Formal language of the logic // Philosophy
Source of image of pixabay

Aristóteles as a manuscript of his History naturalis of 1457, source of image of mastery of Wikimedia Commons, Author: unknown medieval author
The logic aristotélica under the concept where it is an idea, which is obtained abstracting certain characters to all the objects that possess it, in contrast to the image that it represents to a concrete object, the concept represents to all the objects of the same genre. The first logical operation that is realized by the concept is that of compression, the second logical operation is that of extension, which refers to the totality of the objects to which the concept can be applied.
If the first logical form of the human understanding is that of the concept, the second one is that of the judgment the operation by which relations of affirmation are established, the judgment consists of three elements: I hold (S), predicate (P) and coitus or connection of union between both, where it constitutes also the base of the knowledge, since by means of in the particular thing it is included in the universal thing, in order to avoid confusions to the judgment it gets accustomed to naming the proposition. The third form elementary logician is that of the reasoning, operation in which it goes over to the truth or falsity of a proposition from other one, to prove a possible truth or falsity of a particular proposition, the reasoning is deductive, if it happens on the contrary promoting from the particular thing to the general, of that time thing the reasoning it is inductive.
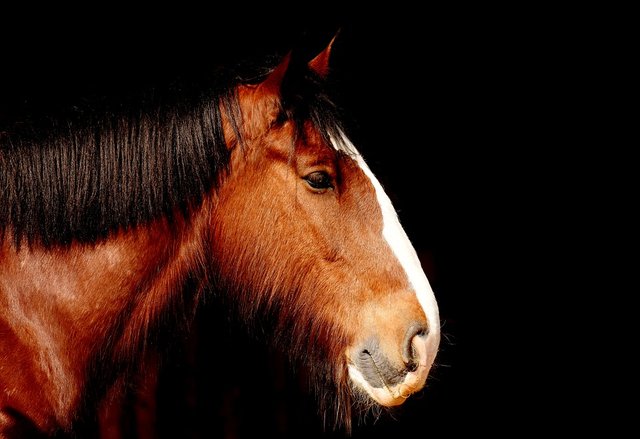

When we see these image, we see a concrete horse, of brown color, black mane and with a spot white and lengthened in his front, on the other hand if we think about the word horse, there will occur to us the concept of horse, which to formed by the vision of other concrete horses, from which we extract different characters that they they all possess and that we generalize in only one idea of horse, source of image of pixabay
One of the traditional forms of the deductive reasoning is the syllogism, Aristóteles distinguished three beginning as it they are: the beginning of identity, the beginning of not contradiction and the beginning of the excluded third one.
1. The beginning of identity affirms that any thing is equal to if THE same (A=A).
2. The not contradiction beginning mentions us that it is impossible, that a thing is and is not at the same time, like also same concepts (To puede to be simultaneously =B≠B).
3. For last the beginning of the excluded third one enunciates that A will prove = B or ≠B, being excluded any other possibility.
This three beginning constitutes the indemonstrable ones, since it are considered that you should provide it based on them they were of for if clear and they did not need any demonstration, Aristóteles supported that it was ontological beginning, in them there was happening the confluence of the structures of the thought with those of the being.

Source of image of pixabay
The syllogism in the logician aristotélica one of the important points, is what they constitute the doctrine of the syllogism, which is the argument in which, established certain things it results necessarily from them, for being what they are another thing different of previously established. While the deductive reasoning, the syllogism contains a conclusion derived from the premises, in the classic example the conclusion of the judgment, Sócrates is a mortal leeway of the premises “ all the men are mortal ”, but these it is an incorrect syllogism from the logical point of view, since a correct syllogism is the one that it supports in the following topic:
If To es preached where it is real of B and B is preached of everything C, where A is preached by it of everything C, Aristóteles thought that it was an excellent method of demonstration, any time it was based on real information.
In contrast to the logician classic and the modern one has rejected any form of consideration ontological, since it does not divide dela idea that the laws of the thought are also those of the being, his essential target is of arranging the formal laws of the thoughts without presupposing for them any reality, which there excludes the dimensione of the metaphysics, which the logician was containing ancient. The modern logician to verify with major rigor the validity of the reasonings, bases on a system of symbolic notation and thanks to this one it uses of the logical calculation.
The modern logic consequently is a symbolic logic and they split into two big paragraphs: that of the logic proposicional the one that analyzes the propositions in his unit and that of the logic of class, which treats of the internal structure of the propositions.
Bibliography
Knowledge, thought and language for Elena Teresa José - 2006.
The logic of the freedom: Reflections and replies for Michael Polanyi - 2009.
Philosophy of the logic for Raúl Orayen, Alberto Moretti - 2004.

Congratulations @ghost78! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click here to view your Board of Honor
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP