A BRIEF EXPLANATION ABOUT THE WORD 'VIRUS' AND HOW TO PREVENT THE DISEASE TRANSMISSION
Good day my beloved people of steem, I will like to talk about or lecture us briefly on the term 'Virus'. Yeah, virus is a living thing, too small to be seen without a microscope, that causes infectious disease in people, animals and plants. In order words, we say that virus is a microscopic organism which cannot be seen by an ordinary microscope but with an electron microscope. Virus does not have a cell structure, but is just made up of a coiled strand of nucleic acid, that is, Ribonuclei acid (RNA) or Deoxyribonuclei acid (DNA) enclosed within a protein coat. Virus is seen as being on the borderline between living cells, it forms crystals and becomes non-living but within the cell, it replicated (reproduced) and becomes living organism.
Examples of virus illness range from the common cold, which ca be caused by one of the rhinoviruses, to AIDS, which is caused by HIV. Viruses may contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material. Herpes simplex virus and the hepatitis B virus are DNA viruses. RNA viruses have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase that permits the usual sequence of DNA-to-RNA to be reversed so that the virus came an make a DNA version of itself. RNA viruses include HIV and hepatitis C virus
Researchers have grouped viruses together into several major families, based on other sharp, behavior, and other characteristics. These include the herpes-viruses, adenoviruses, papovaviruses (including the papillomaviruses), hepadnaviruses, poxviruses, and parvoviruses, among the DNA viruses. On the RNA viruses side, major families include the picorna-viruses (including the rhinoviruses), calciviruses, paramyxoviruses, orthomyxoviruses, rhadboviruses, filoviruses and retro viruses. There are dozens of smaller virus families within these mayor classification. Many viruses are host specific, capable of infecting and causing disease in humans or specific animal only.

Yeah, virus is one of the challenges that human beings encounter,why because it causes destruction to the human immune destruction. And according to science one can contact virus in many physiological event;
Direct contact
Infectious diseases are often spread through direct contact. Types of direct contact include:
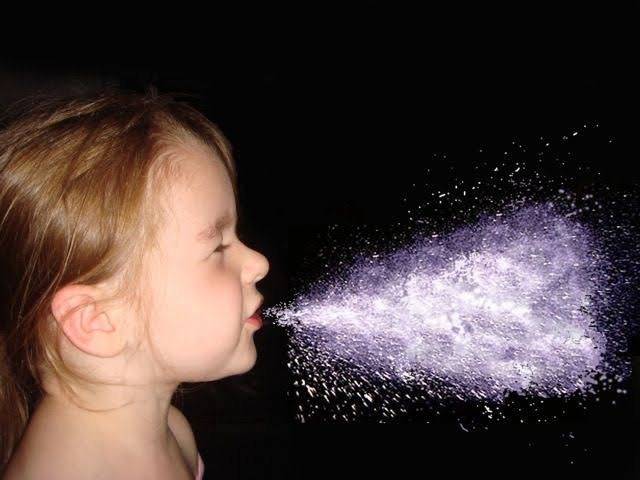

- Person-to-person contact
Infectious diseases are commonly transmitted through direct person-to-person contact. Transmission occurs when an infected person touches or exchanges body fluids with someone else. This can happen before an infected person is aware of the illness. Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can be transmitted this way. Pregnant women can also transmit infectious diseases to their unborn children via the placenta. Some STDs, including gonorrhea, can be passed from mother to baby during childbirth.
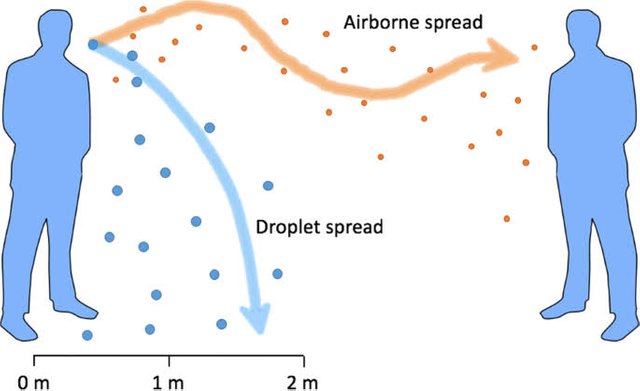
- Droplet spread
The spray of droplets during coughing and sneezing can spread an infectious disease. You can even infect another person through droplets created when you speak. Since droplets fall to the ground within a few feet, this type of transmission requires close proximity.
Indirect contact
Infectious diseases can also be spread indirectly through the air and other mechanisms. For example:
Airborne transmission
Some infectious agents can travel long distances and remain suspended in the air for an extended period of time. You can catch a disease like measles by entering a room after someone with measles has departed.Contaminated objects
Some organisms can live on objects for a short time. If you touch an object, such as a doorknob, soon after an infected person, you might be exposed to infection. Transmission occurs when you touch your mouth, nose, or eyes before thoroughly washing your hands. Germs can also be spread through contaminated blood products and medical supplies.Food and drinking water
Infectious diseases can be transmitted via contaminated food and water. E. coli is often transmitted through improperly handled produce or undercooked meat. Improperly canned foods can create an environment ripe for Clostridium botulinum, which can lead to botulism.Animal-to-person contact
Some infectious diseases can be transmitted from an animal to a person. This can happen when an infected animal bites or scratches you or when you handle animal waste. The Toxoplasma gondii parasite can be found in cat feces. Pregnant women and people with compromised immune systems should take extra care (disposable gloves and good hand washing) when changing cat litter, or avoid it altogether.Animal reservoirs
Animal-to-animal disease transmission can sometimes transfer to humans. Zoonosis occurs when diseases are transferred from animals to people. Zoonotic diseases include:
anthrax (from sheep)
rabies (from rodents and other mammals)
West Nile virus (from birds)
plague (from rodents)Insect bites (vector-borne disease)
Some zoonotic infectious agents are transmitted by insects, especially those that suck blood. These include mosquitos, fleas, and ticks. The insects become infected when they feed on infected hosts, such as birds, animals, and humans. The disease is then transmitted when the insect bites a new host. Malaria, West Nile virus, and Lyme disease are all spread this way.Environmental reservoirs
Soil, water, and vegetation containing infectious organisms can also be transferred to people. Hookworm, for example, is transmitted through contaminated soil. Legionnaires’ disease is an example of a disease that can be spread by water that supplies cooling towers and evaporative condensers.Illness
Something as simple as touching a doorknob, elevator button, light switch, or another person’s hand increases the likelihood of coming in contact with germs that can make you sick. The good news is that a few simple precautions can prevent some disease transmission. For example, make sure you wash your hands frequently and thoroughly. Use soap and warm water and vigorously rub your hands together for at least 20 seconds. If you can’t wash your hands, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. Washing your hands is the gold standard though!
How to prevent disease transmission
Because infectious diseases can spread through direct or indirect contact, everyone is at risk of illness. You have a higher risk of becoming ill when you’re around sick people or in areas susceptible to germs. If you work in or visit a care center, a day-care center, a hospital, or a doctor’s office, take extra precautions to protect yourself.
Other tips to prevent the spread of disease in areas with germs include:
Personal hygiene
Yeah, wash your hands or use hand sanitizer before handling food and after shaking hands
always wash with soap and water if your hands are visibly soiled
*try to minimize touching your mouth or nose with your hands
*avoid sick people, if possible
*wear disposable gloves to avoid contact with blood and feces
*use disposable gloves when caring for an ill person
cover your mouth when you sneeze and cough and wash your hands afterward
*teach children not to put their hands or objects in their mouths
sanitize toys and changing tablesFoodborne illness
Dangerous organisms can thrive in improperly prepared food. Avoid cross-contamination by keeping raw meats and produce separate. Use different preparation surfaces for raw meats and wash surfaces and utensils thoroughly.
Freeze or refrigerate perishable foods and leftovers promptly. According to the United States Department of Agriculture, you should set your refrigerator to 40°F (4°C) or below and your freezer to 0°F (-18°C) or below. Cook meats to a minimum internal temperature of 145°F (63°C). Cook ground meats to 160°F (71°C) and poultry to 165°F (73°C).
Be careful about sources of food when visiting foreign countries.Insects and animals
When camping or enjoying wooded areas, wear long pants and long sleeves. Use insect repellent and mosquito netting. Don’t touch animals in the wild. Don’t touch sick or dead animals.Vaccinations
Stay up to date on vaccinations, especially when traveling. Don’t forget to keep your pet’s vaccinations current, too.
Vaccinations can drastically reduce your risk of becoming ill with some infectious diseases. If you can avoid a particular disease, you can also prevent the spread of the disease. There are different types of vaccinations, such as those to prevent:
*measles
*mumps
*influenza
*human papillomavirus
*Speak with your doctor to discuss the benefits and risks of these and other vaccinations.
The takeaway
Infectious diseases are caused by types of bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi around us. It’s important to understand how these diseases are transmitted. If you understand the transmission process, you can use this knowledge to protect yourself and help prevent the spread of illnesses.
Please don't use Achievement 1 tag in your general posts...
Okay buddy... Thanks
Pls can we chat on telegram via @kizblizx
Hello bro, try to link your image next time. Your article is a good one