General Psychology Summary 13 lessons at Bangkok University
In Lecture 1: Overview and Introduction to general Psychology
Psychology is the study of mind and behavior.

Lecture 2: Psychology as a science dealt with the question: if Psychology is a science?
We came to the conclusion: yes, Psychology is a science because it uses the scientific method ( systematic empiricism, replication, peer review, empirical questions) to gain evidence.
Further pro arguments are the success stories in psychology based upon lab experiments i.e. bystander behavior and the fact that certain areas are scientific e.g. physiological and genetic psychology and neuroscience
Additionally, I learned that Inductive Reasoning is from particular to general e.g. scientists may observe instances of natural phenomenon and derive a general law. And Deductive Reasoning starts from general and ends with a particular statement. E.g. Start with a Theory and look for instances that confirm it.
Lecture 3: Nature Versus Nurture dealt with the question: What makes Us, Us?
Is it our environmental factors like upbringing or life experiences (nurture) or our genetics (nature)?
We came to the conclusion that it is a combination of these two “the Epigenetics” or “above genetics”. It deals with how nature and nurture interact. It is proven that our choices we make during our lifetime that lead to our lifestyle including nutrition, exercise, smoking, stress and love have an effect on our genetics. Epigenetic changes that will activate or deactivate genes happen throughout our lives depending on the lifestyle choices we make.
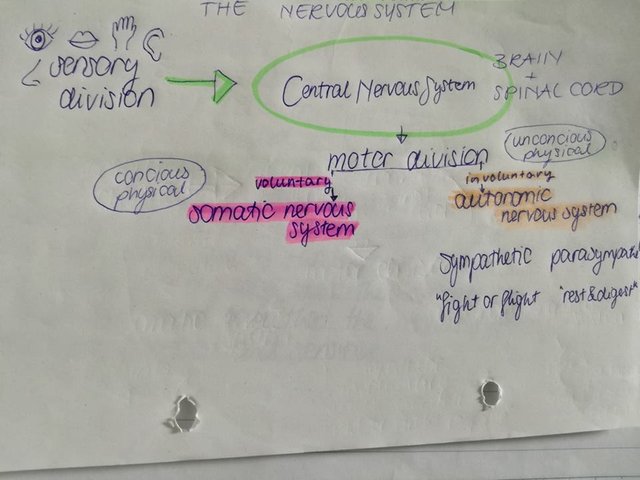
In Lecture 4: The Nervous System I learned that the nervous system plays a vital role in the body because it sends, receives and interprets incoming information. It is divided into two main parts the central nervous system consisting of first of all the brain and the spinal cord which acts like the processing center for all information. And second the peripheral nervous system consisting of the sensory division that sends information from our senses (sight, taste, touch, hearing, motion, smell) to the CNS through sensory neurons. And the motor division which takes the information from the CNS and sends it to the target cells in order to cause an action. In the motor division we have to differentiate between the somatic and autonomic nervous system, where the somatic NS is in control of voluntary movements and the autonomic NS controls involuntary responses in fact it takes information from CNS to target cells involuntarily. The autonomic NS is divided into the sympathetic and the parasympathetic division. The sympathetic division activates in “Flight or fight situations” or during exercise where it speeds up our heartrate involuntarily. The parasympathetic division gets active during resting and digesting where the heartrate slows down.
Lecture 5 was about “The Endocrine System” which consists of several endocrine glands that send specific hormones via the circulatory system towards their target organs in order to regulate their function and activity. The average human as a pineal gland that mainly coordinated our sleeping patterns. A pituitary gland, which leads the Endocrine system and produces growth hormones. A pancreas, which produces the hormone insulin in order to keep our blood sugar level stable and use the glucose in our food in order to transform it into energy. A thyroid, which regulates our metabolism. And adrenal glands, which are mainly producing stress hormones. In addition women have ovaries as reproductive glands and men have testes as reproductive glands.
Lecture 6 was about “Sensation and perception” it mainly focused on whether we use Top-Down or Bottom-Up processing. Bottom- Up processing is a data-driven approach stating that perception directs cognition. Meaning we experience our environment with our senses (sensation) and this information gets processed afterwards (cognition). Top-Down processing states that our behavior is influenced by conceptual data. Meaning that expectations lead our perception and behavior.
During Lecture 7: Personality I got to know the OCEAN model, where personalities are never fixed and that they are always dynamic within a continuum from positive aspects to negative aspects of this triad of personality. O stands for Openness to experience, C is for Conscientiousness, E-Extraversion, A-Agreeableness, N-Neuroticism. Furthermore we discussed CORPS-Experimental-learning where concrete experience (bottom-Up-processing) leads to reflection (analyzing the experience), that leads to abstract conceptualization (imagination, creativity), which leads to active experimentation of the idea.

In Lecture 8 “Learning and Thinking” I learned how we learn trough cognition. Cognition is the process of acquiring and understanding knowledge through thoughts, experiences and senses. Learning means acquiring knowledge through experience, study or tuition. Learning and cognition go hand in hand because learning involves cognition and Cognition involves learning. The first step in the cognitive learning process is attention, the average person can hold 2-4 learned tasks in their attention at the same time. And the average person can only attend to one complex task at a time. The information you are paying attention enters the memory in a process called storage. First step is the sensory register it holds every information you are exposed to for 1 or 2 seconds. If you revise the information or feed it with more memorable details the information moves from the sensory register into the Short-Term Memory which will hold the information from 20 seconds up to a minute. If you rehearse the information it moves to the Long-Term Memory this area will hold the information indefinitely and has unlimited capacity. The only difficulty can be finding information in there. The process of assigning a specific meaning to the learned information called Encoding can help with that difficulty. Encoding is a process where one assigns or feeds information with more memorable details or puts it into a code in order to remember it easily i.e. OCEAN model for triads of personality. Furthermore I learned about two education psychology pioneers. First of all, John Piaget who was a constructivist which means he thinks all knowledge is built piece by piece. Meaning that one idea he called schema is built out of many small parts (schemata) the idea can represent any information. In this way he believed children learn by building up new schema every time they get introduced to some new information/ experience. Next to Piaget one has to mention Robert Gagne who developed the information processing model of learning. Which consists of 3 main parts. Firstly gain students attention (priming), second acquisition and performance (convey the info that you want to teach), encoding is used in order to help students keep the info and students are quizzed for retrieval of the info and the info is reinforced with positive feedback, third transfer of learning is achieved by providing a final quiz to retrieve the info and helping the student to learn how to transfer the info into other areas of life in order to gain more knowledge by themselfs (enhance curiosity)
Lecture 9: Motivation, Drives and Emotion
First of all start with a definition of Motivation. Motivation are feelings or ideas that cause us to act towards a goal. The Instinct theory is one of the basic motivational theories. It says we are motivated by our inborn automated behaviors, but it only explains a small fraction of our behaviors. The Drive Reduction Theory states that our behavior is motivated by biological needs (food, water shelter etc.) in order to maintain balance (homeostasis) in our bodies. The Arousal theory (biological excitement) says that every human is motivated to seek an optimum level of arousal. In addition while talking about motivation we have to mention Incentives. Where our needs push, incentives (positive or negative stimuli) pull us in reducing our drives. Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs suggests that certain needs have priority before others. And that they built up like a pyramid. Starting with physiological needs (Need to satisfy hunger and thirst), second safety needs (need to feel that the world is organized, safe, stable and predictable). Third belongingness and love needs (Need to love and be loved and accepted). Fourth esteem needs (need of self-esteem, achievement, competence, independence need for recognition and respect from others). Fifth and final are the self-actualization needs, this is the need to live up to/realize one’s fullest and unique potential. Which is a very individual need but I is often expressed by creative working, a quest for spiritual enlightenment or the desire to positively influence the world and society around us.
Lecture 10: Mental Illness
Starting with signs for anxiety: reduced concentration, difficulty in making decisions, panic attacks, problems to carry out everyday tasks, reduced memory, irritable and angry they may also run away from their problems.
Signs for Depression are: sadness, anger, low self-esteem, self-blame/criticism, neglecting responsibility, worst case lost in appearance and hygiene.
Bipolar disorder or disorder of the moods:
It is difficult for them to maintain jobs and relationships because they are easily distracted, have huge mood swings from a lot of energy to no energy from sad and pessimistic to talking very quickly.
Schizophrenia is a detachment from reality it can be manifested in visual or auditory hallucinations or sometimes a split personality.
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD):
Feelings of anxiety, obsessive behavior, insecurity manifested in repeated actions like washing and cleaning ritually and sometimes a fixation on numbers.
The Alien Hand’s Disorder:
Patients with this disorder feel that something has taken control over their hands. Symptoms like choking themselves or acting without consciousness are common.
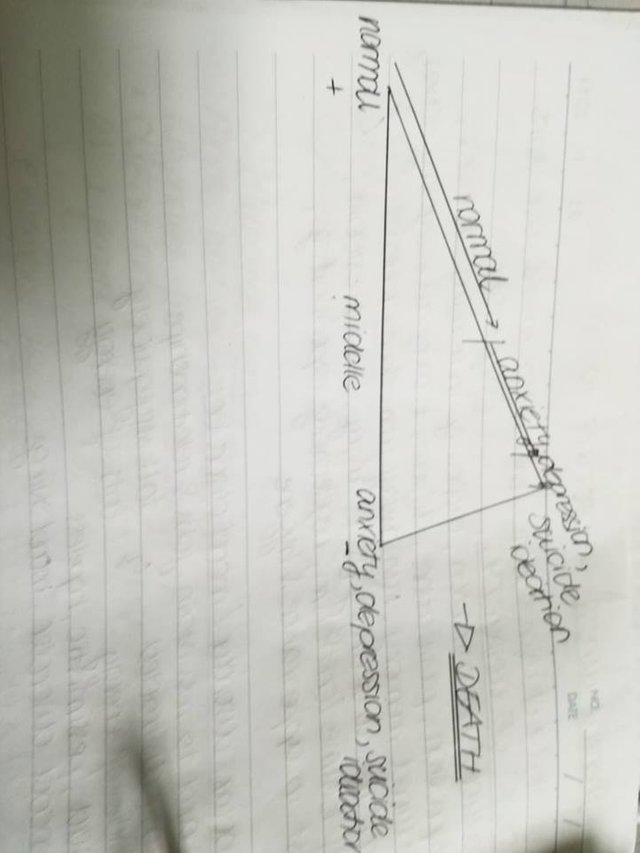
Furthermore I learned that it is possible that stress increases to anxiety, anxiety increases to depression, depression can increase to suicide ideation and if not stopped suicide ideation leads into death.
Lecture 11: Psychological Therapies
Starting with biological therapies. These usually use drugs like antidepressants to make the mental ill patient controllable and stable. Like every drug antidepressants or anti-anxiety-drugs (tranquilizers) have negative side effects and are not a long-term solution.
Another biological therapy is Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a procedure, done under general anesthesia, in which small electric currents are passed through the brain, intentionally triggering a brief seizure. Hoping to cure mental illnesses.
Psychodynamic therapy or Psychoanalysis is the exploration of unconscious motives and conflicts while talking with a therapist. A transference occurs when clients transfer unconscious emotions onto the therapist.
Behavior therapy is classical and operant conditioning to change problematic behavior. For Example conditioning a dog to stay in a cage for a long time. As soon as the dog can leave the cage is is most likely to stay in the cage, because he got conditioned to accept his fate.
Graduated exposure/ systematic desensitization is put into practice by exposing the client to his fears little by little. In contrast Flooding all at once means to take the client directly into the feared situation. This is not a recommended method since the client’s reaction can be fatal.
Another Therapy is Behavioral self-monitoring i.e. writing diary.
Cognitive therapy aims to identify and change irrational and unproductive ways of thinking to reduce negative emotions.
CBT Cognitive-Behavioral-Therapy is widely used because it focuses on the fact that behavior and thoughts influence one another so cognitive and behavior therapy have to go hand in hand in order to help the client.
Carl Rogers had a very large impact on Humanist therapy. It is a method where the therapist treats the client as a friend, it is very client centered. It is for people who seek self-actualization, self-fulfillment and it emphasizes the free will to change
Existential Therapy means exploring the meaning of existence, taking a personal responsibility for life and facing issues of life like death, freedom, free will or loneliness
Finally there is Family or couple therapy, it has the goal is to find out: What is the problem? What are the common solutions? And how everyone can benefit? By the way it is important to mention that a coupe/family therapist never takes sides.

Lecture 12: Stress Management and how to solve problems
What is a problem? It can be a thought, idea or situation that causes you to get stressed. It starts with the problem, then you make a decision whether the issue is solvable= End of problem or unsolvable that leads you back to the problem and causes stress.
How solve problems as a psychologist?
First identify the problem. Second identify solutions and prioritize them. Third implement them according to client’s responses and reactions. Fourth reassess the therapy session by asking 5 questions. 1. What did we cover? 2. Was there any change or improvement? 3. What were the negative indications/responses? 4. What is the next step/ action/ task? 5. Flexibility to flow and how do I decide when therapy ends?

Lecture: 13 Psychological Research
Starting with Informal observations that lead to a research question. Now one has to conduct an empirical study. After that one has to analyze the data and find a conclusion of the research problem which can lead to another research problem. Furthermore one has to research more literature or review it. This can lead to another research question.
Congratulations @annegreat! You have completed some achievement on Steemit and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCongratulations @annegreat! You received a personal award!
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
Do not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!