Yield Farming - Yearn Finance - Crypto Academy S5W3 - Homework Post for @imagen
Hello everyone and welcome to my assignment this week for @imagen. Let's start;


Staking and yield farming are easily confused for each other especially by people who are new to DeFi. I’ll be talking about both below;
Staking is an attribute of Proof of Stake based crypto currencies. In staking, members of a POS based network stake (lock up) coins they have of that network as a mining method to stand a chance to be chosen as a validator. The staked tokens are collateral.
Staking is important in proof of stake based networks as this is how transactions are validated and new blocks are mined thereby securing the network. Only members who stake their coins in that network stand a chance to get chosen to validate transaction. Members who stake their coins in the network get some portion of the network’s token as rewards if chosen to validate a transaction.
Yield farming on the other hand, is lending your crypto tokens to a DeFi network via liquidity pools thereby providing liquidity to the pools and earning yields for lending these tokens like the typical interest collected when you lend a person money.
Usually, investors lend tokens to these pools most of which operate on the Ethereum network using smart contracts and they lend them out and earn interest rates which are distributed to farmers. If the token should also increase in value during that period, the liquidity provider’s profit could also soar.
Example of yield farming protocols includes Compound and Uniswap.
Differences
- Mechanism: Staking can only be done on cryptocurrencies based on proof of stake mechanism. You can stake individually or as a member of a staking pool. In staking, members of the network stake so they can be selected to validate transactions and secure the network. Usually, members with higher stakes have higher chances of being selected. In yield farming, there’s nothing like random selection and it involves smart contracts and DeFi protocols. Yield Farmers lend crypto tokens to liquidity pools and earn rewards.
- Security: In yield farming, money borrowed is locked using smart contracts which are automated. Since this is essentially software there could be glitches or an error during programming. Hackers could also successfully hack it and cart liquidity providers funds and all your money could be liquidated instantly. Also, farmers who got in at the beginning usually hold large stakes. Sometimes, they decide to sell when the value of token appreciates and it could lead to huge crash in the value of the token. In staking however, the major risk could be a malicious validator and this is highly improbable as validators usually have higher stakes in the network and stand to lose more if the network crashes. Validators could also stand the risk of having their staked coins slashed.
- Rewards: In staking members with higher stake in the network have higher chances of being selected as validators and hence earn rewards usually in the form of native token. The rewards percentage however could be of way lower percentage when compared to yield farming. In staking, one could earn an APY of between 5-15% depending on the network and it depends on being chosen as a validator.
In yield farming however, yield farmers could earn up to 100% APY and even more. This is a very wide margin.

Using the link, https://yearn.finance/#/home were taken to the platform where we can see;
“Home”: This is a general overview of your yearn finance account. On the dash board, you can see your balance and earnings as well as yearly yield. Here is a screenshot below;
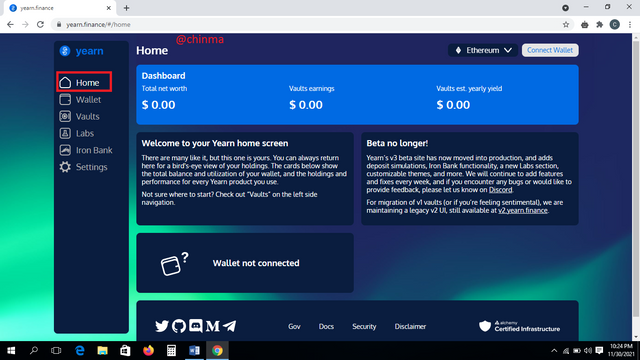.png)
“Wallet”: When you click on wallet, the wallet interface opens and your available balance is displayed above. In my case, this is $0.00
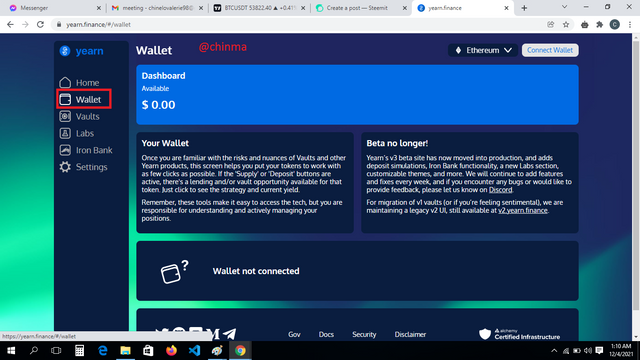.png)
The wallet shows available balance in dollars so a user can easily view his balance.
To connect one’s wallet, one would have to click on the connect button in the screenshot below to connect his wallet. You can connect any wallet hosted on the Ethereum network such as trust wallet or Metamask.
“vaults”: Here is a screenshot of the vaults interface below;
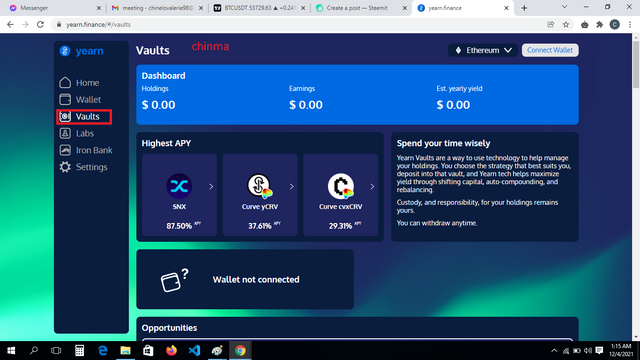.png)
The vault is used by yearn users to deposit tokens in pool options and earn tokens and maximized yields. The vault interface shows “Dashborad”, “Holdings” and “Yearly Yield”. We can also see the highest APY displayed.
To deposit funds, you click on a vault you want to deposit to and enter the amount you wish to deposit. You approve and then deposit.
“Labs”: This contains the newest and riskier options. Here, we can see dashboard showing holdings and APY.
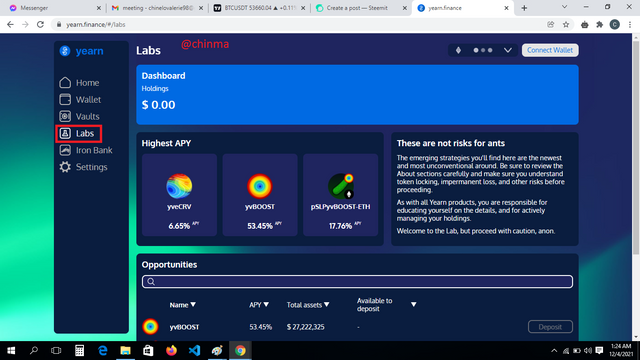.png)
“Iron Bank”: This is particularly useful for users who are not sure where to lend their crypto assets to and can’t decide on an option in the vault. You can borrow and keep your borrowed asset in the iron bank and still earn.
“Settings”: You can customize your slippage tolerance, themes and language here.
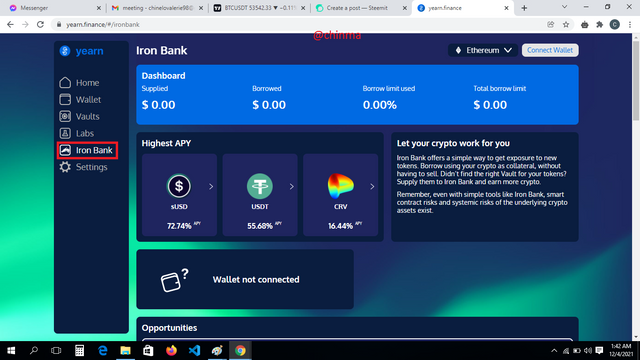.png)
“Settings”: You can customize your slippage tolerance, themes and language here.
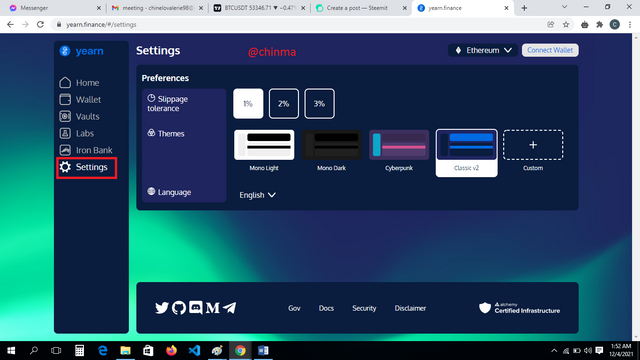.png)

Collateralization, just as the name suggests, has to do with collateral one uses in order to successfully borrow tokens from a liquidity pool, just the way you provide collateral when borrowing from a traditional bank. For you to successfully borrow from a liquidity pool, you must put up a token as collateral to hold you accountable. The collateral value can always be verified and if the borrower fails to repay, his collateral is liquidated.
What is its function?
Collateralization helps to protect interest of the liquidity providers so they still earn interest whether the borrower repays or not.
Usually, different DeFi protocols demand for different collateralization ratios, usually way higher than the amount being borrowed. Some require you collaterize up to 300% value of borrowed tokens or even more. Different assets could also require different collateral ratios. This is advised to prevent your collateral from getting liquidated if market goes sideways and collateral drops below collateralization threshold of that platform.
You can always check your collateralization ratio and top up on your collateral from time to time. Over collateralization is always encouraged in yield farming to be on the safer side.

The TVL stands for Total Value Locked. TVL is to DeFi as Market Capitalization is to Cryptocurrencies.
TVL of the DeFi Ecosystem: $109.07B
TVL of Yearn Finance Protocol: $4.54B
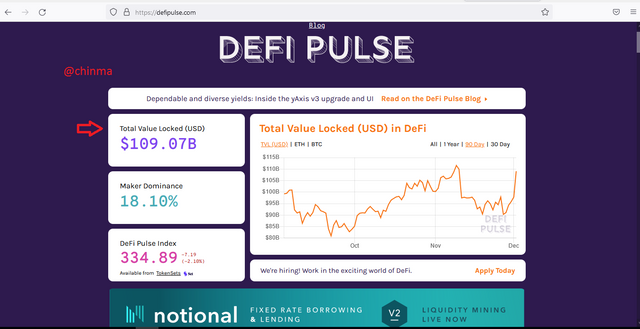.png)
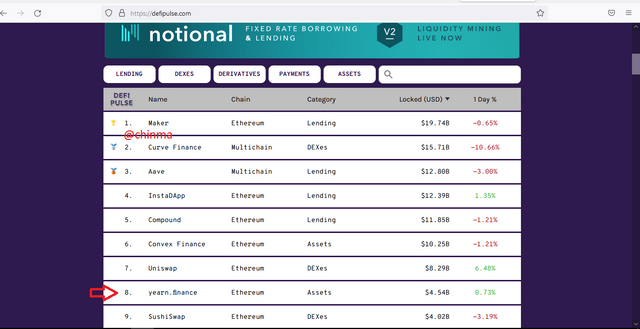.png)
Market Cap/TVL ratio of the YFI token:
According to coinmarketcap, Market Cap is $1,053,393,202
TVL of Yearn Finance Protocol= $4.54B
Market Cap/TVL ratio of the YFI token= 1,053,393,202/4,500,000,000
= 0.2341 (to 4 decimal places)
The YFI token, is it overvalued or undervalued? State the reasons.
The YFI token is undervalued.
The TVL ratio can be used to tell if a DeFi asset is overvalued or undervalued. A ratio below the value of 1 points to the asset being undervalued. In the case of the YFI token, we can see from the calculations above that our ratio is about 0.23, pointing to the fact that the token is undervalued. This means the token still has more potential.
The YFI token is the governance token of Yearn.Finance and can be farmed through different ways like depositing capital into the protocol’s products. It has a market rank of 103 according to www.coinmarketcap.com. Their vault option is a very great option as it helps users maximize yield and its use cases keeps expanding. The Iron bank is another great option too.
It has a maximum supply of 36,666 YFI and a circulating supply of 36,638 YFI source coinmarketcap and with the increasing growth of the DeFi space as a whole, one can see the Importance of holding the governance token and its room for more growth over the years.

For BTC, using the BTC/USDT chart on www.tradingview.com, we can see that;
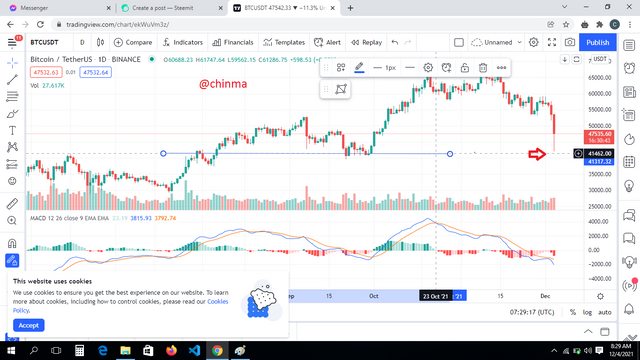.png)
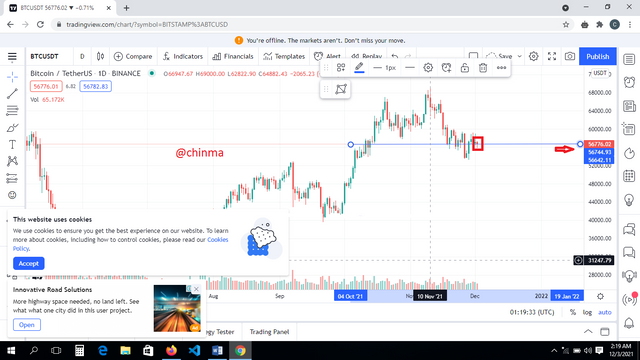.png)
August 1st, price was 41462.00
Right now, price = 56642.11
Clearly, there was an increase.
Percentage increase = [(56642.11 – 41462.00)/ 41462.00 ]100
= (15180.11 / 41462.00) * 100
= 0.36612 * 100
= 36.6121% (4 d.p)
profit on btc = (36.61/100) 500
= 183.06 USD
ROI = 500 +183.06
= 683.06 USD
For the YFI token
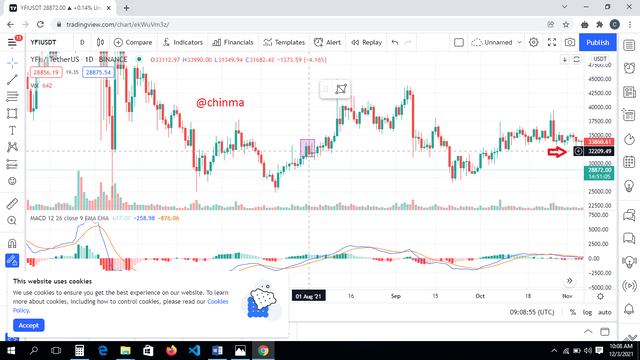.png)
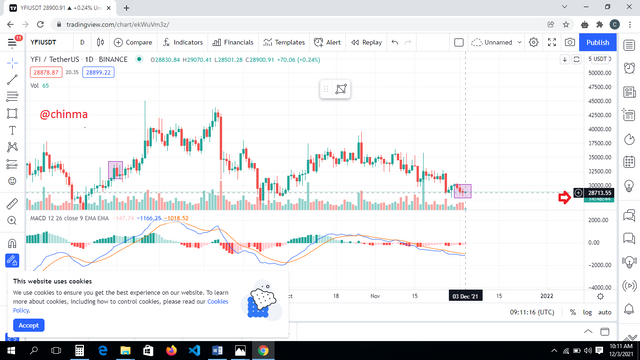.png)
August 1st; 32138.56 32209.49
Right now, price = 28892.98
This showed a decrease in price.
Percentage decrease = [(32209.49 – 28892.98)/28892.98]100
= (3316.51 / 28892.98) 100
= 0.11479 *100
= 11.4786%
Loss = (11.48 / 100) * 500
= 57.4 USD
ROI on YFI = 500 – 57.4
= 442.6 USD
Total ROI = 442.6 USD + 683.06 USD
= 1, 125.66USD
This shows there was a net profit.

DeFi Farming though very profitable could be very risky. Some of the risks include;

The concept of yield farming though new, got widespread acceptance and has since seen tremendous growth after Compound came into the picture. Though it could generate very enormous rewards up to 100% yield or more, it is also very risky and requires thorough research and great strategizing as one could lose all his funds in an instant due to reasons such as a bug in the smart contract even. I hope you enjoyed reading this.