Cryptocurrencies will boost illegal transactions: RBI to SC
Cryptocurrencies will boost illegal transactions: RBI to SC
Details:
The News
• According to Reserve Bank of India (RBI), dealing in cryptocurrency will encourage illegal transactions.
• The RBI has already issued a circular prohibiting use of these virtual currencies.
News Summary
Background:
Status of cryptocurrency in India:
• India accounts for more than 11% of global cryptocurrency trade.
• Though India does not specifically ban Bitcoin trading, but has repeatedly warned the public against cryptocurrencies.
• Platforms like ZebPay, CoinDelta, CoinSecure, etc., trade in Bitcoins, and you would have to pay rupees in exchange for Bitcoins.
Notification from RBI:
• The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) cautioned users, holders and traders of Virtual Currencies (VCs) including Bitcoins regarding the potential economic, financial, operational, legal, customer protection and security related risks associated in dealing with such VCs.
• RBI also clarified that it has not given any licence/authorisation to any entity/company to operate such schemes or deal with Bitcoin or any VC.
Government of India's clarification:
• The Finance Ministry issued a clear and detailed warning against VCs including Bitcoin, likening them to ponzi schemes, and underlining that those who deal with these VCs (will be doing so) entirely at their risk.
• Government clarified that it does not consider cryptocurrencies to be legal tender
Committee on cryptocurrencies:
• Government also constituted a Committee under the Chairmanship of Secretary, Department of Economic Affairs, who is deliberating over all issues related to cryptocurrencies to propose specific actions to be taken.
Legal status across world:
• The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies widely across the world, and is sometimes undefined or fluid.
• Some countries — like Japan — have recognized Bitcoin exchanges as legal.
Petitions before Supreme Court:
• Against cryptocurrency:Some petitions challenged the use of virtual currencies and alleged that they posed grave dangers to the traditional economy.
• And they also sought framing of guidelines to regulate them.
• It has sought to declare virtual currency as illegal and ban all websites, web links and mobile applications which were being used to buy, sell or deal in any manner with illegal virtual currencies.
Challenging RBI notification:
• While few other petitions have challenged the RBI notification on Prohibition on dealing in Virtual Currencies.
• They had said that the RBI, through its circular, had directed banks and financial institutions to freeze the bank accounts of those individuals and companies dealing in the illegal trade of virtual currencies.
• It alleged that the RBI has shrugged aside its duty to conclusively take a stand either in favour or against the illegal virtual currencies like Bitcoins in the interest of people of India.
Direction to Centre:
• They had sought a direction to the Centre to take steps to restrain sale and purchase of illegal cryptocurrencies like Bitcoins, which were being traded openly for illegal activities like funding terrorism and insurgency.
• It also sought a direction to the government to give advertisements and wide publicity through media informing and educating the public in India about the illegalities involved in sale, purchase and dealing of illegal virtual currencies.
• Earlier, the apex court, had transferred to itself the petitions pending in various high courts on virtual currencies and barred them from entertaining any plea in future relating to an RBI circular prohibiting dealings in such currencies.
Hearing in SC over cryptocurrency:
• A three judge bench, led by Chief Justice Dipak Misra, was informed by senior advocate, appearing for the RBI, that a committee has been set up by the Centre to deal with issues relating to cryptocurrencies.
• The federal bank and the Central government sought three weeks’ time from the Bench for filing their responses to a clutch of petitions on the issue.
Additional information:
What is a Cryptocurrency?
• A cryptocurrency is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses cryptography to secure its transactions, to control the creation of additional units, and to verify the transfer of assets.
• A cryptocurrency is difficult to counterfeit because of this security feature.
• A defining feature of a cryptocurrency, and arguably its most endearing allure, is its organic nature; it is not issued by any central authority, rendering it theoretically immune to government interference or manipulation.
What is cryptography?
• Cryptography is associated with the process of converting ordinary plain text into unintelligible text and vice-versa.
• It is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it.
What is Bitcoin?
• Bitcoin is the first decentralized cryptocurrency.
• In 2008, a paper titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System, appeared online via the Cryptography Mailing List.
• The paper came in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, and stemmed from inherent trust problems that the crisis had laid bare in the traditional banking system.
• Bitcoin was the first implementation of the concept of Cryptography based on above paper.
• The first software version of Bitcoin client was released in 2009.
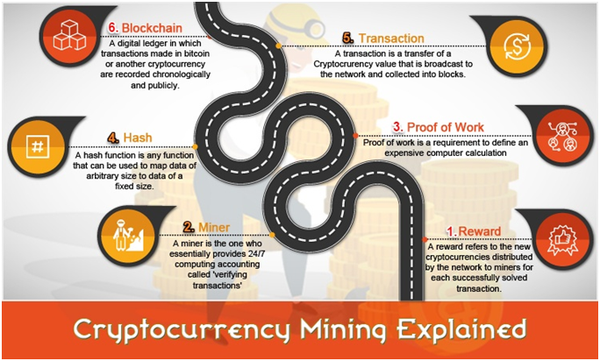
How cryptocurrencies mining works?
• Cryptocurrencies mining is the process through which coins are released to come into circulation.
• And mining happens when computers on the network solve complex mathematical problems, and are rewarded with new coins.
• Basically, it involves solving a computationally difficult puzzle to discover a new block, which is added to the blockchain, and receiving a reward in the form of few cryptocurrency.
• So, it is peer-to-peer based, and functions through a technology called Blockchain — a kind of open ledger that gets updated in real time.
What is Blockchain technology?
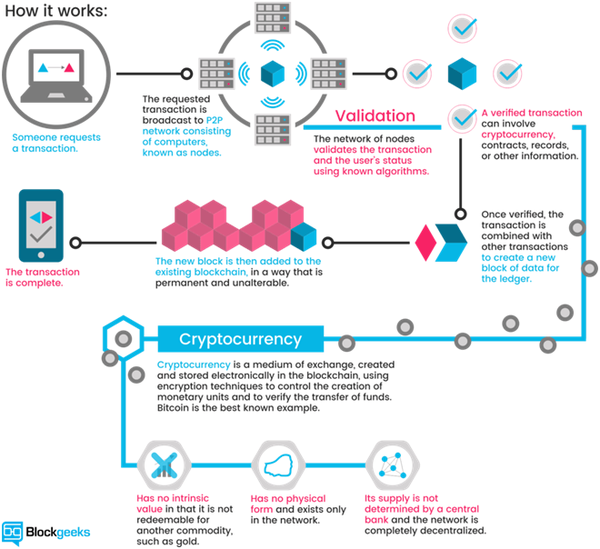
• Blockchain is the core technology on which the cryptocurrency is built. It is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography.
• A new block is effectively added every time a transaction is made.
• Each node (computer) involved in the network helps to maintain this record.
• Each transaction on the network can be traced on this Blockchain.
• Anyone who joins the cryptocurrency network can crosscheck the transactions and help maintain these blocks.
• So it is decentralised ledger system which could replace everything from property transactions to bank records, might just be the future, argue technologists.
How does the Blockchain technology verify transaction?
• Computers on the cryptocurrency network verify transactions on the Blockchain via the digital signatures that are attached to each transaction.
• For example, Bitcoin relies on what is known as elliptic curve cryptography — a form of encryption in which each digital signature has a public key and a private key attached.
• Each cryptocurrency also has its own address. For users who might not necessarily be developers or on the network, there are software and wallets to keep track of the number of coins they have associated with their accounts.
What are issues with cryptocurrency?
• Hacking: Various reports of hackings at several exchanges have exposed the risks attached to such investments.
• Illegal use: They have been used in crime, drug-dealing and other illegal activities on the dark web.
• Volatility: The intense volatility of Bitcoin, in stark evidence last month, makes it an unacceptably risky investment for many. A spectacular rally that saw Bitcoin rise from under $ 1,000 at the beginning of the year to an all-time of high $ 19,000 in mid-December-2017 and then plunge dramatically to $ 12,000 within 10 days.
• Acceptability: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum represent a powerful idea. But they are not widely accepted yet.