Photosynthesis in Marijuana: How It Works
Photosynthesis: every plant on earth does it. Yes, even the cannabis plant. It’s the basis for all plant life. But, it’s not just crucial for plant life, it’s essential for all life. According to Wim Vermaas, “Without photosynthesis, the oxygen in the atmosphere would be depleted within several thousand years…”
If you are as fascinated by the above statement as we are, then you are likely looking for more insight into photosynthesis, and perhaps how it works in marijuana. Photosynthesis essentially involves taking the available light and transforming it into energy. This is the fundamental definition, but it goes a lot further than that.
In this article, we will be taking a closer look at how photosynthesis works in marijuana. If you already have a basic idea on how photosynthesis works for all plants, then the whole process will likely be very familiar to you. But, even if you are an expert, you might learn a thing or two about where the chemical reactions take place in the cannabis plant.

So, without further ado, let’s get into the concept of photosynthesis and marijuana.
How Photosynthesis Works in Marijuana
We will start out really simple, for those who feel like they have no clue about photosynthesis. Ultimately, it’s the process that all plants undergo to receive the energy that they need to grow. While humans - and most animals - need to ingest their food to convert it into energy, plants get theirs directly from the sun.
It’s important to note that this process is known as primary production. This is because plants use the Earth (well, the sun) as their “primary” source of energy to convert water into sugar and sugar into energy. Secondary producers are organisms that get their energy from eating plants, and tertiary producers (humans) are organisms that get their energy from eating the animals that eat the plants.
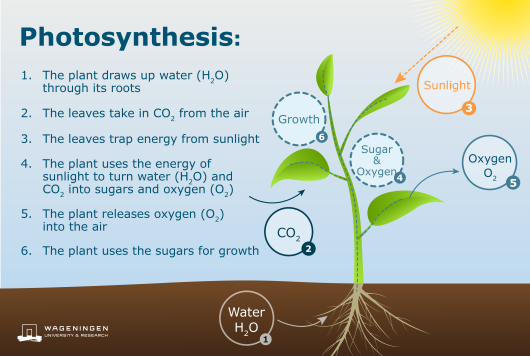
The process of photosynthesis involves turning the sun’s energy into chemical energy, which plants use to grow. The first step to understanding this is recognizing the fact that there’s energy present in sunlight; the brighter and more extreme the sunlight, the more energy is present. Although, even on a cloudy day, there’s typically more than enough sunlight to enable plants to photosynthesize.
Plants receive light through several pigments on their exterior. The most abundant pigment found in cannabis and, in fact, most green plants, is known as Chlorophyll. This is the component of the plant that is mostly responsible for letting in light energy. You could say that the cannabis leaves act as solar panels by extending the area in which the plant can take in light. Primarily, more leaves represent more power producers since you have more energy entering the plant.
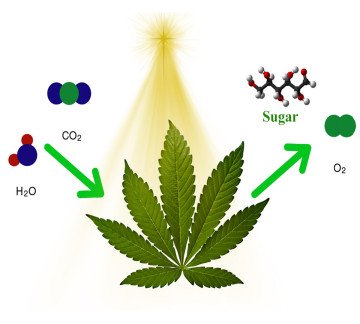
Once the energy from the sun is captured in the chlorophyll pigments, it’s used to break down carbon dioxide and water molecules so that they can be converted into glucose molecules for energy (sugar). This is the reason why plants need to be frequently watered.
Another important fact to note is that plants work in the opposite way to humans. While we breathe in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide, plants breathe in carbon dioxide and expel oxygen. You might call this the perfect balance of life. Here’s the general chemical process of photosynthesis:
Sunlight (energy) + water (H2O) + Carbon dioxide (CO2) → Glucose (sugar, C6H12O6)
Marijuana Plant Structures That Are Used for Photosynthesis
By now, you are probably wondering how this all takes place specific to the marijuana plant. Well, believe it or not, the cannabis plant’s most iconic, deep-green fan leaves that have become recognized as the universal “420” icon, could be classified as the plant’s most crucial structure when it comes to photosynthesis.
Because these fan leaves are long and skinny, they have a large surface area and therefore lots of chlorophyll. This enables them to maximize the amount of sunlight energy that they can capture and thus the amount of glucose that they can produce for growth and reproduction.

The cannabis plant has eight essential parts that you should be familiar with on a general level. The first two are:
- Trichomes: These are the tiny, sticky and shiny little crystals that cover the leaves and buds of the cannabis plant. They often appear as blankets of frost and have an amazing aroma. Originating from the Greek word “Tríchōma,” which means “growth of hair,” this is the part of the plant that produces the many different cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes. These are the elements that make different strains unique, potent, and effective.
- Pistil: Cannabis plants can be male, female, or both (hermaphrodite). The Pistil is the reproductive structure of the female cannabis plant. It’s another part of the plant that is packed with the infamous THC and other cannabinoids. The female plant produces the big, resin-secreting flowers that are cut down to pointed or round buds, while the male produces smaller pollen sacs close to the base of the leaves. Male plants pollinate female plants to initiate seed production (to reproduce).
We get it - this might not make a lot of sense, so let’s break it down. The cannabis plant goes through two stages of life: the vegetative stage and the flowering stage. The vegetative stage can be compared to childhood, since the plant is only focused on growing bigger and taller. Typically, about six weeks later, the plant will switch to the flowering stage. This is when the plant stops growing bigger and taller and spends all its effort growing flowers. This can be thought of as the adult stage, since this is when the plant becomes interested in only growing their male and female parts, and then pollinating. This is when the plant either starts growing buds or pollen sacs.
The male marijuana plants produce only small amounts of THC, and therefore can’t really get you high. This is why a lot of hemp-variety products, such as medical-grade CBD oils, come from the male cannabis plant.
The other six important parts of the cannabis plant are:
- Seeds: We all know what seeds are, and since we already mentioned that you get male and female marijuana plants, it should make sense that you get male and female seeds. If the purpose is to get high, then you would want the female plant. The problem is, it’s practically impossible to know whether a cannabis seed is male or female - usually until the plant flowers.
- Calyx (buds): More commonly known as the “buds,” the calyx is the first part of the flower that forms. It’s composed of a group of small leaves that form in a spiral shape, close to where the flower meets the stem. This part of the plant includes the trichomes, pistil, sugar leaves, and several other functional accessories. It’s ultimately what we break up and put into the grinder to stuff in a vaporizer or roll up in a joint.
- Stalk/stem: Like with all plants, the primary purpose of the stalk and stem is to provide structure to the plant. But, more than just this, they also provide a way for nutrients and other important compounds to be transported from the root of the plant all the way up to the leaves.
- Sugar leaves: These are the small, single-finger leaves that grow out of the calyx and shouldn’t be mistaken for the infamous fan leaves. The term “sugar leaf” is derived from the white frosting of trichomes that they have towards the end of the flowering phase. Fan leaves also have trichomes, but they are far less concentrated and thus less potent. Sugar leaves, on the other hand, produce an excellent high. For this reason, many growers trim the sugar leaves off and use them to make THC-concentrates. Others very much promote grinding them up to smoke, just like regular bud.
Fan leaves: These are the large, primary leaves of the plant that are filled with resin, flavor, and other phytonutrients. Their main purpose is to give a site for photosynthesis in cannabis. They don’t contain much THC, but are packed with chlorophyll, which allows for tons of sunlight energy to be absorbed and turned into sugar for use by other parts of the plant.
Final Thoughts on How Photosynthesis Works in Marijuana
While we have gone into a lot more detail than just photosynthesis, hopefully this article has given you better insight into how the marijuana plant is made up and what makes it so unique. Ultimately, the primary energy provided by the sun is absorbed by chlorophyll pigments found in the fan leaves, where it works to break down carbon dioxide and water molecules in order to produce the sugar needed for the plant to grow and reproduce.

That's a visually pleasing infographic on the female cannabis plant. Very nice! @GirlsofGreen love it! :) <3
Great post on photosynthesis in marijuana. Cannabis is an amazing plant ehuch is very useful to cure several diseases. 🌿🌿🌿🌿
Thanks @medicalmarijuana for sharing this post. ☺
Wonderfully detailed. We've always wanted to know but never before found it assembled so well!
upvote for me please? https://steemit.com/news/@bible.com/6h36cq
Congratulations you've been chosen by our curators at Canna-Curate for great cannabis content! If you'd like to join our curation trail or delegate steem power you can see how and the benefits here. Or if you'd just like to have a chat about cannabis you can join us on our discord server Steem Powered Cannabis