Avalanche Blockchain - Crypto Academy / S5W8 - Homework post for pelon53
Hello everyone.
Welcome to this post. Hopefully, all of you will be good and happy and enjoying your health with the grace and blessings of Almighty God. Today, I am here to present the homework post for dear sir @pelon53 in the last week of Season 5 of Steemit Crypto Academy. The lecture was nicely explained by the professor and I will make homework for it. So, let's start our task without any wastage of time.

There are some questions that are asked by the professor as the assignment for this week and I will explain all of them in the given order.

(01)
Explain X-Chain, C-Chain and P- chain in detail.
As we all know that the blockchain technology is making progress day by day and new blockchains are coming into view with unique and useful features. Blockchain developers try their best to develop such a blockchain that should be more efficient, secure, and decentralized than the previously existing blockchains.
Actually, there is a Blockchain Trilemma that the blockchain developers can only go with two of three factors that are scalability, security, and decentralization. The developers of Bitcoin decided to go with security and decentralization so the scalability of the Bitcoin network is still a problem of this network.
To overcome the scalability problem that is present in the Bitcoin network, a new blockchain is developed that is named Avalanche Blockchain. This blockchain was developed by Kevin Sekniqi, Marfan "Ted" Yin, and Emin Gün Sirer, along with their companions. Avalanche Blockchain was launched in September 2020.
The Avalanche Blockchain is actually a different and unique blockchain as it is composed of three chains that are performing their functions to make the Avalanche blockchain more successful and impressive. In other chains, all the factors (decentralization, scalability, and security) are managed by only one chain. While in this blockchain, all three functions are performed by three different chains. These chains are described in detail.
X-Chain
The first chain of the Avalanche ecosystem is the X-Chain, also known as The Exchange Chain. As the name of the chain refers that it is a chain where the assets can be exchanged and created. The native token of the Avalanche blockchain, AVAX token, and other assets can be created and exchanged in this chain.
This chain allows the users to trade and create tokens that are based on some rules and standards of the Avalanche blockchain just like the Ethereum network. Thus, it allows the users to create other ERC20 tokens also. This chain is based on the Avalanche Consensus Protocol. The transaction fees are paid in AVAX tokens.
C-Chain
The second chain of the Avalanche ecosystem is the C-Chain, also known as The Contract Chain or The Smart Contract Chain. The function of this chain is to allow the developers to create their smart contracts for the Decentralized Applications (DApps). So, the developers of DApps can create their smart contracts in this chain.
This chain is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) so the DApps built on the Etheruem network are in the access of the Avalanche users. This chain is based on the Snowman Consensus Protocol. So, the developers can run their NFTs, ERC20 tokens, and different DApps on this chain. The fees for the generation of smart contracts is charged in the form of AVAX token.
P-Chain
The third chain of the Avalanche ecosystem is the P-Chain, also known as The Platform Chain. The function of this chain is to allow the creation of new subnets, track and manage the active subnets and cooperate with the network validators. Here, the word Subnet means the group of validators that avail the consensus for the custom networks.
A single blockchain is validated by a single Subnet but each subnet has the capacity to validate multiple blockchains. This chain is also based on the Snowman Consensus Protocol that is an extensive version of the Avalanche Consensus Protocol.
So, these are the components of the Avalanche blockchain. All of these chains perform their respective functions and their collective function becomes the function of the Avalanche blockchain. These sub-chains are responsible to improve the transaction speed and scalability of the network. The scalability and transaction verifying speed of Avalanche Blockchain are very much high than the other blockchains of the time.

(02)
Explore the Avax Network platform . Screenshots required.
To explore the Avax Network, I visited the official website of Avax Network. The homepage that appeared before me is shown in the below screenshot.

Let's explore the features that are available on the website. So, have a look at them.
Developers
There are actually two sub-divisions of the Developers page. These are Validators and Start Building.
- Validators:
From this page, we can become a validator in the Avalanche blockchain. The users can become a validator and validate the transactions that are made in the system by staking the AVAX tokens, the native token of the Avalanche network.

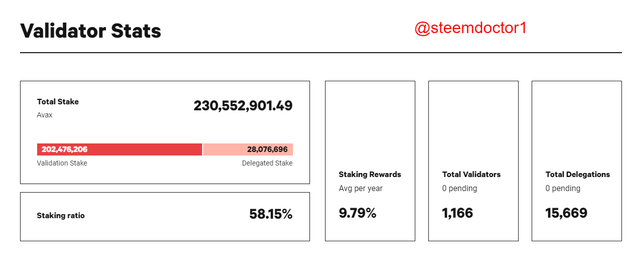
The statics of the validators of the Avalanche blockchain is also shown on this page. You can see this from the below screenshot.
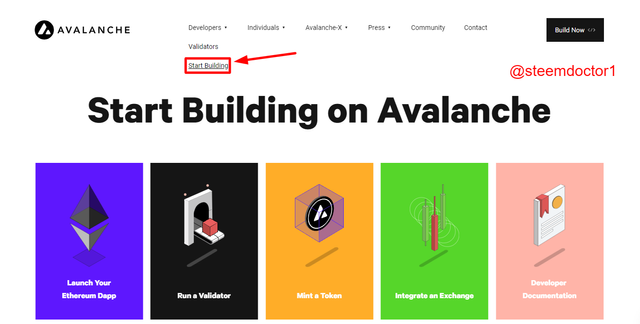
- Start Building:
From this page, the users can act as a developer by building DApps, Running a Validator, Mint a token, Integrate an Exchange. The Developer Documentation is also available on this page.
Indviduals
This page is also divided into six different categories that are explained below.
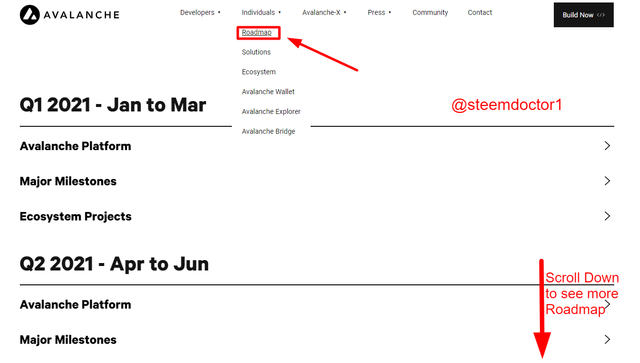
- Roadmap:
From this page, the users can see the Roadmap of the Avalanche blockchain in the respective year 2021. The Roadmap is divided into 4 phases and each phase covers 3 months period.
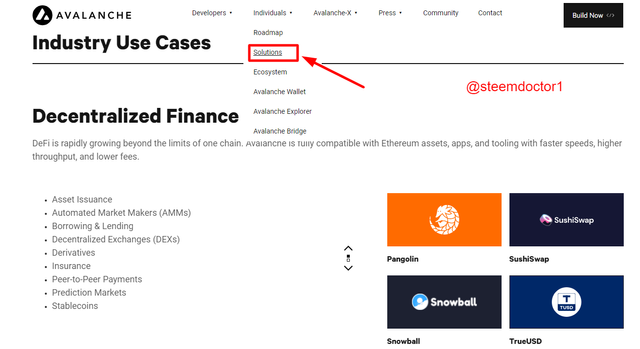
- Solutions:
On this page, the users can explore the solutions that the Avalanche platform introduced in the form of Decentralized Finance, Institutions, Governments, NFTs, etc.
- Ecosystem:
On this page, the users can access the Avalanche ecosystem such as DeFi, Digital Securities, Ecosystem, Exchange, Explorer, Gaming, Identity, Infrastructure, NFT, Nodes, Oracle, Payments, Play to Earn, Security, Stablecoin, Tooling, Trading Bot, Wallet, Wealth Management, etc.
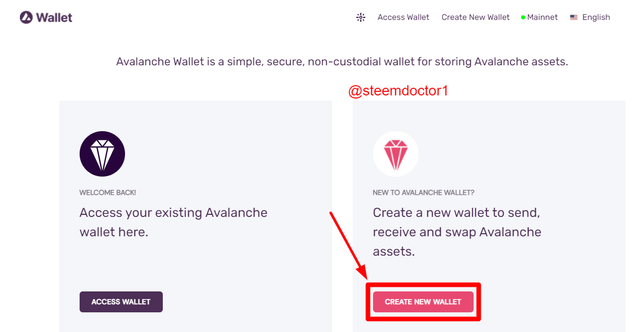
- Avalanche Wallet:
On this page, the users can access their existing Avalanche wallets and can also create new Avalanche wallets. For creating a new Avalanche wallet, click on the Create New Wallet option.
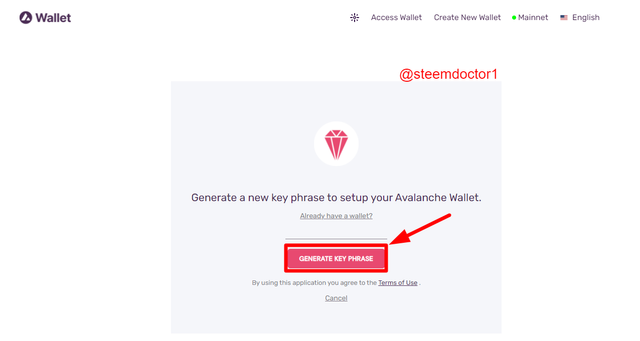
- Now, click the Generate Key Phrase option.
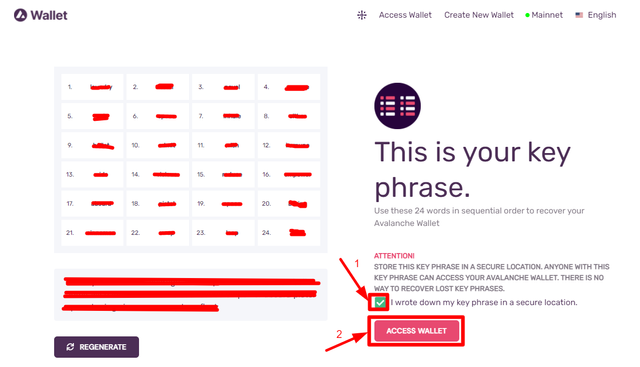
- Now, a Key Phrase will be given to you. Copy this and store it somewhere safe. Now, click the Access Wallet option.
- Now, enter the missing key phrases and click the Verify option.
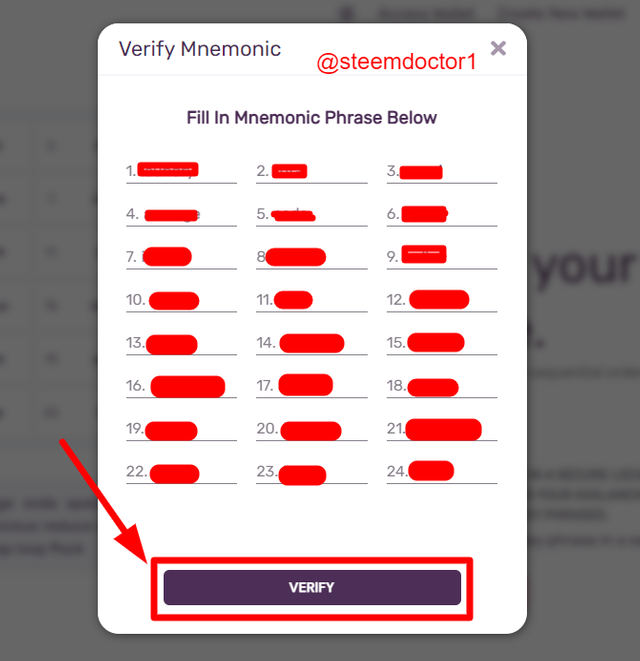
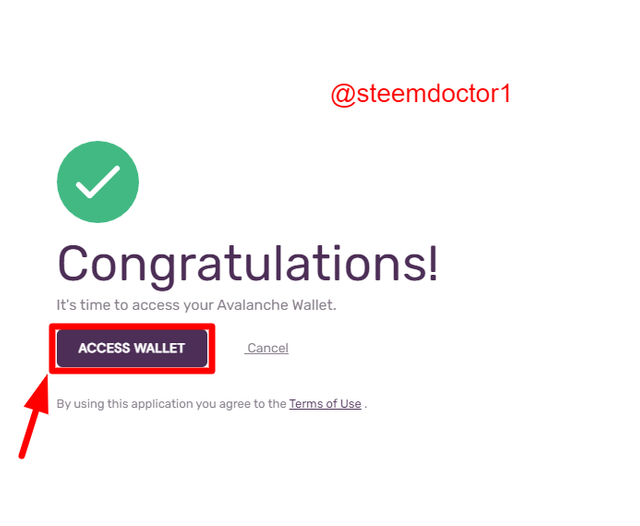
- The wallet will be successfully created and now click the Access Wallet option.
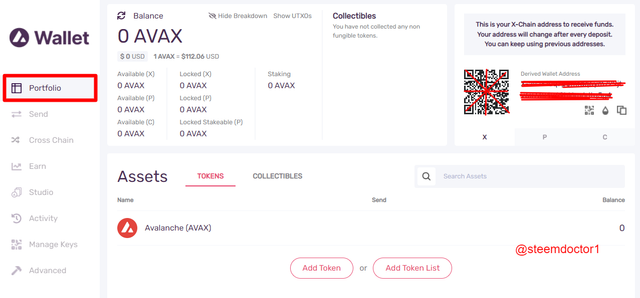
- You can see that my wallet has been created and now I can manage and store the AVAX tokens and other assets.
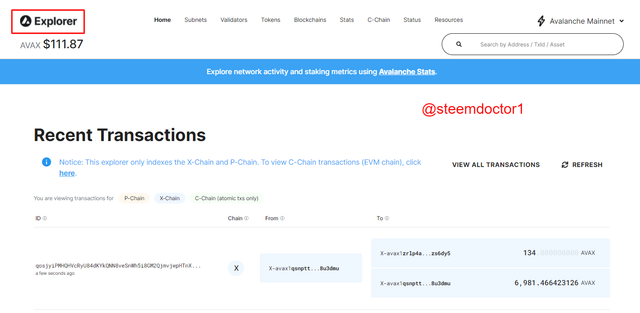
- Avalanche Explorer:
On this page, the users can explore the transactions that are executing or taking place in the Avalanche network.
- Avalanche Bridge:
On this page, we can explore the Avalanche Bridge and connect different wallets like MetaMask, CoinBase Wallet, Wallet Connect, etc.

Avalanche-X
This option is further divided into two different pages. That is,
- Explore Open Grants:
From this page, the users can explore and build different Open Grants like DEXs, Lending, StableCoin, Synthetics and Derivatives, Volatility Index (VIX).
- Submit a General Proposal:
On this page, the users can submit a general proposal in the Avalanche ecosystem. General Proposal means the users can establish their projects on the Avalanche blockchain by going through the application process.
Press
This page allows the users to be aware of the latest news about the happenings and new aspects held in the Avalanche blockchain. This news can be accessed by the press through inquiries and press kits and media assets.
Community
From this page, the users can seek contact opportunities with the management of the Avalanche platform through different social media like Facebook, Twitter, Medium, Telegram, Discord, Forum, Reddit, LinkedIn, YouTube, Meetup, Clubhouse, etc.
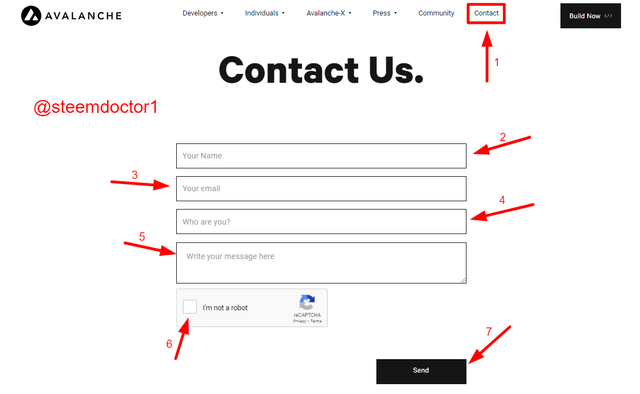
Contact
We can also contact the management of the Avalanche platform from this page.

(03)
Show the last contract verified in the C-Chain network and show the Smart Contract that was generated at that address. Screenshots required.
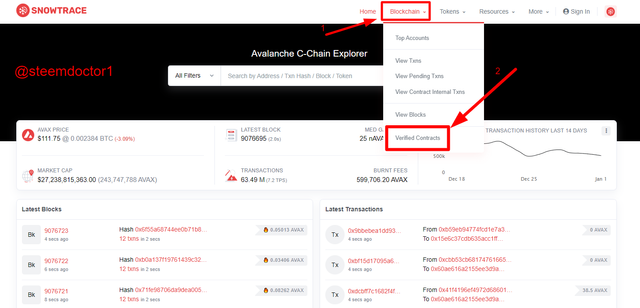
As we have discussed before that the smart contracts are created and explored in The Contract Chain (C-Chain) of the Avalance platform. So, now I will show the latest verified contract. Have a look at the following steps.
- First of all, open the SnowTrace and go to the Verifies Contracts option in the Blockchain menu located at the top bar. This is shown in the below screenshot.
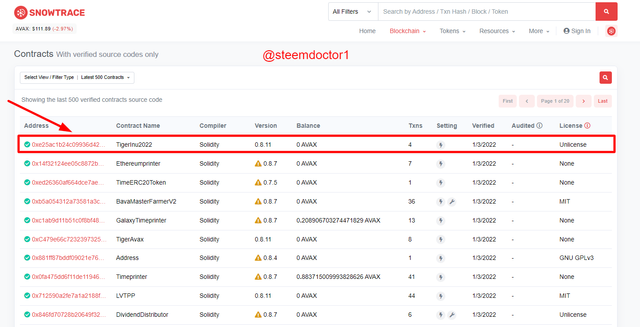
- Now, a list of Verifies Contracts will appear. Click on the first one, it is the latest contract that is verified. In my case, its name is TigerInu2022.
- All the details about the contract will appear after clicking on it. You can see this in the below screenshot.
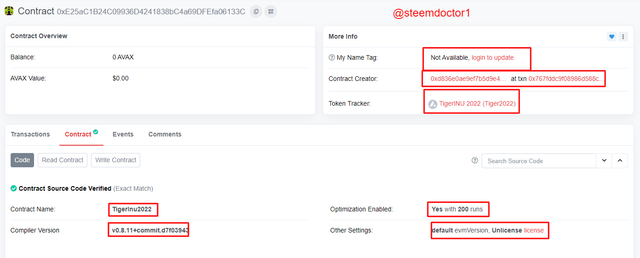
This information can also be expressed in the table. As follows,
| Contract Address | 0xE25aC1B24C09936D4241838bC4a69DFEfa06133C |
|---|---|
| Contract Creator | 0xd836e0ae9ef7b5d9e4dde71887f7219baf2c8012 |
| Contract Txn Hash | 0x767fddc9f08986d588cf209e9d21e1c02c695f864373ef8e0b235b582ae1d029 |
| TokenTracker | TigerINU 2022 (Tiger2022) |
| Contract Name | TigerInu2022 |
| Compiler Version | v0.8.11+commit.d7f03943 |
The Transactions that are made are shown in the following screenshot. One of them is for the creation of a contract and the others are open transactions.
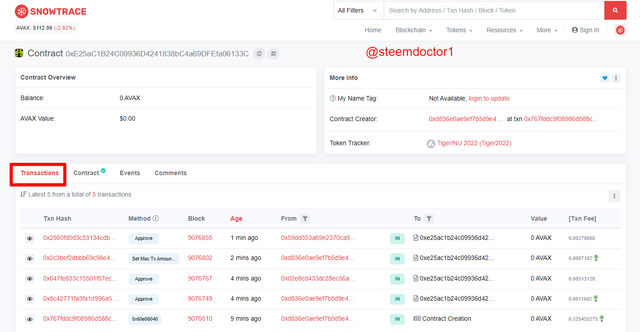
It seemed that the contract creator created a token named TigerINU 2022. The information of this token can be accessed by clicking on the Token Tracker. The information is as follows.
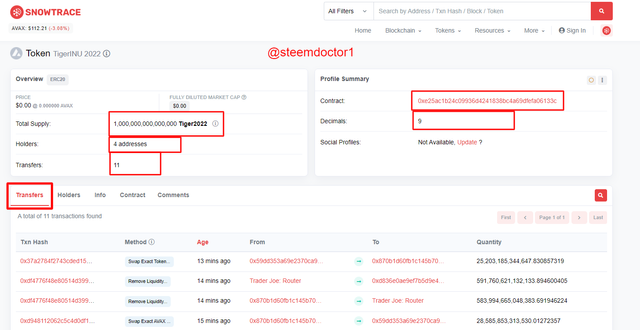
This can be also expressed in the table as follows,
| Token Name | TigerINU 2022 |
|---|---|
| Total Supply | 1,000,000,000,000,000 Tiger2022 |
| Holders | 4 addresses |
| Transfers | 11 |
| Contract | 0xe25ac1b24c09936d4241838bc4a69dfefa06133c |
| Decimals | 9 |

(04)
Explore the last block generated in the C-Chain network. Screenshots required.
For this purpose we have to follow these steps.
- First of all, open the First of all, open the SnowTrace and go to the View Blocks option in the Blockchain menu located at the top bar.
- Now, a list of newly generated blocks will appear. Click on the first block which is 9078844 in my case.
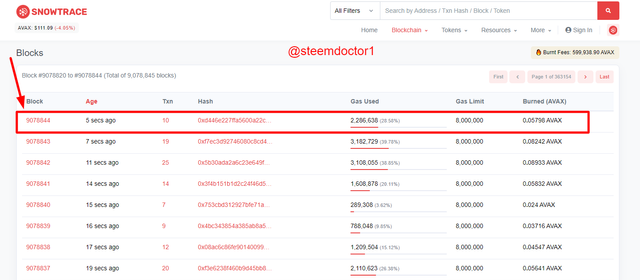
- Now, you will be able to explore the block. All the details about the block are given in the following screenshot.
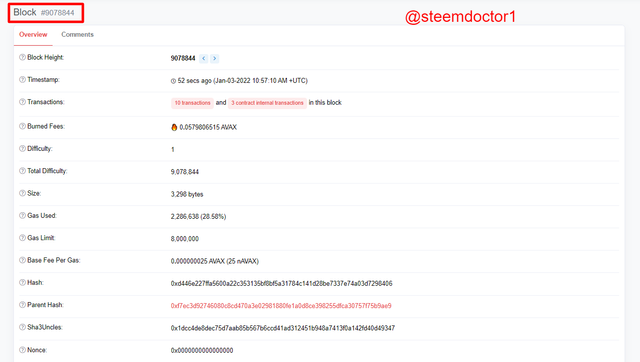
The information can also be shown in the form of a tabular way. As follows,
| Block No. | #9078844 |
|---|---|
| Block Height | 9078844 |
| Timestamp | 52 secs ago (Jan-03-2022 10:57:10 AM +UTC) |
| Transactions | 10 transactions and 3 contract internal transactions |
| Burned Fees | 🔥 0.0579806515 AVAX |
| Difficulty | 1 |
| Total Difficulty | 9,078,844 |
| Size | 3,298 bytes |
| Gas Used | 2,286,638 (28.58%) |
| Gas Limit | 8,000,000 |
| Base Fee Per Gas | 0.000000025 AVAX (25 nAVAX) |
| Hash | 0xd446e227ffa5600a22c353135bf8bf5a31784c141d28be7337e74a03d7298406 |
| Parent Hash | 0xf7ec3d92746080c8cd470a3e02981880fe1a0d8ce398255dfca30757f75b9ae9 |
| Sha3Uncles | 0x1dcc4de8dec75d7aab85b567b6ccd41ad312451b948a7413f0a142fd40d49347 |
| Nonce | 0x0000000000000000 |

(05)
Explain in detail the Avalanche consensus protocol and the Snowman consensus protocol.
As we have discussed that there are three chains that combine to form the Avalanche blockchains. Similarly, there are two consensus protocols that combine to form the consensus mechanism of the Avalanche blockchain. We can also say that Avalanche blockchain is a multi-protocoled blockchain. The occurrence of these two protocols is the main reason for the high scalability and high transaction speed of the network. So, let's discuss both of them.
Avalanched Consensus Protocol
This consensus protocol is used in the X-chain where the AVAX tokens and other crypto assets are traded/exchanged and new tokens are created.
The transactions that are made in this consensus protocol are validated and verified parallelly. This means to say that all the nodes are present equally and verify the transaction efficiently.
Unlike other consensus protocols like Proof-of-Work (PoW), Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPos), there is no need for a leader to reach the consensus.
The absence of any leader increases the decentralization of the blockchain and the scalability is not affected.
In other consensus protocols like PoW, PoS, DPoS, a transaction is processed by a single node and then other nodes validate the transaction. But in Avalanche Protocol, all the nodes process the transaction at the same time by the utilization of a technique known as Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) optimized protocol.
All the transactions are processed and validated efficiently and thus transaction speed is increased.
No block is created for the transaction and the transaction is validated itself in the form of vertices (parented transactions).
Snowman Consensus Protocol
Snowman consensus protocol is considered to be the extensive version of the Avalanche consensus protocol.
This consensus protocol is used in the C-Chain (The Contract Chain) where the smart contracts are created and managed. This is also used in the P-Chain (The Platform Chain) where the creation of subnets takes place.
This consensus protocol is different form of Avalanche consensus protocol as the transactions are ordered linearly, not parallelerly.
The nodes are present variably, not equally/parallel.
The recording of smart contracts and transactions of smart contracts takes place efficiently and easily.
After the processing of transactions, the blocks are created in this consensus protocol.

Conclusions
As we all know that the blockchain technology is growing day by day and new blockchains are coming into view. Blockchain developers are working hard to overcome the scalability problem that is present in the Bitcoin network. To overcome this problem, Avalanche Blockchain was developed. This blockchain comprises three chains that are X-Chain, C-Chain, and P-Chain.
The X-Chain allows the exchange of tokens like AVAX and other assets. The C-Chain allows the users to create and manage the smart contracts and create different DApps. The P-Chain deals with the creation of new subnets and manages previous subnets. There are two consensus protocols that are present in this blockchain. One of them is the Avalanche consensus protocol and the second one is the Snowman consensus protocol that is an extension of the Avalanche consensus protocol.

So, that's all about the homework for this week. Hopefully, all of you will like it. Thanks a lot, dear professor @pelon53 for such an amazing lecture. This is his last lecture in Season 5 and I wish to see him in the next 6th Season of the academy.
Regards: @steemdoctor1 (Crypto Student)

@tipu curate