The human skeleton
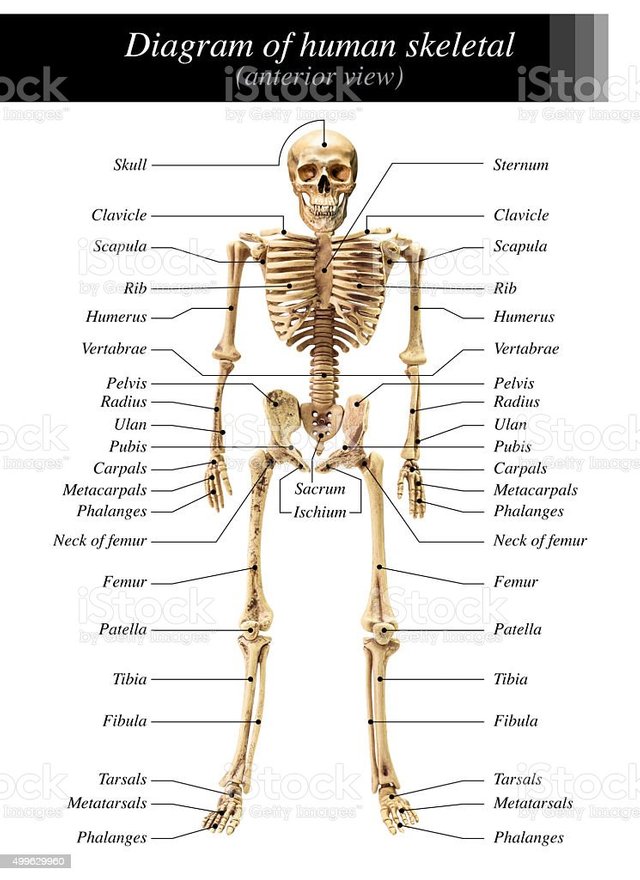
The human skeleton is the solid and rigid structure that forms the body, and the muscles and other soft tissues of the body are attached to it. The skeleton of an average adult human usually consists of 206 bones (not counting the connective vertebrae of the sacrum and cartilage separately). [1] At 21 years of age, skeletal bone density is highest. The human skeleton can be divided into two parts - axial skeleton and appendage skeleton. The skull, thorax, and spine form axial skeletons. The urethra, pelvis, and the bones of the arms and legs, on the other hand, form the marginal skeleton. The skeleton is hard but not heavy, weighing less than 20% of the total human body weight. [2]
The human skeleton performs six important functions. First, it supports the other organs of the body. Second, it plays an essential role in human movement, as the muscles can easily work on this moving but strong and stable structure. In addition, the human skeleton protects many internal organs of the human body. Fourth, different blood cells are produced in the skeletal system. Skeletal bones act as a storehouse of minerals (such as calcium and phosphorus) and fats in the human body. The skeletal system also plays a role in controlling the endocrine system.
Accessory skeleton
The human skeletal system is divided into two main parts. E.g.
• Axial skeleton
• Appendicular skeleton
The following is a detailed description of the appendage skeleton.
The human body consists of a pair of forelegs or arms, a pair of hind legs or legs, a pectoral girdle, and a pelvic girdle.
Pectoral girdle
The two thoracic bones are located in the shoulder area on both sides of the human body. They are located separately from each other. They have a pair of clavicles and a pair of scapula.
Clavicle
Clavicle curved bone. There is no bone marrow in this bone. It consists of a body and two ends, namely the sternal (attached to the sternum's manubrium) and the acromial process (the scapula contains the acromial process).
Scapula
Each scapula is a broad flattened triangular bone. It is located on either side of the upper end of the thoracic cage. It has a horizontal spine on the back, called a scapular spine. The part of the scapular that is adjacent to the head of the humerus is called the glenoid cavity. The extended part of the scapular lateral edge is called the acromial process.
Functions: The main function of the thoracic bone is to attach the muscles of the arm and move the humerus
nice