New treatment to repair damaged brain tissue: exosomes
This treatment, called AB126, is based on the use of extracellular vesicles, also known as exosomes, which are structures filled with fluid, generated in this case by human neural stem cells
Exosomes are small vesicles (30 to 150 nm) that contain complex RNA and protein loads. All types of cells in culture and appear naturally in body fluids, such as blood, saliva, urine, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and breast milk.
This type of regenerative therapy based on extracellular vesicles seems to be effective since exosomes are concealing abilities within the bloodstream, this type of regenerative therapy seems to be the best promise to overcome the limitations of many cell-based therapies, due to the ability of the exosomes to carry and release multiple doses, as well as to store and administer the treatment. Small in size, its tubular shape allows to overcome barriers that cells can not overcome.
These cells may be able to regenerate damaged brain tissue, by integrating into circuits that have been eroded by neurodegenerative diseases, or destroyed by injury.
Tests with this type of treatment showed a 35% decrease in damage size, and 50% less loss of brain tissue.
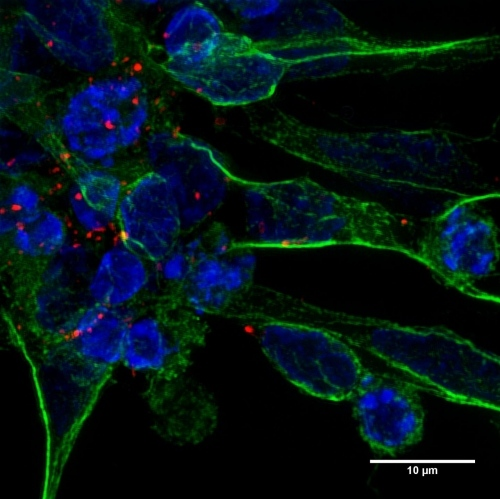
The exosomes, which are shown as small red dotted groups, are absorbed by the neurons, which appear as extensions of green cells surrounding blue nuclei.