THE EYE
Eye are organ of the visual system.they provide animals with vision.the ability to receive and receive visual details,as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision.Eyes detect light and convert it into electro chemical impulses in neutrons.
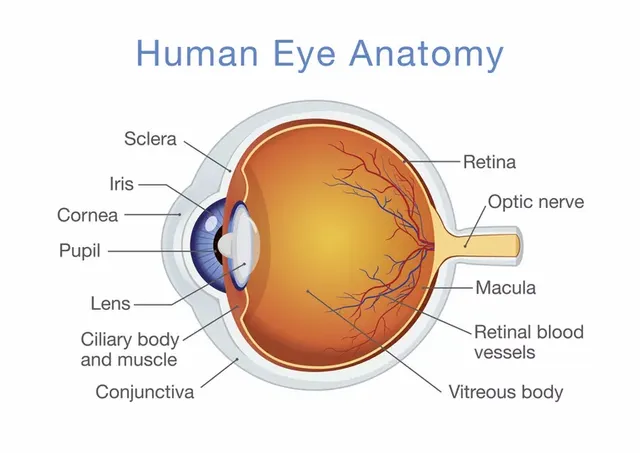
Human eye,in humans specialised sense organ,capable of receiving visual images,which are then carried to the brain cross section of human eye,showing the major part of the eye,including the protective covering of the cornea over to form the eye.
THE EYE PARTS
Conea: this is the front lay of the eye.
Pupil:the pupil is the black dot in the centre of your eye that acts as a gateway for light.
Iris:this part is typically referred to as your eye color.
Lens:the lens is behind the iris and pupil.
Each eye constantly adjucts the amount of light it lets in,focuses on objects far and near and produces continuos images that are instantly transmitted to the brain.The orbit is the bony cavity that contains the eyeball,muscles,nerves and blood vesels,as well as the structure that produces and drain tears.
STRUCTURE OF THE EYE
The structure and function of the eyes are complex,each eye constantly adjusts amount of light.it lets in.
A structure is an arrangement and organizations of interrelated elements in a material object or system,or object or system so organized.
FUNCTIONS OF THE EYE
1,the eye is a sensory organ.it collects light from the invisible world around us andconvert it into nervers impulses.the optic nerves transmits these signals to the brain when forms an image so thereby providing sight.

2,Human eye,specialized sense organ in human that is capable of receiving visual images.
3,the eye receives oxygen through the equeous.it functions is to nourish the conea,iris, and lens by carrying nutrients.
Science, Tech, Math ›
By Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph.D.
Updated December 02, 2019
Members of the animal kingdom use different strategies to detect light and focus it to form images. Human eyes are "camera-type eyes," which means they work like camera lenses focusing light onto film. The cornea and lens of the eye are analogous to the camera lens, while the retina of the eye is like the film.
Key Takeaways: The Human Eye and Vision
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea, iris, pupil, aqueous humor, lens, vitreous humor, retina, and optic nerve.
Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor. The iris controls the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. Light is focused by the lens and goes through the vitreous humor to
Eye Structure and Function
To understand how the eye sees, it helps to know the eye structures and functions:
Cornea: Light enters through the cornea, the transparent outer covering of the eye. The eyeball is rounded, so the cornea acts as a lens. It bends or refracts light.
Aqueous Humor: The fluid beneath the cornea has a composition similar to that of blood plasma. The aqueous humor helps to shape the cornea and provides nourishment to the eye.
Iris and Pupil: Light passes through the cornea and aqueous humor through an opening called the pupil. The size of the pupil is determined by the iris, the contractile ring that is associated with eye color. As the pupil dilates (gets bigger), more light enters the eye.
Lens: While most of the focusing of light is done by the cornea, the lens allows the eye to focus on either near or distant objects. Ciliary muscles surround the lens, relaxing to flatten it to image distant objects and contracting to thicken the lens to image close-up objects.
Vitreous Humor: A certain distance is required to focus light. The vitreous humor is a transparent watery gel that supports the eye and allows for this distance.
Continue Reading Below
The Retina and the Optic Nerve
The coating on the interior back of the eye is called the retina. When light strikes the retina, two types of cells are activated. Rods detect light and dark and help form images under dim conditions. Cones are responsible for color vision. The three types of cones are called red, green, and blue, but each actually detects a range of wavelengths and not these specific colors. When you focus clearly on an object, light strikes a region called the fovea. The fovea is packed with cones and allows sharp vision. Rods outside the fovea are largely responsible for peripheral vision.
Rods and cones convert light into an electric signal that is carried from the optic nerve to the brain. The brain translates nerve impulses to form an image. Three-dimensional information comes from comparing the differences between the images formed by each eye.
Continue Reading Below
Common Vision Problems
The most common vision problems are myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), presbyopia (age-related farsightedness), and astigmatism. Astigmatism results when the curvature of the eye isn't truly spherical, so light is focused unevenly. Myopia and hyperopia occur when the eye is too narrow or too wide to focus light onto the retina. In nearsightedness, the focal point is before the retina; in farsightedness, it is past the retina. In presbyopia, the lens is stiffened so it's hard to bring close objects into focus.
Other eye problems include glaucoma (increased fluid pressure, which can damage the optic nerve), cataracts (clouding and hardening of the lens), and macular degeneration (degeneration of the retina).
Weird Eye Facts
The functioning of the eye is fairly simple, but there are some details you might not know:
The eye acts exactly like a camera in the sense that the image formed on the retina is inverted (upside down). When the brain translates the image, it automatically flips it. If you wear special goggles that make you view everything upside down, after a few days your brain will adapt, again showing you the "correct" view.
People don't see ultraviolet light, but the human retina can detect it. The lens absorbs it before it can reach the retina. The reason humans evolved to not see UV light is because the light has enough energy to damage the rods and cones. Insects do perceive ultraviolet light, but their compound eyes don't focus as sharply as human eyes, so the energy is spread out over a larger area.
Blind people who still have eyes can sense the difference between light and dark. There are special cells in the eyes that detect light but aren't involved in forming images.
Each eye has a small blind spot. This is the point where the optic nerve attaches to the eyeball. The hole in vision isn't noticeable because each eye fills in the other's blind spot.
Doctors are unable to transplant an entire eye. The reason is that it's too hard to reconnect the million-plus nerve fibers of the optic nerve.
Babies are born with full-size eyes. Human eyes stay about the same size from birth until death.
Blue eyes contain no blue pigment. The color is a result of Rayleigh scattering, which is also responsible for the blue color of the sky.
Eye color can change over time, mainly due to hormonal changes or chemical reactions in the body.
References
Bito, LZ; Matheny, A; Cruickshanks, KJ; Nondahl, DM; Carino, OB (1997). "Eye Color Changes Past Early Childhood". Archives of Ophthalmology. 115 (5): 659–63.
Goldsmith, T. H. (1990). "Optimization, Constraint, and History in the Evolution of Eyes". The Quarterly Review of Biology. 65(3): 281–322.
Cite this Article
Cats can see in dim light, but not truly in the dark.
Can Cats See in the Dark?
Young girl reading braille
What Do Blind People See?
Festival Goers Covered in Colorful Powder
How Colors Affect Human Behavior
Reading-Westend61-Getty-Images-138311126.jpg
6 Speed Reading Secrets for Adult Students
Babies are born with blue eyes
Why Are Babies Born With Blue Eyes?
Indonesia, Oval squid
Cephalopod Class: Species, Habitats, and Diets
Common Cuttlefish with black background
10 Cuttlefish Facts
Cherenkov Radiation
Why Is the Water Blue in a Nuclear Reactor? Cherenkov Radiation
Tarantula on the sand next to scattered rocks.
Tarantula Anatomy and Behavior
Colorful female eye.
The write up is good, but you need to work on paragraph/spaces in between text to make it look much good..
Also, any photos copied from Internet for usages you need to credit/cited the location or perhaps the link you copy it from.
I mean you should be providing the source from which the photos is/was copied.
Keep the work.
Regards,
@davidad
Ok thanks
Nice writing please keep it up
Thanks
Nice article
Well detailed...Beautiful write up
Thank you
Nice one 🌹
Thanks
U did a great job rita