Periodontal diseases: causes, consequences and treatment | أمراض اللثة: الأسباب والعواقب والعلاج
Very frequent, periodontal diseases remain however unknown by the Moroccans. It is considered that they concern half of the adult subjects in our country. And their consequences can be serious and irreversible on the health of patients.
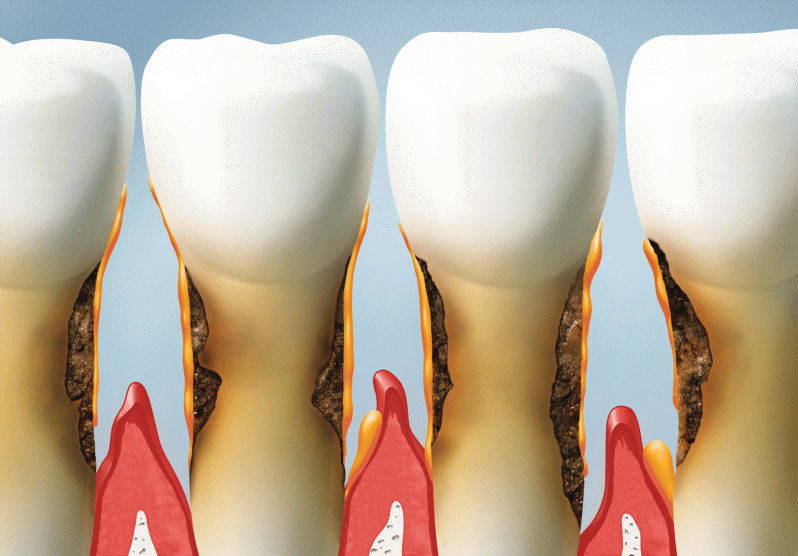
Periodontal diseases: infectious diseases to be taken seriously
These infectious diseases are due to the presence of pathogens contained in the dental plaque formed between the gingiva and the tooth. A large microbial mass can eventually attack the periodontium through the gingival sulcus (equilibrium zone between the tooth and the gum).
There are two types of periodontal disease, which correspond to two stages in the course of inflammation and then infection of the gingiva.
Gingivitis
Very common in adult patients (one person in two in Morocco), gingivitis is an inflammation caused mostly by poor dental hygiene. The affected gum is manifested by its red color and its swollen and smooth appearance. Brushing is painful and easily causes bleeding because of the sensitivity of the gums.
The causes of gingivitis are varied. Mild dental hygiene and incomplete brushing of teeth allow plaque and tartar to accumulate and trigger inflammation. But other circumstances can be the cause of gingivitis. This is particularly the case of hormonal changes during pregnancy. Tobacco, alcohol, and certain medications such as antidepressants are also identified as triggers for gingivitis.
Treatment of gingivitis
Treatment of gingivitis is done locally by the dentist, who performs a complete descaling. Thereafter, the patient will have to brush the teeth thoroughly and use dental floss to clean the interdental areas and remove the plaque. Rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash is also recommended.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can lead to worsening periodontal disease that will directly attack the periodontium and cause inflammation of the tooth support tissues. Periodontitis is particularly characterized by the formation of a periodontal pocket at the root of the tooth, in which the bacteria will proliferate. The alveolar bone, directly exposed to infection, will then resorb against microbial growth. This bone loss is usually associated with a gingival recession.
This stage of periodontal disease is of particular concern because the loss of alveolar bone, which supports teeth, ligaments and tissues, is irreversible.
The consequences on the teeth but also the health of the patient are potentially serious: tooth loosening, loss of all teeth, proliferation of bacteria in the body through the gingival tissue that can lead to serious complications (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, premature deliveries ...).
It is estimated that 25% of Moroccans suffer from periodontitis.
Treatment of periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis is necessarily longer and more complex than that of gingivitis.
The dentist usually performs a prophylactic check-up during a first consultation. This diagnosis based on salivary or even bacterial tests will enable the practitioner to identify pathogenic microbes in order to provide the most appropriate treatment.
Thereafter, the practitioner will employ conventional methods such as scaling and polishing of the affected teeth.
If there are significant periodontal pockets, and if it becomes necessary to operate, the dental surgeon may use root planing, which consists of directly treating the roots to eliminate bacteria using ultrasonic instruments. Once the gum is cleared of the periodontal pocket, the gum will then be able to re-adhere to the tooth. An antiseptic chemical treatment may be prescribed to accelerate healing.
The loosening of teeth can be restored through two complex procedures that only competent dentists can master:
- Guided tissue regeneration: this involves stimulating the patient's cells to repair lesions in the gingiva and eradicating the destructive effects of periodontal disease.
- The gingival graft: it consists in giving back the thickness and the height to the gingiva in order to stop the gingival recession. The practitioner takes a fragment of gum or palate in order to graft it at the level of the bare roots and restore the loopholes.
If bone loss is important, the dentist can use bone-substitute materials - called bio-bones - to fill the periodontal pockets and restore bone loss from gingiva caused by periodontitis.
ولا يزال المغربيون غير معروفين بشكل متكرر لأمراض اللثة. ويعتبر أنها تتعلق نصف البالغين في بلدنا. ويمكن أن تكون عواقبها خطيرة ولا رجعة فيها على صحة المرضى.
** أمراض اللثة: الأمراض المعدية التي ينبغي أخذها على محمل الجد **
وتعزى هذه الأمراض المعدية إلى وجود مسببات الأمراض الواردة في لوحة الأسنان التي تشكلت بين اللثة والسن. يمكن للكتلة الميكروبية الكبيرة في نهاية المطاف مهاجمة بيريودونتيوم من خلال التلم اللثوي (منطقة التوازن بين الأسنان واللثة).
هناك نوعان من أمراض اللثة، والتي تتوافق مع مرحلتين في مسار الالتهاب ثم عدوى اللثة.
التهاب اللثة ** **
شائع جدا في المرضى البالغين، التهاب اللثة هو التهاب الناجمة عن سوء نظافة الأسنان. تتجلى العلكة المتضررة من خلال لونها الأحمر ومظهرها المتورم والسلس. الفرشاة مؤلمة وسهولة تسبب النزيف بسبب حساسية اللثة.
وتتنوع أسباب التهاب اللثة. تنظيف الأسنان المعتدل والفرشاة غير مكتملة من الأسنان والجير لتجميع وإطلاق الاشتعال. ولكن يمكن أن تكون الظروف الأخرى سبب التهاب اللثة. هذا هو على وجه الخصوص حالة التغيرات الهرمونية خلال فترة الحمل. كما يتم تعريف التبغ والكحول وبعض الأدوية المضادة للاكتئاب كمحفز لالتهاب اللثة.
** علاج التهاب اللثة **
يتم علاج التهاب اللثة محليا من قبل طبيب الأسنان، الذي يؤدي إزالة الترسب الكامل. بعد ذلك، سوف يكون المريض لتنظيف الأسنان وإزالتها من لوحة. الشطف مع غسول مطهر ينصح أيضا.
اللثة ** **
التهاب اللثة غير المعالج يمكن أن يؤدي إلى تفاقم أمراض اللثة التي سوف تهاجم مباشرة بيريودونتيوم وتسبب التهاب الأنسجة دعم الأسنان. يتميز التهاب دواعم السن بشكل خاص بتشكيل جيب دواعم السن لجذور السن، حيث تتكاثر البكتيريا. والعظم السنخي، يتعرض مباشرة للعدوى، ثم ريسورب ضد النمو الميكروبي. وعادة ما يرتبط فقدان العظام هذا بالركود اللثوي.
هذه المرحلة من أمراض اللثة هي مصدر قلق خاص بسبب فقدان العظام السنخية، التي تدعم الأسنان والأربطة والأنسجة، لا رجعة فيه.
العواقب على أسنان المريض قد تكون خطيرة: تخفيف الأسنان، وفقدان جميع الأسنان، وانتشار البكتيريا في الجسم من خلال الأنسجة اللثوية التي يمكن أن تؤدي إلى مضاعفات خطيرة (أمراض القلب والأوعية الدموية والسكري والولادات المبكرة .. .).
وتشير التقديرات إلى أن 25٪ من المغاربة يعانون من التهاب اللثة.
** علاج التهاب اللثة **
علاج التهاب اللثة هو بالضرورة أطول وأكثر تعقيدا من التهاب اللثة.
وعادة ما يقوم طبيب األسنان بفحص وقائي أثناء االستشارة األوىل. ويستند هذا التشخيص على الاختبارات اللعابية أو حتى البكتيرية، وسوف تستخدم لتحديد الميكروبات المسببة للأمراض من أجل توفير العلاج الأنسب.
بعد ذلك، سيتم استخدام الممارس مثل توسيع وتلميع الأسنان المتضررة.
إذا كان هناك جيوب اللثة كبيرة، وإذا أصبح من الضروري للعمل، جراح الأسنان قد تستخدم تخطيط الجذر، والذي يتكون من معالجة مباشرة الجذور للقضاء على البكتيريا باستخدام أجهزة الموجات فوق الصوتية. مرة واحدة يتم مسح اللثة من جيب اللثة، فإن اللثة ثم تكون قادرة على إعادة التمسك الأسنان. ويمكن وصف العلاج الكيميائي مطهر لتسريع الشفاء.
يمكن استعادة تخفيف الأسنان
تجديد الأنسجة الموجهة: وهذا ينطوي على تحفيز خلايا المريض لإصلاح الآفات في اللثة والقضاء على الآثار المدمرة لأمراض اللثة.
- الكسب غير المشروع اللثوي: ويتكون في إعطاء الظهر سمك وارتفاع إلى اللثة من أجل وقف الركود اللثوي. يأخذ الممارس قطعة من اللثة أو الحنك من أجل طعمه على مستوى الجذور العارية واستعادة الثغرات.
إذا كان فقدان العظام مهم، يمكن لطبيب الأسنان استخدام المواد البديلة للعظم - ودعا العظام الحيوية - لملء الجيوب اللثة واستعادة فقدان العظام من اللثة الناجمة عن التهاب اللثة.
موضوع جيد تستحق% 100
thanks brother @digi5952 :)
Chokran fakartini rah darini chi darssate
HHHHhh sir zrab 3lihom 9bal matwada3hom. :D