry and the medical sector. Let's explain it on a sample. Thalidomide, which is used with the aim of preventing bulanitis especially in pregnant women, has been used for many years. However, besides its therapeutic effect it has been determined poison effect by many researchers.
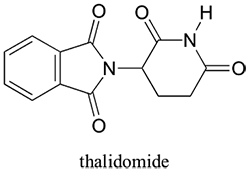
As I mentioned in the example, asymmetric syntheses have a considerable place especially in the pharmaceutical industry. Even this simple matter reveals the fine line between the life and death of the synthesis and use of only one of the enantiomers. It is known that each enantiomer in the structure of the drug substance has a different effect. Preparation of drugs in high enantiomeric purity is very important for stereoselective synthesis. Furthermore, the synthesis of enantiomers in high purity is an important problem.
References
- Solomons, W.G.T., Fryhle, C.B., Organic Chemistry, Wiley, 2011, s.210.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chirality
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3614593/
img credz: pixabay.com
Nice, you got a 3.0% @minnowbooster upgoat, thanks to @kedi
Want a boost? Minnowbooster's got your back!
The @OriginalWorks bot has determined this post by @kedi to be original material and upvoted(1.5%) it!
To call @OriginalWorks, simply reply to any post with @originalworks or !originalworks in your message!
Thalidomide is a classic example. The correct enantiomer is still sold, but many are too afraid to buy it.
Nice post and helpful well done my friend
Congratulations @kedi, this post is the eighth most rewarded post (based on pending payouts) in the last 12 hours written by a User account holder (accounts that hold between 0.1 and 1.0 Mega Vests). The total number of posts by User account holders during this period was 2082 and the total pending payments to posts in this category was $2133.89. To see the full list of highest paid posts across all accounts categories, click here.
If you do not wish to receive these messages in future, please reply stop to this comment.