Physics - Classical Mechanics - Cross-Sectional Stress and Strain
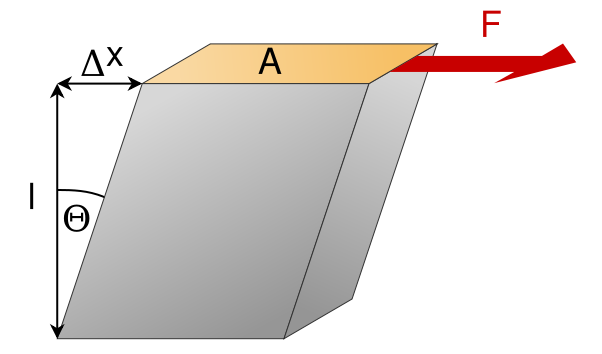
[Image 1]
Introduction
Hey it's a me again @drifter1! Today we continue with Physics and more specifically the branch "Classical Mechanics" to continue with the chapter of Equilibrium and Elasticity. In this article we will get into Cross-Sectional Stress and Strain. So, without further ado, let's dive straight into it!
Shear Stress
Shear stress arises from parallel forces that tend to cause deformation along a plane or planes parallel to imposed stress. What differentiates shear stress from "normal" stress is that "normal" stress arises from forces perpendicular to a cross-sectional area of the material, whilst shear stress is parallel to the cross-sectional area. Such forces cause the material to rotate about the application point.Mathematically, the shear force per unit area on the face of a cross-section is defined as:
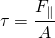
The most common symbol of shear stress is τ (tau). Shear stress is measured in force per unit area (N/m2) or pascals (Pa).
Shear Strain
The deflection of a point B per unit length, as a result of shear stress, is defined as shear strain. Its equal to the translation of point B, x, divided by the initial height of the material, L. Mathematically speaking: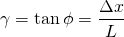
Shear strain γ is positive when it causes the right angle of the 1st quadrant to decrease. In the same way, shear strain is negative if it causes that same angle to increase. The angle is measured in radians, which is a non-unit, making shear strain dimensionless.
Shear Modulus
In the same way as we defined Young's modulus for tensile stress and strain, and Bulk's modulus for volumetric stress and strain, we can also define a modulus for shear stress and strain. Shear Modulus is a value that can be used for measuring the ability of a material to withstand shear stress. Shear Modulus is also defined as the modulus of rigidity. Mathematically: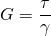
- G, shear modulus
- τ, shear stress
- γ, shear strain
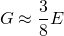
RESOURCES:
References
- https://www.britannica.com/science/shear-stress
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/shear-strain-definition-equation.html
- http://www.ah-engr.com/som/3_stress/text_3-2.htm
Images
Mathematical equations used in this article, where made using quicklatex.
Previous articles of the series
Rectlinear motion
- Velocity and acceleration in a rectlinear motion -> velocity, acceleration and averages of those
- Rectlinear motion with constant acceleration and free falling -> const acceleration motion and free fall
- Rectlinear motion with variable acceleration and velocity relativity -> integrations to calculate pos and velocity, relative velocity
- Rectlinear motion exercises -> examples and tasks in rectlinear motion
Plane motion
- Position, velocity and acceleration vectors in a plane motion -> position, velocity and acceleration in plane motion
- Projectile motion as a plane motion -> missile/bullet motion as a plane motion
- Smooth Circular motion -> smooth circular motion theory
- Plane motion exercises -> examples and tasks in plane motions
Newton's laws and Applications
- Force and Newton's first law -> force, 1st law
- Mass and Newton's second law -> mass, 2nd law
- Newton's 3rd law and mass vs weight -> mass vs weight, 3rd law, friction
- Applying Newton's Laws -> free-body diagram, point equilibrium and 2nd law applications
- Contact forces and friction -> contact force, friction
- Dynamics of Circular motion -> circular motion dynamics, applications
- Object equilibrium and 2nd law application examples -> examples of object equilibrium and 2nd law applications
- Contact force and friction examples -> exercises in force and friction
- Circular dynamic and vertical circle motion examples -> exercises in circular dynamics
- Advanced Newton law examples -> advanced (more difficult) exercises
Work and Energy
- Work and Kinetic Energy -> Definition of Work, Work by a constant and variable Force, Work and Kinetic Energy, Power, Exercises
- Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces -> Conservation of Energy, Conservative and Non-Conservative Forces and Fields, Calculations and Exercises
- Potential and Mechanical Energy -> Gravitational and Elastic Potential Energy, Conservation of Mechanical Energy, Problem Solving Strategy & Tips
- Force and Potential Energy -> Force as Energy Derivative (1-dim) and Gradient (3-dim)
- Potential Energy Diagrams -> Energy Diagram Interpretation, Steps and Example
- Internal Energy and Work -> Internal Energy, Internal Work
Momentum and Impulse
- Conservation of Momentum -> Momentum, Conservation of Momentum
- Elastic and Inelastic Collisions -> Collision, Elastic Collision, Inelastic Collision
- Collision Examples -> Various Elastic and Inelastic Collision Examples
- Impulse -> Impulse with Example
- Motion of the Center of Mass -> Center of Mass, Motion analysis with examples
- Explaining the Physics behind Rocket Propulsion -> Required Background, Rocket Propulsion Analysis
Angular Motion
- Angular motion basics -> Angular position, velocity and acceleration
- Rotation with constant angular acceleration -> Constant angular acceleration, Example
- Rotational Kinetic Energy & Moment of Inertia -> Rotational kinetic energy, Moment of Inertia
- Parallel Axis Theorem -> Parallel axis theorem with example
- Torque and Angular Acceleration -> Torque, Relation to Angular Acceleration, Example
- Rotation about a moving axis (Rolling motion) -> Fixed and moving axis rotation
- Work and Power in Angular Motion -> Work, Work-Energy Theorem, Power
- Angular Momentum -> Angular Momentum and its conservation
- Explaining the Physics behind Mechanical Gyroscopes -> What they are, History, How they work (Precession, Mathematical Analysis) Difference to Accelerometers
- Exercises around Angular motion -> Angular motion examples
Equilibrium and Elasticity
- Rigid Body Equilibrium -> Equilibrium Conditions of Rigid Bodies, Center of Gravity, Solving Equilibrium Problems
- Force Couple System -> Force Couple System, Example
- Tensile Stress and Strain -> Tensile Stress, Tensile Strain, Young's Modulus, Poisson's Ratio
- Volumetric Stress and Strain -> Volumetric Stress, Volumetric Strain, Bulk's Modulus of Elasticity, Compressibility
Final words | Next up
And this is actually it for today's post!Next time we will get into the Elasticity and Plasticity of common materials...
See ya!


Keep on drifting!
Congratulations @drifter1! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPThis post has been voted on by the SteemSTEM curation team and voting trail. It is elligible for support from @curie and @minnowbooster.
If you appreciate the work we are doing, then consider supporting our witness @stem.witness. Additional witness support to the curie witness would be appreciated as well.
For additional information please join us on the SteemSTEM discord and to get to know the rest of the community!
Please consider using the steemstem.io app and/or including @steemstem in the list of beneficiaries of this post. This could yield a stronger support from SteemSTEM.
Hi @drifter1!
Your post was upvoted by @steem-ua, new Steem dApp, using UserAuthority for algorithmic post curation!
Your UA account score is currently 3.527 which ranks you at #6775 across all Steem accounts.
Your rank has not changed in the last three days.
In our last Algorithmic Curation Round, consisting of 101 contributions, your post is ranked at #23.
Evaluation of your UA score:
Feel free to join our @steem-ua Discord server
Congratulations @drifter1! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard: