Edelman, neural darwinism, biology of consciousness
First i would encourage to read the two previous articles i made, as they are part of a same serie.
https://steemit.com/spirituality/@h0bby1/metaphysics-alchemy-and-algebra
https://steemit.com/spirituality/@h0bby1/kundalini-chakra-and-veda
Some peoples can frown when they see talks about chakra or alchemy because they are esoteric topics, but in reality, they are ancient science who are both accurate when it come to modern discovery, and can help understand modern science at its fundemental level.
I always find this amazing how for example the veda could figure out the structure of the mind through kundalini and chakra relatetively accurately, when one compare this to classic freudian psychology, can see the same pattern, as well as how hinduism could find the evolution order by studying level of consciousness of vegetals, fish, land animal to humans.
To put it in the context of freudian psychology, it can be matched that way
root chakra = 'unconscious'.
sacral and solar chakra = 'ego'.
throad chakra/third eye = 'super ego'.
The hearth being a thing of its own and often escape the scope of classic psychology, and only start to appear in the field of transpersonal psychology, as hearth apply mostly as in relation to external objects.
Jung also wrote about this correlation between chakras/kundalini and depth psychology.
Even the model of the triune brain ( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triune_brain ) can also fit this pattern.
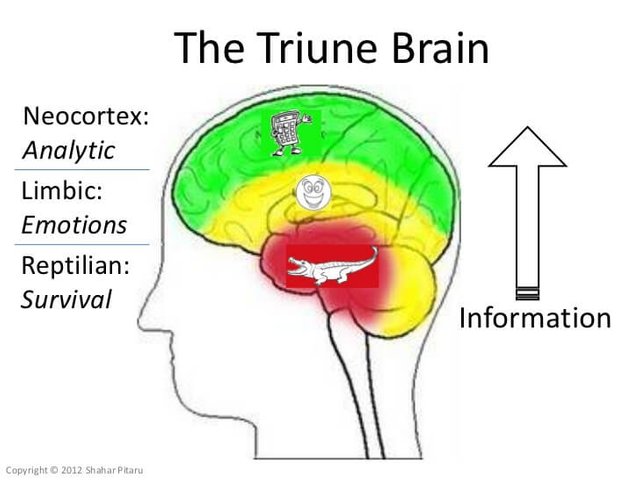
But even classic psychology is not exactly science, freud as well as jung as still considered being more philosophy than 'hard science', and it's where Edelman comes in with hard neurology science, to make great advance in the objective study of the brain and cognitive functions, and come up with a coherent model to explain its formation.
For edelman, the consciousness as the rest of biology is the product of evolution, and he study the natural mechanism that lead to the formation of the brain, based on hard empirical study, and even some computer modeling with self learning and pseudo sentient robot 'darwin'.
For him the brain is made of different layers, that form on top of each others, with a system of reentrant neural connections, who acts as receptors for the input of a certain part of the brain, and reenter the centers from which the input originate in order to get some feedback, and adapt it's wiring depending on how it's reaction fit with the function that is expected from the other center.
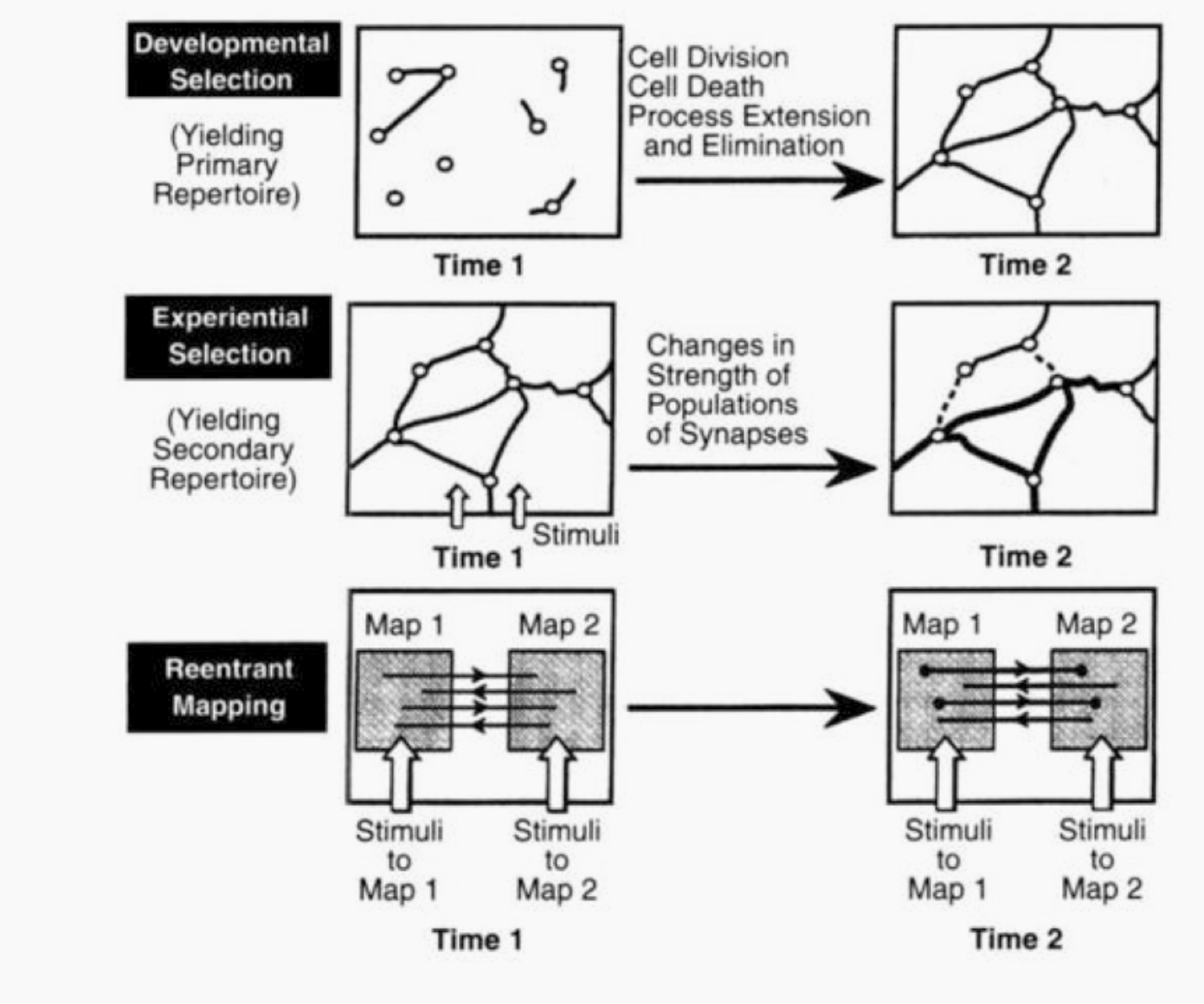
( diagram from edelman biology of consciousness )
Primary consciousness
The first center that developped historically is what he calls the 'primary consciousness', and is roughtly equivalent to the so called 'reptilian mind', or R-complex.
It's mostly concerned with direct perception of the physiological constant, especially body temperatures as reptiles are cold blood creatures, but also all the constants of pshsiological and physical biology, and is directly connected to the nerve, cells, and physical structure of the body.
It has very limited capacity of memory, empirical studies tend to confirm reptiles have very poor memory, and are mostly concerned with immediate reaction to environment, and see the world mostly as threats or prey, hence the fight or flight reaction often associated with the R-complex functions.
It's mostly concerned about the immediate correlation with perception through sensorial input, and identifying objects or conditions as harming, or potentially good for the physical aspect of biology.
This concept of positive or negative feedback is crucical to his theory of neural darwinism, as it will say that wiring that yeld positive feedback will stick, the wiring that yeld negative feedback will be rewired, in sort to maximize positive feedback from the physical biology correlated with perception of environment triggering a certain reaction.
Memory
http://www.jneurosci.org/content/34/14/4766
From there, the second part of the brain that started to develop is short term memory, according to his theory of re entrant neural network, its function is mostly to 'map' sensorial input into another network in the brain, and then form a matching between the mapping of immediate sensorial input, and a mapping reccorded from previous sensorial input.
This mechanism of mapping from a zone of the brain to another is very important in his theory of the remembered present, as when taken from the point of view of the higher consciousness, the conception of the present we have is never only directly sensorial input, but also coming from lot of feedback from associated memory.
The information the brain form from sensorial perceptions to constitute the conception of the present also come from lot of different centers of the brain.
According to him, this system of reentrant neural network associated with short term memory, and ability for the hypotalamus to move certain of this mapping to long term memory, is what give the birth to the concept of objects, of categories, and the whole science of ontology developped by aristotle.
As by matching different sensorial properties of sensorial input with memory, one can deduce comon point between diferent sensorial objects, and start to form relation between them, and categories as in ontology.
This function of the brain almost empirically proove the whole metaphysics, as in property that the mind associate with perceived objects based on analogies, and allow to induce properties of such objects, and the essence of what constitue an object as such, even if the actual instance of the perceived object has never been seen before.
It's also empirically verified that mamals develop more sense of memories, rats are supposed to be about the first mamals in the history of evolution, and the main experience to test an animal capacity of memory is capacity to decrease time to solve a maze after several times, and it's well known rats excel at this game.
Secondary consciousness
Edelman then say there is another level of bootstraping that came after the apparition of long term memory, and capacity of analogy, in order to make sense of the scene, leading to what can be called 'meta cognition', aka ability of the mind to auto analyze its own infered meaning and ontology, formed directly by association of memory through the remembered present.
It can be explained very simply with the same mechanism of neural mapping of the zones that analyze memory, into another higher layer, and allow to have an higher overview of those infered categories based on anology, and even having a way to understand this mechanism of how concept of metaphysics form in the mind.
It's interesting to see here the antic battle between plato and aristotle, aristotle being mainly concerned with bare metaphysics, property of objects, which is often considered as empiricism, or hard natural science, whereas plato is more concerned with idealism, rationalism concept of good, truth, that are more immaterial, which could correspond to the emulation of secondary consciousness, and meta cognition to give an higher meaning to the categorisation of objects.
According to edelman, the rise of secondary consciousness is what distinguish animals with semantic or linguistic capacity, as in ability to grasp the true meaning of words, and the mechanism of emergence of such concepts, instead of just memorizing them as formulas or natural science encylopedia.
This is also the part of the brain potentially associated with lucid dreaming, as in understanding one is in a dream, and ability to change the perception of the dream according to higher principle of cognition, rather than just 'following' the dream like a script in a movie, and being able to pierce dream meaning at a deeper level instead of just undergoing it passively.
Semantic computing often use similar scheme.
https://pierrelevyblog.com/tag/semantic-computing/
Freewill ?
This model is also interesting to understand this concept of freewill, as it shows very well some part of the brain truly are mechanistic, as the primary consciousness is merely physical wiring from sensorial and physiological input, and can hardly be influenced at all.
Whereas with the two levels of bootstrapping, leading toward understanding of metaphysics and then semantic, one can have more influence on how the brain wire itself, and influence its perception of the remembered present, how the categories and infered properties that will influence our reaction can be formed into the higher level of consciousness.
In a way it can be told free will action is limited to the higher level of consciousness, as in validating or not the lower level wiring of sensorial input to categories, and infered effect on the physiology and physical well being. Knowing that if something actually have immediate negative effect on the body, freewill as such has no effect to stop it.
It's also relatively in tune with the system of hinduist kosha, where all the different layers of being inter penetrate each other, and influence each others, and how one need to become conscious of lower layers through certain practice of meditation in order to develop the being as a whole.
.jpeg)