Does Your Brain Wake Up When You're Dreaming? If you’ve ever wondered what happens in your brain when you fall asleep.
- This week is the Brain Awareness Week: every Sunday of this week, leading researchers from the International Association for Dream Studies are reviewing their work on dreaming and the brain. to run daily life in the health of the human body.
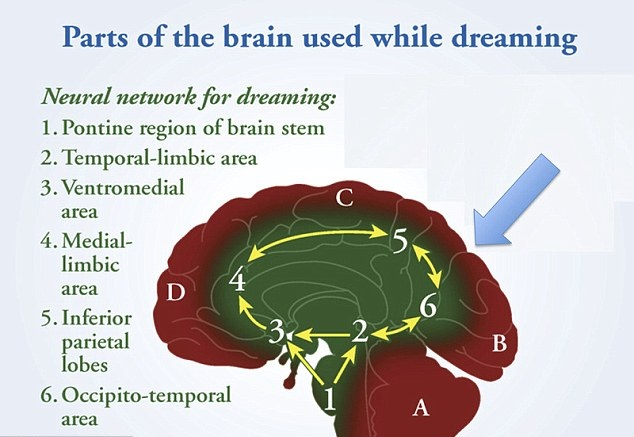
Our brain cycle passes through 4 stages of sleep, each characterized by a unique brain wave pattern - the electrical pulse generated by the communicating neuron. Slower brain waves indicate deep sleep or meditation or when we feel tired or listless, higher frequencies stand out in a state of alertness and awake. Researchers use Electroencephalography (EEG) to record this brain activity through electrodes placed on the scalp to maintain our sleep balance. and the brain can maximize our thoughts to think tomorrow.
As we pass through the four stages of sleep, brain activity becomes slower and more synchronized: in order to maximize the thinking of brain patterns.
Stage 1 is a very light sleep that is mixed with wake-like alpha waves (8-12 cycles per second)
Phase 2 is a slightly deeper sleep with a slower theta wave (5-7 cycles per second)
Stage 3 is the deepest sleep and is characterized by slow delta waves (0-4 cycles per second).
Finally, we enter REM sleep, a period marked by "Rapid Eye Movements (REM)", in which brain activity increases to a wake-up level, although the entire body is essentially paralyzed.
The process of dreaming through the sleeping stages to keep the brain's balance on performance
Stage 1
The stage 1 dream comes in a foggy state when you fall asleep, nodding for a moment, or when you wake up as you would like to continue sleeping again and it is very tiring for a brain work that is not maximal.
Stage 1 dreams are usually very short, but often have clear visual or visceral content, such as the general 'falling' sensation for sleep that does not awaken in our subconscious.
Because his brain is still awake, this dream often incorporates real-world stimuli, such as an alarm clock or barking dog that is really an illusion of our brain's performance.
Stage 2
Phase 2 dreams are often short, and incorporate fragments of life awakened recently to dreams in no time.
Stage 2 dreams are usually described as 'thinking', they may feel like thinking during sleep
However, as the night passes, Phase 2 dreams gradually become longer and more alive in deeper sleep and the brain works maximally.
Stage 3
Dreams are: the most obvious of stage 3 is sound sleep, although they do occur in a short process.
in Early researchers believed physiologically impossible for any cognition to occur in deep sleep that does not know anything in self awareness to sleep.
Today, researchers acknowledge that even in sleep, the brain is active, processing memory and restoring cognition.

REM Sleep
REM sleep dreams are: dreams that are usually the longest, clearest and most strange and truly enjoy the brain can catch clearly.
Since we have plenty of REM sleep in the morning, this is the kind of dream that is most often raised in the overslept and remembered people in their daily lives.
The emotional part of the brain is most active during REM sleep (see below). This is probably part of what makes REM sleep sleep so emotional and meaningful.
Dreaming and the brain
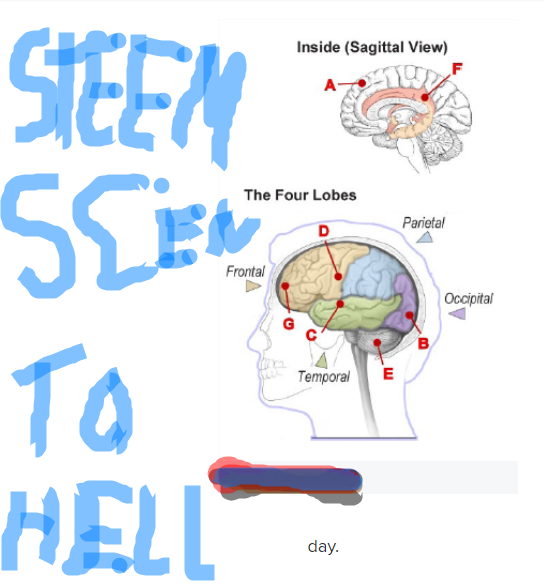 The content of dreams is largely provided by the cortex, where we keep many memories of our autobiographical life: friends become dream characters, TV shows into dream settings.
The content of dreams is largely provided by the cortex, where we keep many memories of our autobiographical life: friends become dream characters, TV shows into dream settings.
Sensory cortex: is also active in giving perceptual details, especially the visual and auditory cortex, although a small portion of the dream contains odor or taste.
The motor cortex: which controls our movements in real life can work in parts of the brain in dreams, is also active. In fact, neuroimaging has shown that brain activity is similar during dream action and wakefulness. So, practicing sports in a dream can give you an amazing game day and brain fitness to continue your maximum thinking.
The limbic system: is also active in REM sleep, and is responsible for handling emotions. The dream of REM sleep is thus more emotional than the dream of another stage.
Unusual dream experiences in the brain
Lucid dreams: where the dreamer realizes that they are dreaming in an imperfect sleep to wipe off the otok, and are attracted by an increase in prefrontal activity during REM sleep. Therefore, the dreamer has a cognitive ability similar to real life, including mind control and voluntary action.
Nightmares are: intense and emotionally arousing dreams that often culminate in a sudden resurgence. These dreams are also most common in REM sleep. However, contrary to lucid dreams, nightmares seem to be marked by declining prefrontal activity, which leads to inadequate emotional control, and tremendous passion.

upvote follow resteem
I am very grateful to you for supporting me.
Your post has been selected on my station, continue contributing quality content hoping curation hunters will find your post
Dont forget to follow us and upvote this post inorder to grow our community thank you and more power..