THE EVOLUTION OF MONEY


Hello everyone , my greetings to you all. hope everyone is great.
I want to use this article to talk about the evolution of money or simply how people started interacting with each other when it comes to money.
INTRODUCTION
Money is the most important invention of modern times. It has undergone a long process of historical evolution. Human beings passed through a stage when money was not in use and goods were exchanged directly for one another. Such exchange of goods for goods was called Barter Exchange. this rings me to talk about the different stages of the evolution of money.

STAGES OF THE EVOLUTION OF MONEY
Bartering system
In trade, barter (derived from baretor) is a system of exchange in which participants in a
transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using
a medium of exchange, such as money. A barter system is an old method of exchange.
This system has been used for centuries and long before money was invented. People
exchanged services and goods for other services and goods in return. The value of
bartering items can be negotiated with the other party. Things like Livestock, Skills and
Talents, people and salt
bartering system.jpg
image source

Why was the bartering system so flawed?
image source
The Bartering system had some issues which include;
• Having something that no one wanted
• Limited shelf life
• Fair exchange
• Transportation and storage
• Hard to repay debt
1.Commodity system
Commodity money(system) is money whose value comes from a commodity of which it
is made. Commodity money consists of objects having value or use in themselves
(intrinsic value) as well as their value in buying goods. This is in contrast to
representative money, which has little or no intrinsic value but represents something of
value, and fiat money, which has value only because it has been established as money by
government regulation. Examples of commodities that have been used as media of
exchange include gold, silver, copper, salt, peppercorns, tea, decorated belts, shells,
alcohol, cigarettes, silk, candy, nails, cocoa beans, cowries and barley. Several types of
commodity money were sometimes used together, with fixed relative values, in various
commodity valuation or price system economies
Some commodity systems which exist before include;
• Ancient China, Africa, and India used Cowry shells
• Trade in Japan was based on the Koku- a unit of rice
• The Shekel was a specific weight of barley
• Yap stones
Commodity-Trading.jpg
image source
2.Metallic Money
Coins are money made from metals. In the past, coins were sometimes made from
valuable metals such as gold and silver. Today, most coins are made with some
combination of copper, zinc, and nickel.
Some significant to these change from the bartering system to coins include;
• People could actually trade what they wanted for what they needed
• Coins were also easier to transport
• Uniform coins
And some setbacks they face were;
• Coin’s weight could change over time
• Coins could be counterfeited
• Coins were also very heavy to carry
coins.jpg
image source
3.Paper Money
The Chinese inverted paper money in the form of notes, or IOUs. Paper bills were first
used by the Chinese, who started carrying folding money during the Tang Dynasty (A.D.
618-907) mostly in the form of privately issued bills of credit or exchange notes and used
it for more than 500 years before the practice began to catch on in Europe in the 17th
century.
China invented paper money during the Tang Dynasty that ruled between 618 and 907,
and they used this currency for a long time before it found its way to other countries. ...
Being shrewd business people, the Chinese found the weight of the coin money to be
cumbersome and figured that printed money would be more efficient
paper money.jpg
image source
- Paper Money
The Chinese inverted paper money in the form of notes, or IOUs. Paper bills were first
used by the Chinese, who started carrying folding money during the Tang Dynasty (A.D.
618-907) mostly in the form of privately issued bills of credit or exchange notes and used
it for more than 500 years before the practice began to catch on in Europe in the 17th
century.
China invented paper money during the Tang Dynasty that ruled between 618 and 907,
and they used this currency for a long time before it found its way to other countries. ...
Being shrewd business people, the Chinese found the weight of the coin money to be
cumbersome and figured that printed money would be more efficient
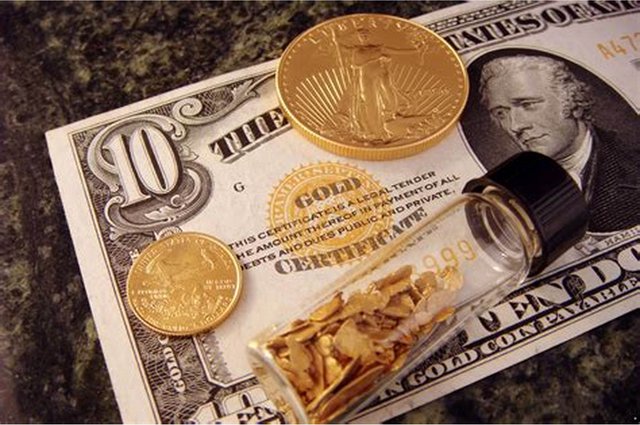
- Gold standard
The gold standard is a monetary system where a country's currency or paper money has a
value directly linked or backed by gold. With the gold standard, countries agreed to
convert paper money into a fixed amount of gold. A country that uses the gold standard
sets a fixed price for gold and buys and sells gold at that price. That fixed price is used to
determine the value of the currency. For example, if the U.S. sets the price of gold at
$500 an ounce, the value of the dollar would be 1/500th of an ounce of gold.
The gold standard is not currently used by any government. Britain stopped using the
gold standard in 1931 and the U.S. followed suit in 1933 and abandoned the remnants of
the system in 1973.1
The gold standard was completely replaced by fiat money, a term to describe currency
that is used because of a government's order, or fiat, that the currency must be accepted as a means of payment. In the U.S., for instance, the dollar is fiat money, and for Nigeria, it
is the naira.
Some advantages to the gold standard include;
• Most people were familiar with it
• Naturally occurring material
• Kept inflation in check
• Fixed exchange rate
Disadvantages of this system include;
• Gold had to be free flowing
• All countries needed to maintain money supply to fixed quantity of gold
• If there was a net transfer of currency from one country to another gold would
have to follow
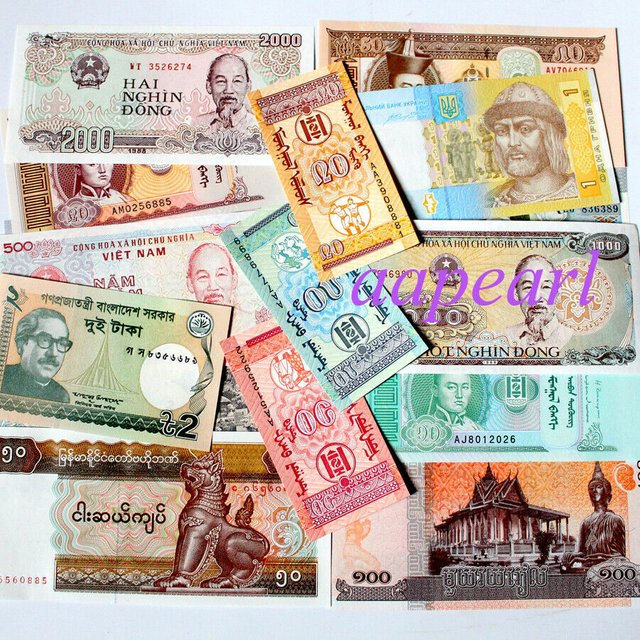
- Floating exchange rate system
A floating exchange rate is a regime where the currency price of a nation is set by the
forex market based on supply and demand relative to other currencies. This is in contrast
to a fixed exchange rate, in which the government entirely or predominantly determines
the rate.
Floating exchange rates mean that currencies change in relative value all the time. For
example, one U.S. dollar might buy one British Pound today, but it might only buy 0.95
British Pounds tomorrow. There are two types of currency exchange rates—floating and
fixed. The U.S. dollar and other major currencies like Euros and pound (GBP) are
floating currencies—their values change according to how the currency trades on forex
markets.


I will give a conclusion on this post here for today and more article will come up later concerning the evolution of money.
Thanks guys
@thegreens
@saxopedia
@steem-cameroon
@fombae
@majerius
@chiabertrand


Wao this is actually a good content that you put up. I have actually acquired knowledge the bartering system .
Great. am happy you learn something out of it
I never knew all this , I learned the little I could learn thank you so much
Great at least you pick out some knowledge about this content
Woow woow this is a great article and I have learned so much about the evolution of money. Thanks a lot for sharing this beautiful article with us @fafiboss. Please keep on sharing quality and original content here with us
thanks man. A knowledge of the evolution of money is important in order to know how to move forward.
Exactly buddy
Great write up here. You know so many people don't know how money manage to come in to existence especially this children of today. Is good they should feed their eyes.
Thanks really for the content.
That is where I got inspired to write this . Thanks for appreciating the content
Wasn't easy to read everything though but it's really worth reading
We now know exactly why the batter system was faulty and how money came about