Tutorial post || Powder Metallurgy part 2 || Mechanical Engineering|| by @deepak94||#burnsteem25

Hello friends, how are you all, hope all is well, today I am going to write my eighth post about my subject. Today in this post we discuss Powder Metallurgy of different processes in the manufacturing process. So let's start with the topic.
Blending
- Blending or mixing operation can be done either dry or wet.
- For reducing the strength some of the materials like lubricants such as steric acids improve the characteristics and compressibility.
- Binders produce the reverse effect of lubricants. Thermoplastics or water-soluble methyl cellulose binder is used.
- Many of the binder products are not used as the final product.
Compacting
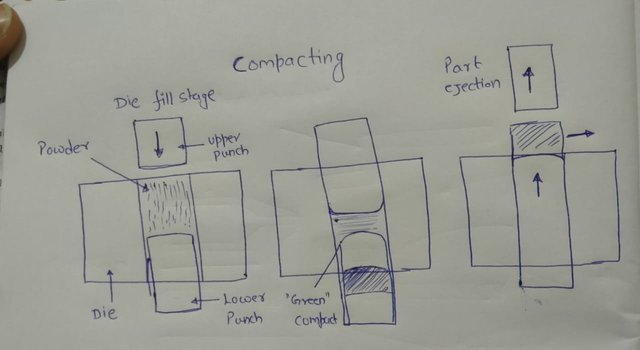
- Powder is pressed into a "green compact".
- 40 to 1650 Mpa pressure (Depends on materials, and product complexity)
- Still very porous, -70% density.
- Maybe done cold or warm (higher density)
Sintering
- Controlled atmosphere with no oxygen.
- Heat to 0.75-degree temperature melt.
- Particles mind together diffusion recrystallization and grain growth take place.
- Part shrink in size.
- Density will increase up to 95%.
- Strength increases brittleness and porosity decreases. Toughness increases.
Cold Isostatic pressing (CIP)
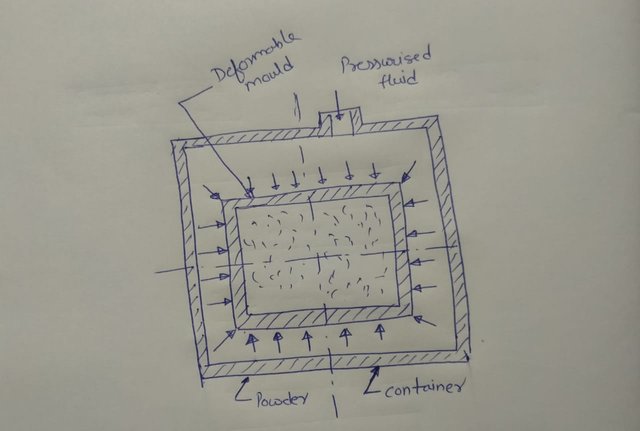
- The Powder is contained in a flexible mould made of rubber or some other customer materials.
- The flexible mould is then pressurized using high-pressure water or oil.
- No lubricant is needed.
- Density achieved very high.
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Is carried out at a high temperature and pressure using a gas such as Argon.
- The flexible mold is made of sheet metal. Due to high temperature.
- Compaction and sintering are completed simultaneously.
- Used in the production of Bill gates of superalloys, high-speed steels, titanium, ceramic, etc. Where the integrity of the material is a prime consideration.
Production of Magnets
- Half and half Fe, Al alloy used for magnetic parts.
- Sintering temperature of Hydrogen is up to 600-650 degrees Celsius.
- Sintering is usually done in wire coils.
- Total Shrinkage is approximately 4-7%.
Advantages
- Good surface finish we get.
- we made high complex shapes very easily and quickly.
- Porosity can be controlled to some extent.
- Can produce porous parts and hard-to-manufacture materials (for example cemented oxide).
- Surface can have high wear resistance.
- Automation is very easy.
- Physical properties controlled.
- Hard-to-machine metal can be used easily.
- No molten metals and very low waste.
- No need for any kind of finishing operation.
- variation low.
Disadvantages
- If the metal powder is not used properly then it will be destroyed quickly.
- set up costs are high.
- It will be hard to produce a sharp corner.
- Impossible to produce Non-moldable features.
Engineer is best profession right now. but in the india less scope compare to foreign and gulf countries.
Your diagram is really good compare to me.
We would like to thank you for publishing your article in the Steem India community today. Based on our review of your article, we present the following result of our assessment:
We appreciate your consistency in sharing your activities here and posting in the Steem India community. Thank you from the bottom of our hearts.
Your presentation of this information is extremely commendable and I am hoping that users will be able to gain some insight from it.
Regards
@cryptogecko (Admin)
Steem India - @steemindaa
Diligent