Introduction to Industry 4.0
Production of goods underwent lot of changes during human history, industrialization in period starting 1760 to 1840 brought mechanization and steam power, this represented a radical shift away from an agrarian economy. In the beginning of 20th century came mass production famously represented by Ford Motor Company with Ford Model T. Modern manufacturing utilizes computers for automatization and optimization of production starting in the late 1960s. Next development is heading towards technological evolution from embedded systems to cyber-physical systems, this trend is known under term Industry 4.0, also the fourth industrial revolution.
“Industry 4.0 represents this coming fourth industrial revolution on the way to and Internet of Things, Data and Services. Decentralized intelligence helps create intelligent object networking and independent process management, with the interaction of the real and virtual worlds representing a crucial new aspect of the manufacturing and production process. It represents a paradigm shift from centralized to decentralized production. This in simplicity means that industrial production machinery no longer just “processes” the product, but that the product communicates with the machinery to tell it exactly what to do.” Industry 4.0 refers to the technological evolution from embedded systems to cyber-physical systems.
Technological Background: Embedded Systems and Networks
The bedrock of tomorrows innovative solutions are information and communication technologies (ICT), embedded systems and global networks are two major ICT motors driving current technological progress. Embedded systems are the intelligent central control units at work in most modern technological products and devices. They typically operate as information-processing systems “embedded” within and “enclosing” product for a set range of device-specific applications. These “connect” with the outside world using sensors and actuators; allowing embedded systems to be increasingly interconnected with each other and the online world.
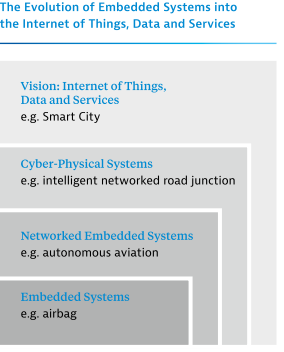
Cyber-Physical Systems and Industry 4.0
“CPSs (Cyber-physical systems) are defined as the systems which offer integrations of computation, networking, and physical processes, or in other words, as the systems where physical and software components are deeply intertwined, each operating on different spatial and temporal scales, exhibiting multiple and distinct behavioral modalities, and interacting with each other in a myriad of ways that change with context. These are controlled by computer-based algorithms, tightly integrated with the internet and its users.”
Some of the defining characteristics of CPS include:
a) cybercapability in every physical component,
b) high-degree of automation,
c) networking at multiple scales,
d) integration at multiple temporal and spatial scales,
e) reorganizing/reconfiguring dynamics
Examples of CPS include smart grid, autonomous automobile systems, medical monitoring, process control systems, robotics systems, and automatic pilot avionics.
Cyber-physical systems are enabling technologies which bring the virtual and physical worlds together creating a truly networked world in which intelligent objects communicate and interact with each other. Together with the internet and the data and services available online, embedded systems join to form cyber-physical systems. Cyber-physical systems provide the basis for the creation of an Internet of Things, which combines with Internet of Services. They are “enabling technologies” which make multiple innovative applications and processes a reality as the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds disappear.
Cyber-physical systems also represent a paradigm break from existing business and market models, as revolutionary new applications, service providers and value chains become possible
Industry sectors including the automotive industry, the energy economy and, not least, production technology will in turn be transformed by these new value chain models. In the future, cyber-physical systems will make contributions to human security, efficiency, comfort and health in ways not previously imaginable.