Volume transfer calculation !!
Flow calculation (volume transfer) using logaritme.
When you want to calculate a constant outlet flow from the left balloon (tank) to the right balloon (tank) , you can use a logaritmic function. Volume will change during this transfer in both balloons (tanks) as well as pressure.
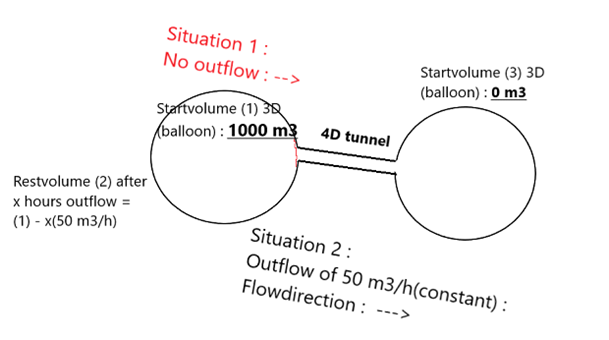
On earth using natural pressure using a higher placed (minimum 1 meter) , open cubitainer (1m³) , filled with water and using a bottompipe which is designed for an outlet flow of exact 50m³/h. Than let this flow into another cubitainer. There is a pressure difference of 1 meter water column (+/-0.1bar) in the beginning and because of , volume change in both cubitainers //and therefore also atmospheric pressure on both open cubitainers, during the transfer. You can eliminate volume and pressure (variables) using this method. Calculating a variable outlet flow and a residual volume in the left balloon (tank) , when it’s a closed system !!! (cubitainer will empty complete , but also here you’re able to calculate the flow at any time of the transfer.
You have a change of dimension here. Well it’s with a twist actually. A balloon with a volume of 1000 m³ transferring to a balloon with 0 m³ with a constant outlet flow of 50 m³/h does not seem to change dimension because it’s all m³. However the outlet flow through that ‘limited’ 50m³/h pipe is measured in m² (diameter of that pipe). So there is a change in dimension.
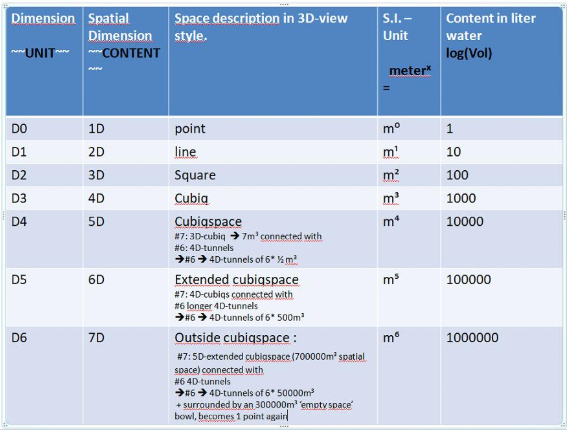
Here is a dimension table I’ve made for built up 3D ‘inside the box’ dimensions connected with ‘outside the box’ 4D energy tunnels. Imagine 3D ‘inside the box’ as a box with solid walls and ‘outside the box’ with open walls. Off course in the most ‘vast’ open minded way.
Next formula came out :
The logaritme of the constant outflow minus the restvolume in the first balloon (absolute value of this , so this is always the correct ‘positive’ residual volume in the left balloon) equals the outlet flow at any time.
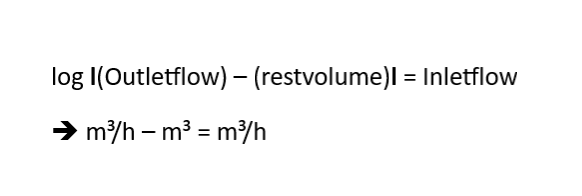
The outlet flow (positive flow into balloon 2) stops when log l1l = 0 is reached. Going over this point , which is impossible in a closed natural system where pressure balances out , log l0l = ∞. But going over this point means you have backflow and put a minus before this formula: – log l-1l = 0 (startingpoint of backflow)
Let’s see in an example :

And this formula looks very usefull for ‘Space’ calculations. mass that dissolves in black holes and the corresponding space shrinkage. This will eventually lead to an 'everlasting' process of big bangs (not from a point but an area equal to the residual volume of this formula log (1-1) till an 'infinite' log (0) 'big bang' , imo ). That's the goal in one , not sure if it's possible but insecure ET in everything is the nature (which is not required for anything at all , I know) but it is what it is. Please
