MUSCLE SPASMS OR CLAMBRES
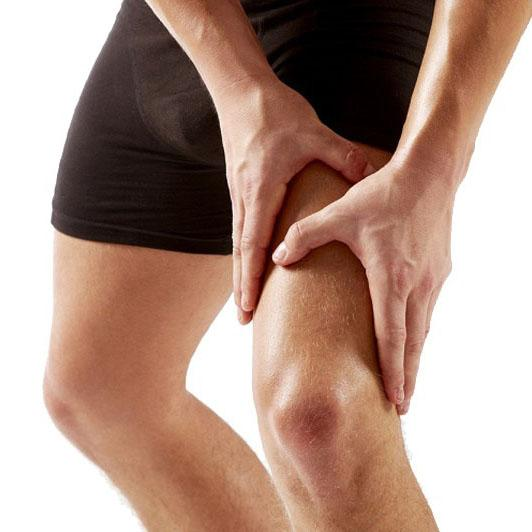 )
)MUSCLE SPASMS
Muscle spasm
Soldier running in water original.jpg
Spasms are common in athletes when they do not warm up
Classification and external resources
ICD-10 R25.2
ICD-9 728.85
CIAP-2 L14
DiseasesDB 3151
MedlinePlus 003193
MeSH D013035
Synonyms
Muscle cramp
Muscle contracture
Wikipedia is not a medical office Medical notice
[edit data in Wikidata]
Muscle spasm or cramping (from fr. Crampe, and this perhaps from the frank * kramp; see ramp) 1 is a sustained and involuntary contraction of a muscle or group of muscles, which presents with mild or intense pain, and which can make these muscles harden or bulge. It can occur due to insufficient oxygenation of the muscles or the loss of fluids and mineral salts as a result of prolonged effort, sudden movements or cold. In most cases it is harmless and disappears after a few minutes (it is also known as muscle "pull"). Poisoning or certain diseases can also cause cramping, particularly in the stomach. Normally they can be relieved or eliminated by performing stretching exercises on the affected area, resting and, in more persistent cases, taking some type of muscle or anti-inflammatory relaxant
In the case of people who perform a lot of exercise or a continuous exercise, it is advisable to drink isotonic drinks, which contain the ions that the muscles need to reduce fatigue or recover earlier. The spasms produced in a fibromyalgia box occur in the same way, but their recovery is slower and almost always causes contracture in the spasmed area.
The spasm of muscle contracture should be distinguished. The latter, being also a painful and involuntary shortening of a muscle, is more lasting (can last from days to months) and less painful than a muscle cramp; In addition, lengthening or massage does not relieve symptoms.2 Possible causes of a contracture are nervous tension, poor posture, excessive exercise, fibromyalgia, psycho-emotional problems, and other pathologies that cause muscle blockage.
types of muscle spasms:
there are two basic classifications
During the effort: the spasms are produced by the accumulation of metabolic waste within the muscle fiber; They are usually caused by sudden movements

After the effort: the spasms occur by the stretching of the muscle fiber or by the excessive work that was done during the effort.

Treatment
At the first sign of muscle spasm, it is recommended to suspend the activity and try to stretch and massage the affected muscle. Initially, heat helps relax the muscle, although the application of ice may be useful after the initial spasm and when the pain has subsided. If muscle pain persists, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be used and, in more severe cases, the doctor may prescribe antispasmodic or muscle relaxant medications. After the initial treatment, the cause of the spasm should be determined to prevent recurrence and if there is an irritated nerve compromise, it may be necessary to resort to physiotherapy or even surgery
prevention
Do stretching to improve sensitivity.
Modify training sessions to exercise within the capabilities
Drink plenty of fluids while exercising and increase the intake of potassium that can be found in sources such as orange juice, bananas and tomatoes
Occasionally, preventive treatment with calcium dobesilate or aluminum hydroxide can help reduce the frequency of seizures
THANK YOU FOR READING MY POST


Soldier running in water original.jpg
Spasms are common in athletes when they do not warm up
Classification and external resources
ICD-10 R25.2
ICD-9 728.85
CIAP-2 L14
DiseasesDB 3151
MedlinePlus 003193
MeSH D013035
Synonyms
Muscle cramp
Muscle contracture
Wikipedia is not a medical office Medical notice
[edit data in Wikidata]
Muscle spasm or cramping (from fr. Crampe, and this perhaps from the frank * kramp; see ramp) 1 is a sustained and involuntary contraction of a muscle or group of muscles, which presents with mild or intense pain, and which can make these muscles harden or bulge. It can occur due to insufficient oxygenation of the muscles or the loss of fluids and mineral salts as a result of prolonged effort, sudden movements or cold. In most cases it is harmless and disappears after a few minutes (it is also known as muscle "pull"). Poisoning or certain diseases can also cause cramping, particularly in the stomach. Normally they can be relieved or eliminated by performing stretching exercises on the affected area, resting and, in more persistent cases, taking some type of muscle or anti-inflammatory relaxant
The spasm of muscle contracture should be distinguished. The latter, being also a painful and involuntary shortening of a muscle, is more lasting (can last from days to months) and less painful than a muscle cramp; In addition, lengthening or massage does not relieve symptoms.2 Possible causes of a contracture are nervous tension, poor posture, excessive exercise, fibromyalgia, psycho-emotional problems, and other pathologies that cause muscle blockage.

types of muscle spasms:
there are two basic classifications
During the effort: the spasms are produced by the accumulation of metabolic waste within the muscle fiber; They are usually caused by sudden movements

After the effort: the spasms occur by the stretching of the muscle fiber or by the excessive work that was done during the effort.

Treatment
prevention
Do stretching to improve sensitivity.
Modify training sessions to exercise within the capabilities
Drink plenty of fluids while exercising and increase the intake of potassium that can be found in sources such as orange juice, bananas and tomatoes
Occasionally, preventive treatment with calcium dobesilate or aluminum hydroxide can help reduce the frequency of seizures
THANK YOU FOR READING MY POST

